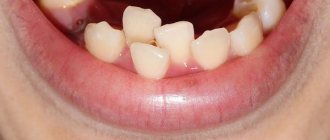
Almost every person experiences difficulty breathing through the nose. This is the most commonly diagnosed complaint among patients, because the symptom is associated with a deviated nasal septum. This diagnosis occurs to varying degrees in 80% of the world's population. However, not every patient is bothered by severe discomfort, and therefore not everyone is interested in treatment methods.
In addition to difficulty breathing, patients may experience other symptoms, the intensity of which directly depends on the degree of curvature of the nasal septum.
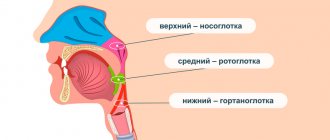
Why is the nasal septum deviated?
The cartilage tissue that represents the septum does not have such a dense structure as bone, so it is prone to deformation as a result of injuries, falls, and also against the background of long-term inflammatory processes. The septum consists of quadrangular cartilage and three bones - the perpendicular plate, the vomer and the premaxillary bone from the upper jaw. It is curved due to the fact that there is a discrepancy in the growth of the cartilaginous part and the bone part - something grows faster and, since there is nowhere to grow, goes to the side, or there was an injury, and because of this the septum is bent. Therefore, there are deviated septums without injury.
Until the age of 21, a person’s cartilage tissue still continues to grow, so surgical intervention is considered unacceptable. In many cases, natural self-correction is possible during the growth process. The septum is now operated on at any age, despite the fact that it grows. But if the septum is severely deviated, surgery is performed at any age, including children.
Despite encouraging forecasts, damage not only to the septum itself, but also to internal structures is possible. As a result of such deformation of the internal cavity, serious chronic processes develop, characterized by the accumulation of mucus inside. In this way, indications for surgical intervention are formed.
Sputum due to pneumonia is yellow in color
The appearance of a yellow tint in the sputum may indicate the development of acute pneumonia and acute bronchitis. It can also be a sign of allergies and asthma.
Yellow sputum indicates the body is fighting the virus and the immune system is functioning normally. Thick, dark yellow mucus may be due to a bacterial infection in sinusitis. If such a symptom appears, you should immediately seek medical help.
Trust your health to professionals. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are leading specialists in Russia who, based on the test results, will make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan for each patient.
Pneumonia is often a consequence of improperly prescribed treatment. In public clinics, quite often patients are treated for pathologies that they have never had, while the underlying disease develops at a faster rate. This picture is observed due to the low qualifications of doctors in state clinics, poor equipment of hospitals with modern medical equipment and the lack of medicines.
How to correct a deformed nasal septum?
In cases where a deviated nasal septum requires surgical intervention, endoscopic septoplasty is performed. This operation is performed according to indications and is not aesthetic. But often rhinoplasty is performed together with septoplasty, since a deviated nasal septum can have pronounced signs, as a result of which the shape of the nose also changes.
The indications for endoscopic septoplasty are as follows.
- Impaired nasal breathing. This is the main symptom requiring septoplasty.
- Constant swelling of the mucous tissues in the nasopharynx.
- Frequent sinusitis.
- Snoring, wheezing breathing.
- A constant sensation of a lump of mucus in the nasopharynx due to improper outflow.
With a chronic inflammatory process, benign neoplasms – polyps – can form. That is why it is recommended not to delay treatment, and if you have problems with nasal breathing, frequent colds, or you constantly feel a lump of mucus in your throat, then you should contact specialists who can diagnose the degree of curvature of the nasal septum and perform surgical intervention if necessary.
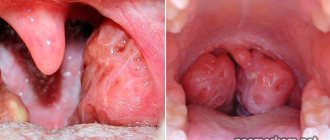
Chronic tonsillitis
A lot is known about tonsillitis - inflammation of the tonsils - so much so that the information is available to almost anyone. In the context of a condition that is described as a “sore throat” and characterizes the dysfunction of an organ, which is usually called in the French manner, le glande (“acorn”), the choice of a treatment plan is often considered. The success of the latter does not always lie in surgical removal or persistent conservative treatment.
Let's try to understand what follows the appearance of the diagnosis of tonsillitis and what forms the disease takes. To do this, we need a “patient model”: a description of a group of potential owners of unhealthy “tonsils”. By the way, healthy palatine tonsils often have the shape of an “acorn” (le glande), and with tonsillitis, the latter acquire a spherical shape.
- Tonsillitis is more common and, accordingly, the number of cases of its surgical treatment is increasing among children 4-12 years old and adults 20-30 years old. These periods correspond to the restructuring of the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx, maturation and implementation of barrier properties in accordance with the characteristics of the microflora inhabiting it.
- Our patient is often sick - these are viral infections, somatic diseases associated with immune disorders, and various congenital syndromes.
- Enlargement of the palatine tonsils and, often, the nasopharyngeal or adenoid tonsil does not allow free breathing: both the lymphoid tissue itself and swelling of the nasal mucosa are an obstacle. Nasal obstruction syndrome develops.
