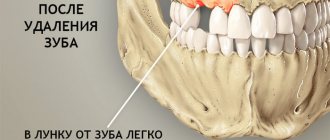
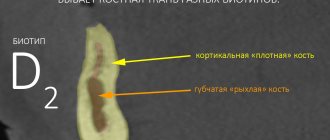
Bone tissue atrophies after tooth extraction unless steps are taken to preserve it. Moreover, degradation occurs quickly - loss of up to a quarter of the volume within one year. The consequences of such a loss are the most serious. These include problems with bite, rapid aging of the face, and mobility of the remaining teeth in the jaw. To prevent this from happening, the patient should discuss preventive measures and preventive measures with the doctor before tooth extraction. Options for solving the problem can be very different, so consultation with an experienced dentist is necessary.
We lose not only teeth, but also bone tissue
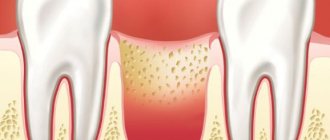
We lose not only teeth, but also bone tissue. Its atrophy occurs after tooth extraction, its long absence, as a result of maxillofacial injuries, with certain anatomical features and congenital anomalies, as well as with a number of systemic diseases. In each specific case, the problem may be insufficient thickness (width) or height of the bone of the alveolar process; in rare cases, there is a deficiency of bone tissue in both height and width.
Expert opinion
Emir Romanovich Omerelli
Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist
Experience: more than 13 years
If, based on the results of the examination, the doctor diagnoses a lack of bone tissue, it is necessary to increase its volume before implantation. Placing implants in low or narrow bone carries serious risks. The bone may fracture or the implant itself may fall out after a short period of use. To prevent this from happening, before classical implantation of the upper teeth, it is necessary to carry out a sinus lift, and for the lower teeth, extension through osteoplasty. The only exception is the basal protocol, according to which implants can be installed without bone grafting and without risks.
If the bone tissue is not wide enough, that is, it is very thin, the operation can be performed by splitting the alveolar ridge: first the gums are exfoliated, then the bone is cut along the length and artificial or natural bone material is placed inside.
Also, the problem of narrow bone tissue is solved by transplanting a bone block borrowed from another bone of the patient himself. To do this, a piece of bone is placed under the gum, fixed with special screws, sprinkled with bone chips around it, covered with a barrier membrane and gum - the mucous membrane is sutured. This option is more preferable, since in most cases the own bone survives.
Bone tissue augmentation surgery, depending on the indications, can be performed simultaneously with the installation of classical implants without their subsequent loading. That is, the artificial roots are fixed in the bone, but are covered by the gum - the dentures will be fixed in 3-4 months. In order for classical implants to take root in the bone, it is necessary to ensure their rest and relieve any pressure.
Complications after bone tissue regeneration
The operation of bone tissue augmentation is considered one of the safest in dentistry, complex, but if carried out correctly, without any unpleasant consequences. In the first days after the operation, it becomes clear whether the block will take root or the operation will have to be performed again. Among the unpleasant sensations are slight tissue swelling and pain in the area where the bone block was taken and the site where it was transplanted. But after 2-4 days, all unpleasant sensations go away on their own.
After bone augmentation
After the bone regeneration procedure, the patient must take precautions: be sure to take medications prescribed by the doctor to quickly restore the body, and do not ignore painkillers. You should refrain from eating food for 2-3 hours after surgery; afterwards it should be warm, but not too cold or hot. It is recommended to chew foods on the side opposite the surgical procedure. In addition, it is necessary to give up physical activity for a while and provide the body with rest for a couple of days after the operation. Do not forget to visit your doctor for a preventive examination and monitor the results of treatment.
Other jobs
Bone regeneration before implantation
Dental implant placement has become a common practice in modern dentistry. But it is not uncommon for a doctor to puzzle a patient with an unexpected proposal to first go through the process of restoring jaw bone tissue. Do not be upset if you are one of those patients who cannot have an implant installed immediately without bone grafting. And in no case should you look for doctors who will agree to follow your impatience and not carry out restoration of the jaw bone tissue - in the end this will end in even bigger problems.
