1004
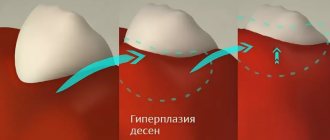
Gum tissue pathologies do not always manifest themselves as soreness, swelling or redness of the periodontium. Excessive growth of this tissue, which is called fibromatosis or gingival hypertrophy, has also been identified as a disease.
In addition to physical and aesthetic discomfort, this pathology can provoke various complications.
Brief description of the disease
Fibromatosis of the gum tissue is represented by its proliferation, which can cover single crowns or spread throughout the entire dentition.
This pathology is most often diagnosed in adults , but in isolated cases it also occurs in children, with the main peak of the disease occurring when the child is under 1 year of age or 10–11 years of age .
The pathology is not accompanied by hyperemia and bleeding of the periodontium. As the tissue grows, no transition to the buccal, lingual or palatal surface is observed. The process can be either slow or aggressive , in which partial or complete overlap of the crowns occurs.
Complications
Gum hyperplasia may be accompanied by concomitant diseases. Overgrown connective tissue disrupts the normal functioning of the entire oral cavity. The consequences of pathology can be:
tartar growth; atrophy of the bone tissue of the upper jaw; loosening of teeth; tooth loss.
An increase in connective gum tissue leads to enlargement of the gum pockets of the teeth. This pathology makes quality cleaning difficult, and food debris accumulates in the pockets. Bacteria accumulate on unremoved food particles, forming plaque, and then on its basis the formation of tartar occurs.
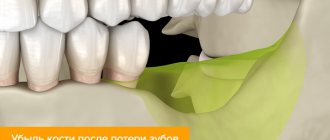
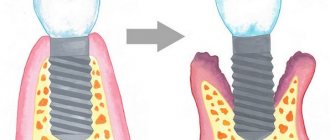
In severe cases, atrophy of the bone tissue of the upper jaw occurs. The patient's interdental septa and alveolar process are dissolving. The gum tissue becomes loose and cannot hold the tooth, which causes premature loss of the tooth or dentition.
Forms
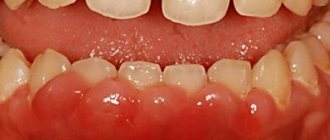
Periodontal fibromatosis is characterized by several forms of manifestation, which are considered depending on the location: focal and generalized.
Photo (from left to right): focal and generalized forms
Focal (limited)
Focal fibromatosis is characterized by a slow pace of gum development, covering 1–2 crowns . This form of pathology most often affects the periodontal tubercles of the alveolar ridge and the lingual surface of the gums on the lower jaw in the anterior region.
The growth is characterized by a dense structure and regular round shape . The surface of the pathological tissue is smooth, shiny, and does not differ in color from healthy periodontal tissue. With an increase in the volume of periodontal tissue, overlaps by 2/3 of its height.
In isolated cases, complete overlap of the tooth is observed.
Generalized
Fibromatosis of the generalized type is an extensive periodontal lesion, in which the formation of several foci at a distance from each other is noted. As the disease develops, merge and the volume of gum tissue increases, overlapping the crown part of the tooth.
The pathological tissue has a heterogeneous granular structure, a smooth surface and, in some cases, a hyperemic tint. This form is divided into two types: nodular and diffuse .
With nodular fibromatosis, periodontal enlargement appears in the form of the formation of dense, limited nodes. Diffuse - like a compaction that has no boundaries.
Mechanism of development of hyperplasia
The mechanism of development of the hypertrophic process remains not fully understood. However, scientists have discovered that the pathogenesis of the disease is influenced by impaired calcium transport. This leads to increased production of collagenase, which causes the gums to grow. Hyperplasia develops gradually, so patients do not pay attention to it right away.
Stages of the disease:
- First: the tissue covers a third of the tooth, there are no signs of an inflammatory process.
- Second: covers half of the tooth, bleeding may occur, especially with mechanical impact.
- Third: overlap from two-thirds to the entire crown, sometimes even the cutting edge and chewing surface are covered with soft tissue, granulations are visible over the entire surface.
Causes
The main reason for the development of hypertrophy of gum tissue is a violation of periodontal metabolic processes, in which active accumulation of fibroblasts . These cells are distinguished by increased production of collagen , due to which an increase in fibrous tissue is provoked.
Phenytoin
Long-term observations have made it possible to identify only two main groups of factors that trigger this complex process:
- Medications .