- Breathing disorders are especially pronounced during sleep, when there is no possibility of using additional muscular effort, the patient breathes only due to the work of the diaphragm. Snoring appears, and less often, episodes of short pauses in breathing during sleep. As Yevgeny Vaganovich Petrosyan said, “when I sleep, I don’t control myself.”
- Microbial communities in the form of colonies covered with a “shell” of complex carbohydrates (“films”) are expressed on the root of the tongue, the posterior wall of the pharynx and in the recesses (crypts) of the tonsils. Excess microflora creates conditions for unpleasant odor from the mouth (halitosis).
- Sometimes inflammation in the tonsils causes problems with the functioning of the throat muscles and makes swallowing difficult (dysphagia).
The choice of the “optimal” method of treating tonsillitis led in the 40-50s of the 20th century to their widespread removal in almost all patients, starting from the period of physiological enlargement in childhood. The price for this was a sharp deterioration in the body's anti-infective defenses. Already in the early 50s, the authors refuted their point of view, calling the method of treating tonsillitis without specifying the indications “orgy.” About 50 years have passed, and the criteria (also known as indications for surgery) for tonsillectomy have become generally accepted (Paradise, 1984):
- Number of relapses of tonsillitis: more than 7 in the previous year, or more than 5 in each of the 2 previous years, or more than 3 in each of the previous 3 years (from the patient’s perspective).
- Sore throat and one of the signs: body temperature more than 38.3, cervical lymphadenitis (node more than 2 cm), exudate in the tonsils, culture of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS).
- Previous treatment: Antibiotics against GABHS in every episode.
- Condition: each episode of tonsillitis is documented by a doctor, or the doctor observed 2 episodes in the patient.
Tonsillitis has acquired the status of an infectious disease with systemic complications, which often have a more negative impact. One of the most severe diseases aggravating the course of tonsillitis is kidney damage.
Sound phenomena produced by the patient during sleep: loud labored breathing, extraneous noises - vibrations of the soft tissues of the pharynx, or short episodes of lack of breathing. However, in addition to the reaction of those around you, you should pay attention to the structural features of the patient’s face (see figure). A small lower jaw (micrognathia) and a small narrow laryngopharynx are anatomical prerequisites for poor breathing, even with a slight increase in lymphoid tissue. And, on the contrary, a deep bass voice is a sign of a large-volume laryngopharynx - even a significant increase in the palatine tonsils will not immediately affect breathing characteristics.
Intoxication, prolonged episodes of a slight increase in body temperature (to subfebrile values) over several weeks are a formidable sign of a harmless enlargement of the tonsils. In such patients, the risk of diseases not apparently related to tonsillitis increases. And one more quote from the repertoire of Faina Georgievna Ranevskaya. “Medicine is making amazing progress. Previously, at the reception they told me to “take off your clothes.” Now, just “open your mouth.” That's all." Most likely, F.G. Ranevskaya unconsciously emphasizes the attention of therapists to the condition of the palatine tonsils. And it's not a joke.
Even charismatic doctors, supporters of “evidence-based medicine” (EBM), allow themselves to ask the question of the appropriateness of choosing a treatment method. In the following, we briefly summarize EBM's position on tonsillectomy (TTE).
In the “infectious model” of the disease:
- Recurrent acute tonsillitis is considered an indication for TE, but indications for “essential TE” vary - see Paradise criteria. “Chronic tonsillitis” is not a strictly determined concept, because The time factor in adults is difficult to take into account, but in children the period of onset of tonsillitis is more understandable.
- Peritonsillar abscess (it is better to use the differentiated concept of “peritonsillitis”, but it is not in ICD-10 - Yu.N.). Fine needle aspiration of the abscess contents may be sufficient. If there is effective anesthesia during the operation, in addition to puncture of the abscess, one-stage removal of the tonsils (abscess tonsillectomy) can be performed. The risk of postoperative bleeding is equal to traditional TE. Traditional TE in the treatment of peritonsillar abscess in the “era of antibiotics” is not strictly necessary.
- Infectious mononucleosis. TE is justified in cases of airway obstruction or tonsil bleeding. TE may shorten the duration of the disease, but compromises the immune system.
- Angina of Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent. There is no data on TE, as well as on frequent sore throats of this kind.
- Sinusitis. There is no rigorous level A evidence.
- Bronchitis or cough. Not shown - strictly level A.
- Chronic otitis media with exudate. Some reviews contain the statement that in case of CSO, adenotomy is indicated, TE is not necessary.
Somatic local and systemic diseases:
- IgA nephropathy. TE has a positive effect (see picture above)
- Arthropathy (joint pain). The positive effect in children; in adults, the effect of TE has not been proven.
- Dermatoses. At the case-effect level: psoriasis, palmoplantar pustulosis.
- Intestinal diseases. TE has no effect in nonspecific ulcerative colitis or celiac disease. TE may be considered a risk factor for chronic intestinal diseases.
- Heart diseases. No Category A data.
- Vague fevers. There is no data in children, unlike adults, when after TE the risk of fever of “unexplained origin” decreases.