What does it lead to?
Many patients believe that atrophy is a completely harmless consequence of tooth loss. After all, visually this problem almost does not manifest itself at all. But that's not true. As the bone subsides, aesthetic defects in appearance arise and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs occur.
The most common consequences of decreased jaw bone volume are:
- change in appearance - an asymmetrical oval of the face appears, lips and cheeks seem to fall inward;
- a large number of wrinkles form in a short period of time;
- diction changes - the person becomes “lisp”;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract occur (this is due to poor quality of chewing food, swallowing large pieces);
- changes in bite, displacement of teeth adjacent to the atrophied area;
- impossibility of implantation without prior bone grafting.
How is bone volume restored?
To restore the volume of bone tissue in a very thin area at the site of the dental alveolus, bone is split and the cavity is filled with bone tissue (an auto-, allo-, or synthetic graft is used). Then, after bone regeneration is complete, the implant itself can be installed. When it is necessary to increase the height of the bone, simultaneously with the implantation, bone tissue is increased with a special preparation that replaces it. A membrane coating is applied on top. The alveolar bone with various extension designs should heal and strengthen within 4–6 months, after which an artificial tooth (ceramic or metal-ceramic crown) can be installed.
To restore jaw bone tissue, an autogenous graft is used (bone is taken from the patient himself from another part of the jaw); allograft (donor bone is taken from another person) or synthetic materials that mimic bone (they contain calcium and phosphorus).
How to recover
Most often, to eliminate the effects of atrophy, dentists prescribe surgery. Medicines cannot correct the situation. They often turn out to be useless, even if they just need to slow down regression.
Among the most effective methods of returning the original volume of the bone structure:
- Sinus lift. Suitable for working on the upper jaw only. During the intervention, the surgeon raises the bottom of the maxillary sinus to the height required for implantation. He fills the resulting cavity with special shavings. After sinus lift, you can proceed to implantation.
- Osteoplasty. An operation to transplant a small area of donor/own material. If necessary, the doctor can use synthetic material. The technique is popular because it takes little time. At the same time, the risk of rejection of the transplanted area is minimal.
- Tissue regeneration. An innovative technique that involves growing new bone tissue directly in the patient’s mouth. To obtain the desired result, a special protective membrane is placed in the deformed area. It creates a space in which regenerative processes take place as actively as possible.
- Transplantation of the prepared block. Indicated if you need to restore a large atrophied area of the jaw. The doctor takes material for transplantation from the patient’s bone, obtained from the palate, beard. It is also possible to use donor blanks.
The specialist decides which of the available methods is suitable for a particular patient on a personal basis.
Is bone restoration necessary after tooth extraction?
It is imperative to remember that with any tooth extraction, even if there are no signs of periodontitis or other diseases leading to atrophy, the bone tissue at the site of the dental alveolus atrophies quite quickly (within several months). Restoration of bone tissue after tooth extraction is mandatory.
A serious bone defect of the jaw can also appear with the development of purulent complications - osteomyelitis, which occurs after complex tooth extraction (for example, removal of an unerupted or impacted tooth, removal of bone tumors). Both the operation itself, which injures the bone, and postoperative purulent complications lead to bone tissue atrophy. In such cases, in addition to filling the bone defect with a graft, various agents are used to stimulate osteogenesis. For example, osteoplastic biocomposite materials (Kollapan), photodynamic therapy, electric vibration massage.
Rules of patient behavior after osteoplastic surgery.
The speed of rehabilitation, the absence of complications and the quality of the result obtained depend 80% on how the patient behaves AFTER THE OPERATION. All prescriptions of a dental surgeon in this regard are not advisory, but MANDATORY.