It has been noted that long-term use of certain medications provokes the development of pathology. Periodontal hypertrophy occurs in 1/3 of patients taking phenytoin, cyclosporine and drugs containing estrogen. Also, there are frequent cases of diagnosing this disease after taking calcium antagonists, amlodipine and sodium valproate. The pathology caused by medication is characterized by the rapid growth of fibrous tissue and its redness. - Genetics. The provoking factor in this case is the mutation of the SOS1 gene.
As a rule, the disease is diagnosed in early childhood and progresses as people grow older. At the initial stages of its development, it manifests itself weakly, but during hormonal changes in adolescence, with certain diseases or pregnancy, the symptoms become pronounced.
What periodontitis looks like in the photo. A selection of illustrations.
This article describes what to do if a child has an abscess on his gum.
Follow the link https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/desnyi/antibiotiki-naznachaemyie-pri-flyuse.html for a list of antibiotics that should be taken for flux.
Let's sum it up
Mucous fibroids on the inside of the cheeks, gums, lips, and tongue grow very slowly and do not cause severe discomfort. They do not pose a danger to the patient, but the problem must be eliminated as early as possible. The fact is that a benign seal in the oral cavity with regular trauma can degenerate into a malignant one, and the oncological process requires serious therapy and is extremely dangerous to life and health.
It is impossible to get rid of the disease using traditional methods. It is important to undergo high-quality dental diagnostics and consult with specialists. In most cases, surgical excision is indicated, but with small growths, the absence of severe symptoms and the elimination of provoking factors, there is a possibility of rapid tissue restoration without external influence.
There is no need to worry if the doctor has decided to undergo surgery. Modern clinics practice laser or radio wave removal on an outpatient basis. These are the most gentle and highly effective methods. An extremely important point in a positive prognosis for the treatment of dental fibroids is an early visit to a doctor and proper excision by an experienced physician.
Symptoms
The entire process of development of pathology was divided into 3 degrees, each of which is characterized by its own symptoms:
- 1st degree. There is an increase in the volume of the gingival papillae and the periodontal edge in the area of the tooth neck. They take the form of a roller, the height of which is about 1/3 of the crown part of the tooth.
A particularly strong modification is noted at the base of the gingival papillae. In this area, the growth can be either round or irregular in shape.The first degree is characterized by the relief of the pathological surface with an uneven increase in periodontal tissue for each individual area;
- 2nd degree. It is distinguished by a pronounced progression of hypertrophy, in which both the edge of the gum and the papillae move away from the surface of the tooth and rise in the form of a dense ridge to ½ the height of the crown.
- 3rd degree. It is characterized by extensive periodontal growth, reaching more than 2/3 of the height of the coronal part or completely covering it.
In this case, the gum tissue has pronounced hyperplasia and a smoothed surface. Due to constant trauma, numerous granulations with bleeding wounds can be seen on the growths. Depending on the degree of tissue enlargement, granulations can be either small or large in size.
Third degree
Anatomy, physiology
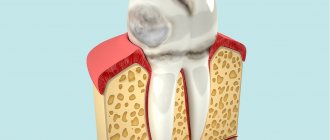
The periodontium
is a complex organ of the oral cavity surrounding the teeth, formed from specialized tissues. It is located on the jaws and its main functions are to support (support) the teeth and their nutrition and innervation.
Nutrition (trophism) is provided by blood and lymphatic vessels that supply oxygen and metabolic products to the periodontal tissue.
There are four main anatomical and functional elements of the periodontium:
- gum,
- periodontium,
- alveolar bone with periosteum,
- root cement
The gum is a soft tissue - a mucous membrane covering the alveolar processes, with an underlying connective tissue layer.
It contains lymphatic vessels (they are involved in regulating fluid pressure in tissues and protecting against microbial agents).
Through the periodontium - the ligament of the tooth, the latter is fixed in the jaw bone.
Periodontium
(otherwise known as desmodont) is a connective tissue formation surrounding the tooth and located between the root cement and the inner cortical plate of the alveolar bone.
This ligament, consisting of the main substance, fibers and cellular elements, like an elastic gasket, absorbs the load on the tooth, giving it minimal mobility. When periodontal disease and death occur, fusion of the bone with the tooth – ankylosis – can occur.
The next element of the periodontium is cement, which is also a hard tissue covering the root of the tooth. It is formed by collagen fibers directed along the root and an adhesive substance.
Bone
The alveolar process, in which the tooth is strengthened by periodontium, is composed of outer and inner dense plates and a spongy part between them.
Spongy bone consists of trabecular septa, the direction and shape of which is determined by the load on the jaws and teeth, and bone marrow.