- Atopy
- Bronchial asthma. In children, TE does not affect the course of asthma or allergic rhinitis. There are no category A data for adults.
- Atopic diseases have never been a contraindication to TE. In adults, no connection was found.
"Unclassified indications":
- Malocclusion, cleft palate. There are no correlations. Indications for TE are determined individually.
- Halitosis. In some cases, TE reduces halitosis. There is no category A evidence.
- Hemorrhagic tonsillitis. Rarely seen in adults.
- In case of tumors, there is no need to discuss the advisability of TE. TE is considered as a biopsy option.
- Growth disorders – micrognathia (see picture above). Considered in the context of airway obstruction.
- Enuresis (bedwetting). The opinion about improving the quality of night sleep in enuresis after TE (considered last in the review by the authors) can be considered a “subtle German joke” based on isolated publications.
Individual states:
- Down syndrome. Macroglossia in hyperplasia of the palatine tonsils – in the context of respiratory disorders.
- Spindle cell anemia. Recurrent episodes of tonsillitis may be followed by hemolytic fever or another aplastic crisis. TE improves the condition of these patients.
- Cerebral paralysis. Limited indications for TE.
Thus, the indications for removal of the palatine tonsils are formulated quite clearly. An alternative is the method of “minimally invasive surgical treatment” of tonsillitis: in the presence of inflammatory cysts (the majority of them), limited in the volume of scar-inflammatory changes, less radical effects can be used. Vaporization (evaporation) using high-frequency electrocoagulators or lasers, argon plasma coagulation, etc. have become the most popular options for surgical treatment of patients with chronic tonsillitis.
Author of the article:
otorhinolaryngologist surgeon, professor, doctor of medical sciences Nazarochkin Yuri Valerianovich
How is endoscopic septoplasty performed?
The essence of the operation is to excise those areas of bones and cartilage that have been deformed. The mucous membrane is not subjected to excision, since it is pre-exfoliated, which allows its integrity to be preserved and the rehabilitation period to be significantly reduced.
Modern medicine allows surgical intervention to be performed in an extremely gentle way, so in most cases only that part of the septum that is deformed and causes discomfort is excised.
The operation is performed using an endoscope. During the intervention, a thorough examination of the deformed area is performed. The necessary areas are removed using low-traumatic microtools. The operation is monitored using an endoscope.
Sputum due to pneumonia is dark in color
The appearance of rust-colored sputum can be observed in smokers. This suggests that you need to get rid of the bad habit urgently. Also, dark color of sputum can be observed when consuming certain foods and drinks, for example, chocolate, coffee, red wine.
If dark-colored sputum is present for a long time, this may be a sign of:
- chronic pneumonia;
- chronic bronchitis;
- tuberculosis;
- lung cancer;
- pneumoconiosis.
In any case, the patient should consult a doctor.
Why choose Elena Malysheva Medical Center?
When choosing a doctor and a clinic for septoplasty, it is necessary to establish a trusting contact between the specialist and the patient. World-class doctors work at Elena Malysheva’s clinic. Dmitry Semenovich Gorin is a certified ENT doctor who has practiced in famous institutions in the USA (Ear, Nose and Throat Institute in New York) and Germany (University of ENT Diseases).
Dmitry Semenovich works with both adult patients and children. Having extensive practical experience behind him, Dr. Gorin performs ENT operations at the highest level. Thanks to the coordinated work of the entire medical center, preliminary diagnosis and basic treatment are carried out with a high degree of efficiency. The modern equipment used allows endoscopic septoplasty to be performed in a gentle manner, reducing the duration and intensity of rehabilitation.
Swelling after surgery persists for a week, and you can start working in 10-14 days.
Endoscopic septoplasty is a gentle surgical method that will solve your breathing problem. Elena Malysheva's clinic will free you from problems and allow you to freely take a deep breath through your nose!
More detailed information and registration by phone: 8.
White or gray sputum
Transparent sputum, discharge of white and gray shades are absolutely normal. But their excessive quantity may indicate various pathologies, namely:
- allergies;
- chronic bronchitis;
- respiratory tract infections;
- pulmonary edema.
Gray sputum may be the result of smoking or severe air pollution.
Diagnostics at the Yusupov Hospital will either refute the suspicion of pathology, and the patient will know for sure that nothing threatens his health, or will allow a timely course of effective treatment to be prescribed and prevent the development of severe complications.
To make an appointment with a doctor at the Yusupov Hospital, you do not need to stand in queues, adjust your work schedule, the hospital administrators will coordinate a visit to the doctor at a time convenient for each patient.
Sputum from pneumonia mixed with blood
The presence of a pinkish tint of mucus, streaks and blood stains in it may indicate various diseases, the most dangerous of which is lung cancer.
But sputum mixed with blood can also appear when:
- pneumococcal pneumonia
- internal bleeding;
- tuberculosis;
- pulmonary edema due to chronic heart failure;
- lung abscess.
The appearance of sputum with blood is always a sign of a serious illness and requires urgent medical intervention. The Yusupov Hospital accepts patients 7 days a week, 24 hours a day. You can make an appointment with a doctor in advance by calling the clinic’s phone number.