After bone grafting, the patient is prohibited from:
- Eat and drink hot.
- Take a bath, go to the bathhouse, sauna, swim in the pool.
- Engage in sports and physical labor.
- Lift weights.
- Fly on an airplane for 3 months.
- Drink alcohol.
- Smoking.
After bone grafting, the patient should:
- Eat light, liquid and only warm food.
- Maintain oral hygiene, but do it very carefully.
- Take all medications prescribed by your doctor strictly as scheduled.
- Use antibacterial mouth rinses.
Restoration of bone tissue in periodontitis and periodontal disease
Almost every adult faces the problem of losing molars. The most common reason leading to tooth extraction is periodontitis (progressive destruction of the structure of the alveolar process of the jaw). This disease is very common; its initial signs (bleeding gums, exposure of the neck of the tooth) can be found in everyone after 40–50 years. Less common is periodontal disease, which develops in the absence of normal blood supply to the periodontal tissues. For example, with diabetes and atherosclerosis. Restoration of bone tissue during periodontitis or periodontal disease is required when atrophy of the bone tissue of the alveolar processes of the jaws occurs.
When is bone augmentation contraindicated?
Any surgical operation requires a thorough preliminary examination of the patient’s condition and cannot be performed on everyone without exception.
Bone augmentation is contraindicated if:
- blood diseases and bleeding disorders
- diabetes mellitus
- acute inflammation in the oral cavity
- mental disorders
- autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency, HIV/AIDS
- osteoporosis, loose bones
- oncology
- heavy smoker
- pregnancy and lactation
In addition, a sinus lift cannot be performed for sinusitis, nasal polyps and after surgery on the maxillary sinuses.
Restoration of bone tissue after implant removal and surgery
Unsuccessful implant installation (the doctor’s choice of a very thin or short implant, its incorrect installation without taking into account the bite) leads to tissue inflammation - peri-implantitis, loosening, breakage or rejection of the implanted tooth. In such cases, the implant fragments are removed from the bone, and then a major reconstruction of the alveolar process is required.
When can you do without bone grafting?
You can always do without bone grafting when you can install an implant of the required diameter and required length into the remaining bone.
And, in fact, you shouldn’t do bone grafting just to assert yourself. Some doctors suffer from this, trying to prove to themselves or someone else how they can do bone grafting.
But, as they say, the best bone grafting is the one we don’t do: if the patient can be rehabilitated without bone grafting, then it’s better to do just that. Since volume can be added with soft tissues, connective tissue can be transplanted - a graft, or drugs can be added to replace the volume of soft tissues - and achieve an excellent result!
Peptides for bone tissue restoration in dentistry
There are peptide bioregulators that specifically stimulate the regeneration of jaw bone tissue and promote bone formation. They are also called odontotropic regulatory peptides. Peptides for bone tissue restoration in dentistry are used both for treatment and for preventive purposes. First, you must definitely visit a dentist and, on his advice, choose a drug - balm, capsules or toothpaste. For example, Revidont toothpaste contains three types of peptide complexes (A-3, A-4, A-6) and superoxide dismutase. The therapeutic effect of the paste includes strengthening the structure of teeth, normalizing microcirculation in the oral cavity, restoring bone tissue and having an anti-inflammatory effect.
What other types of osteoplastic operations are there?
For the patient, the doctor chooses the most suitable method of bone grafting.
It could be:
Bone block transplantation involves autotransplantation of bone tissue taken from the patient himself. The main advantage of the method is that this type of bone material takes root very well. But there are also many disadvantages: the main one is triple surgical intervention:
- First, bone material is collected from the patient.
- Then the bone material is transplanted into the jaw.
- Implants cannot be installed simultaneously with this type of osteoplasty. Therefore, implantation must be carried out separately, after complete healing.
The method of directed tissue regeneration using dental membranes involves stimulating the body's own process of bone tissue regeneration.