Bone tissue contains mainly crystals of hydroxylapatite (inorganic) and small amounts of water and organic substances.
The cellular elements of bone - osteoblasts, osteoclasts and osteocytes, under the influence of the nervous and humoral system, determine changes in the shape, volume and quality of this tissue.
The bone tissue of the alveolar process is covered with a dense connective tissue structure - the periosteum; it, with the vessels located in it, plays a significant role in the blood supply to the bone.
The blood supply provides tissues and anatomical formations with organic and mineral substances.
At the level of the enamel-cement junction (neck of the tooth), an anatomical formation stands out in the marginal part of the gum - a vascular cuff, which, like an elastic band, ensures a tight fit of the gum to the tooth due to hydrostatic pressure.
The main source of blood supply to periodontal tissue is the external carotid artery with the maxillary and mandibular arteries branching from it.
Venules and veins collect blood into the internal jugular vein. The periodontium is innervated by the trigeminal nerve and the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion.
Among others, there is an anatomical formation - the dentogingival junction
. This is the connection between the gum epithelium and the neck of the tooth.
It is physicochemical: molecules of epithelial cells adhere to cement structures through gingival fluid cells.
Gingival fluid produced by periodontal tissue plays the role of a protective barrier against microorganisms through the activity of phagocytes and its chemical properties. It should be noted that the periodontium is washed by saliva. It is secreted by the major and minor salivary glands.
In addition to water (99.42%), saliva contains organic substances, salts and trace elements. Organic substances enter the oral fluid from blood serum and are secreted by the salivary glands and microorganisms present in the mouth.
Of the inorganic substances, calcium phosphate and calcium bicarbonate (they take part in the formation of tartar), phosphate and sodium chloride are important.
Diagram 1: periodontium
. a – submucosal layer with lymphatic vessels; b — mucous membrane of the attached gum; c - spongy bone of the alveolar process between the plates of the compact substance; d – periodontal fibers are woven into the root cement; e – gingival margin with vessels of the gingival cuff; e – dentogingival junction; g – tooth enamel; h – dental pulp; and – root cement; j – root dentin.
Age-related changes in periodontium
In the periodontium, with age, there is a decrease in the number of collagen fibers and a decrease in their quality. The epithelial layer of the mucosa becomes thinner, and keratinization is disrupted.
The bone tissue of the alveoli becomes less dense, the cortical layer atrophies.
Diagnostics
For an experienced doctor, visually identifying fibromatosis is not difficult. But to obtain an accurate clinical picture, additional diagnostic methods are used. One of the first is an instrumental method that allows one to determine the quality of enlarged gums and the depth of the periodontal pocket.
It is mandatory to use radiography with a targeted or panoramic image. In order to differentiate hypertrophy from other diseases, it is necessary to collect pathological material for histological analysis .
To exclude a provoking factor, a hormone test is prescribed.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of fibroids is performed by doctors of various specializations - dermatologists, oncologists, surgeons, gynecologists, etc. Methods for confirming the primary diagnosis are determined by the location of the benign neoplasm. At the first stage of the examination, patients receive a referral for radiography. Computed tomography allows you to determine the exact size of the tumor and identify signs of its invasion into adjacent organs.
Fibrous formations in bone and cartilage tissue are detected during scintigraphy. If necessary, the doctor can take a biopsy sample for laboratory tests. Microscopy of the obtained biomaterials will allow doctors to assess the morphological structure of tumor cells and the likelihood of their malignant degeneration.
Benign neoplasms of the female reproductive system are often detected during ultrasound examinations. The focus of the pathological process has less echogenicity compared to adjacent tissues.
How is the treatment carried out?
The choice of treatment method will depend on the cause of periodontal growth. If the provoking factor is the use of medications, then a gentle technique is used with the withdrawal of the medication and the appointment of accompanying measures.
Otherwise, only surgery is used to relieve the problem.
What to do if the gum has moved away from the tooth? Treatment methods at home and in the clinic.
How to treat a fistula on the gum with folk remedies? Here is a selection of recipes.
Here https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/desnyi/parodontoz/otkryityiy-i-zakryityiy-kyuretazh-karmanov.html reviews about closed curettage of periodontal pockets.
Surgical intervention
Surgical removal of pathological periodontal disease is performed in a hospital setting and requires the use of local anesthesia. For large growths, general anesthesia may be chosen. Excision of tissue is carried out using a carbide bur with a turbine attachment or laser .
The second option is preferable, as it minimizes blood loss and reduces tissue healing time. The entire procedure takes from 15 to 40 minutes , depending on the volume of growth.
The operation is carried out according to a specific algorithm :
- Treatment of the operated surface with aseptic solutions.
- Excision of overgrown periodontal tissue, including the periosteal tissue. Deeper cutting is carried out in rare cases, as it often provokes a relapse. In this case, the development interval of secondary growth can be from 5 months to several decades.
- If the pathology has affected both jaws, then removal is first carried out on the upper one, and only after 3 weeks on the lower one.
- After removal, electrocoagulation is performed to stop bleeding.
- If a large area is affected, apical positioning of a gum flap is carried out, intended to cover the wound surface. To fix it, several simple surgical sutures are applied.
If the affected area is small, then a special bandage made of iodoform turunda or a silicone membrane is applied to the operated surface, which is fixed with a continuous surgical suture.Of these two options, preference is given to the second, since iodoform turunda can subsequently become a source of infection, which will lead to periodontal inflammation.
- The operated area is treated with saline and betadine.
In the first week after surgery, anti-inflammatory drugs and B vitamins 7–10 days after the persistent granulation phase has begun, the periodontal bandage is removed , and the excision area is re-treated with betadine.
The next examination is scheduled in a month . During this time, the gum tissue is granulated and completely epithelialized.
With limited growth, removal is carried out in one visit. If the pathology is diffuse in nature, then the operation consists of several stages, with an interval of 20 days. In this case, treatment takes about 80 days.
Elimination of drug-induced fibromatosis
Therapy for this form of fibromatosis consists of discontinuing and replacing the drug used with a drug with a similar effect, but a different composition.
To quickly eliminate the problem, professional teeth cleaning is prescribed, during which all hard deposits are removed from the extended periodontal pockets.
In severe cases, taking antihistamines and agents that reduce the saturation of the gums with blood is indicated. As a rule, after stopping the drug and using additional restoration methods, the gums regain their previous shape .
In the absence of a positive result, surgical removal of pathological periodontal disease is prescribed.
What is fibroma
This is a benign neoplasm in the form of a small node on a stalk or broad base, which consists of fragments of connective tissue. In most cases, it is localized on the mucous membranes of the gums, lips, palate, on the inside of the cheeks, and a little less often on the tongue. The pathological process is more often encountered by primary schoolchildren and adolescents aged 6-15 years.
The patient is not in pain; at a very early stage he does not notice the pathology. As the thickening grows, it is easily felt and accidentally injured.
Can fibroids in the mouth resolve on their own, without medical intervention? In most cases, surgical excision of the tumor is required. However, do not worry about the complexity and duration of the operation. In less than an hour, an experienced doctor will eliminate the defect without subsequent complications and a long rehabilitation period. Currently, clinics use laser and radio wave techniques.
Despite the relative harmlessness of fibrous growths, they still need to be treated even in the absence of discomfort. If the seals increase in size and are constantly exposed to traumatic effects, it is highly likely that an infection will enter the wound. In this case, treatment will be very long, difficult and will not always lead to positive dynamics. In addition, the lack of therapy sometimes leads to the degeneration of a neoplasm into a malignant one.
Prevention
The only measure to prevent this disease is high-quality oral hygiene, which consists not only of regular brushing of teeth and the use of additional devices.
To do this, you need to regularly visit the dentist, who will not only examine the oral cavity, but also remove various deposits from the teeth that provoke periodontal inflammation.
In addition, the likelihood of injury to the gum tissue should be reduced and for this, first of all, it is necessary to remove or cure all problematic decayed teeth.
It wouldn’t hurt to periodically use folk remedies to care for your gums. In this video, a recipe for two rinses based on mint and oak bark:
Forecast
With a timely and early visit to the clinic, the prognosis for the condition of the gums after fibroid removal is almost always favorable.
The operation allows you to avoid the resumption of its growth and degeneration into a malignant tumor. Complications are likely when the doctor’s advice on caring for your gums and teeth during the postoperative period is not followed.
Possible consequences of the disease
The prognosis for fibromatosis is not favorable in all cases - relapse or malignancy of the process is possible. In children, hyperplasia causes a delay in the change of bite, which adversely affects the further development of the dental system.
Reviews
Most reviews about the treatment of the disease are positive. Patients note rapid tissue healing and no relapses.
We invite you to share your feedback about gum fibromatosis and its treatment in the comments to this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags gum disease gum inflammation treatment of gums fibromatosis
Did you like the article? stay tuned