Gum contour restoration is carried out in order to strengthen loose teeth due to bone atrophy and gum loss. In this case, osteoplastic surgery is performed to cover the exposed roots of the teeth.
Is it possible to restore bone tissue in osteoporosis?
Reduced bone density, or osteoporosis, is more common in women, especially postmenopausal and postpartum women, and in people of both sexes with hormonal imbalances. In such cases, you need to consult a therapist and endocrinologist and take prescribed medications. Restoration of bone tissue in osteoporosis is complicated by systemic reasons for its decrease throughout the human skeleton. However, modern technologies and materials used to restore bone during implantation make it possible to successfully implant new artificial teeth, saving patients from wearing removable dentures.
What materials are used to build bone tissue?
| Type of graft material for bone grafting | pros | Minuses |
| The patient's own bone tissue - autograft | Fully biocompatible, take root well | Obtaining the material is traumatic, because additional surgery is needed to remove it. |
| Donor human bone tissue - allograft | They also have a high survival rate and do not require additional surgical intervention. | They have a psychological barrier to use, because are often cadaveric material. |
| Synthetic bone tissue substitutes - alloplasts | They are becoming more and more popular as their quality improves all the time. Very common as additional material. | May cause allergies. |
| Bone tissue of animal origin - xenografts | It survives worse than human ones, but is accessible and does not require additional surgical intervention. | Unacceptable for some patients due to religious beliefs. |
Sinus lifting – briefly about the method
When implanting in the lateral areas of the upper jaw, in the vast majority of cases, raising the level of bone tissue is required. The upper jaw is an air-bearing organ. It contains the maxillary sinuses, lined with ciliated epithelium, which is responsible for purifying the air we inhale. The sinus lift operation involves carefully lifting the mucous membrane with curettes and performing bone grafting. In fact, a sinus lift is a version of the GBR for the upper jaw in the projection of the maxillary sinuses. The success of bone grafting for alveolar process atrophy depends on the patient's compliance with doctors' recommendations, strict adherence to the postoperative regimen, non-smoking, and of course, on the experience and qualifications of the operating surgeon!
How is implantation performed during bone grafting?
Implantation during bone grafting can be carried out either simultaneously with bone grafting, or delayed - when the implants are installed in the new “grown” bone.
As an experienced implant surgeon, in my practice, in 80-90 percent of cases I perform bone grafting at the same time
with implantation.
I will explain why I perform plastic surgery with implantation at the same time, and what is the advantage of this approach. Bone grafting itself requires a long healing period, from 4 to 9 months. And if we maintain this period and then do implantation, then we have to wait another 4 months. That is, the time frame in this case increases significantly.
And if I do implantation along with bone grafting, then the implant takes root along with the bone. A good implant has an excellent osteogenerating surface, and when fused, an excellent result
.
This reduces the patient’s rehabilitation time. And most importantly, the patient DOES NOT NEED
second surgery. We understand that a large number of surgical interventions do not improve trophism, mucous membranes, or bone tissue.
Everything we do at the German Implant Center, from tooth extraction to implantation, is carried out as atraumatically as possible for the patient.
How many implants are placed during a total restoration?
We specialize very broadly in total implant rehabilitation. In the upper jaw, 6-8 implants are recommended according to our protocol; in the lower jaw, 6 implants are sufficient for total rehabilitation.
Often, implantation occurs simultaneously with the installation of temporary teeth, that is, the patient leaves the clinic “with teeth”, and not on the second or third day, but on the same day when implantation is done:
Preliminary implantation planning is carried out using CBCT, the implants are placed in the required positions.
After this, a surgical template is made, according to which the implants are installed. And based on the same computed tomography (CBCT) and images, a temporary structure is made that will be attached to the implants installed for the patient.
And it turns out the so-called “full case” is when the patient comes, if necessary, if circumstances require it, teeth are removed (or they have already been removed/lost earlier), implants are placed on the patient and an orthopedic structure is fixed - his new teeth.