- Advantages
- Doctors
- Contacts
- Licenses
Advantages
- The latest, constantly updated equipment
- Interest-free installments for all services
- Online consultations with an ENT doctor
- Visit of an ENT doctor to your home
- Friendly and qualified staff
- 24/7 ENT assistance
Olfactory hallucinations are the sensation of smells that are not there. Most often, a person feels unpleasant aromas that can cause significant discomfort in everyday life. They may be present constantly or appear periodically without connection with any factors.
Olfactory hallucinations occur for varying durations. In some cases they last for several minutes, and in others for several hours or even days. Unfortunately, neither fragrances, nor air fresheners, nor any other means help in such a situation. And this can knock a person out of the usual rhythm of life. Your doctor will tell you how to treat olfactory hallucinations after a detailed examination and an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of olfactory hallucinations
Recently, doctors have increasingly had to deal with olfactory hallucinations after coronavirus. Previously, similar disorders could have appeared after ARVI, but the new covid infection has a particularly aggressive effect on the neuroepithelium of the nasal cavity and the nervous tissue of the brain.
In addition to olfactory hallucinations during coronavirus, other causes of this disorder may be:
- concussions and bruises of the brain, especially those involving the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex in the pathological process;
- epileptic disease - the appearance of phantom odors is often an aura preceding a convulsive attack;
- neurodegenerative diseases of the brain - Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, storage pathologies and others;
- toxic damage to neurons due to chronic smoking, alcohol abuse;
- migraine - in the case, as with epilepsy, the sensation of non-existent odors can be the aura of a severe headache attack (usually the smell of burnt or spoiled food appears).
Sometimes the feeling of non-existent odors can be associated with pregnancy. Most often, this condition is observed in the first trimester, and then goes away on its own without leaving a trace.
It is also worth knowing that olfactory hallucinations appear when there is damage to the blood vessels of the brain and may even indicate an increased risk of stroke. Therefore, such a symptom is a good reason to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Causes of sweet taste in mouth
Poor nutrition
The most common causes of a sweetish taste in the mouth are chronic overeating, abuse of simple carbohydrates and fatty foods.
As a result, carbohydrates are intensively broken down into glucose, the penetration of which into saliva causes the sensation of sweetness. An obsessive unpleasant taste often bothers you in the evening. You can get rid of it by brushing your teeth or rinsing your mouth. A sweet taste is often found in people following a low-carbohydrate diet for a long time. The feeling of sweetness is caused by the intensive breakdown of fatty acids for the body's energy needs, which produces ketone bodies and other chemical compounds that have a sweetish taste. The symptom bothers the patient constantly. It is accompanied by general weakness, decreased muscle strength, and regular severe headaches.
To give up smoking
A common cause of a sweet taste in the mouth in men is disruption of the taste buds due to smoking cessation. Periodically, there is a cloying sweetish sensation in the mouth that is not associated with food. The symptom is most pronounced in the first months of getting rid of a bad habit, then the functioning of the taste apparatus returns to normal. The symptom is aggravated by constantly sucking lozenges, which is often done by smokers during the period of quitting cigarettes.
Stress
An increase in the concentration of first adrenaline and then corticosteroids in response to a psycho-emotional shock contributes to an increase in glucose levels in the blood and, consequently, in saliva. This is perceived by the patient as a feeling of sweetness in the mouth. Taste discomfort may be accompanied by thirst, dry mucous membranes, fear, anxiety, and muscle tremors.
The condition is more pronounced at night, decreases or temporarily stops after drinking large quantities of ordinary water and completely normalizes on its own after the end of the traumatic situation. Less commonly, stress glycogeusia persists for longer than 6-8 days and serves as one of the possible signs of developing depression or emerging neurosis.
Diabetes
Complaints about the periodic occurrence of a sweet taste without an obvious reason are a typical sign of impaired carbohydrate metabolism and incipient diabetes. Patients complain of severe dryness in the oral cavity, against the background of which an unpleasant sweetish taste sensation appears. Also characterized by a strong feeling of thirst, increased appetite and an increase in the amount of daily urine.
A feeling of sweetness in the mouth, accompanied by increasing malaise and headache, indicates the risk of developing ketoacidosis, a complication of diabetes mellitus in which the formation of toxic compounds occurs. At first, patients feel a sweet taste, then it changes to a bitter taste, and the smell of acetone is felt from the mouth. This condition is an indication for emergency medical care.
Pregnancy
During a normal pregnancy, women often experience atypical taste sensations that are not associated with food intake. The sweetish taste appears at any time of the day. It is often enhanced by the use of vitamin complexes and other supplements that doctors prescribe for pregnant women. With toxicosis, an unpleasant taste aggravates nausea and provokes vomiting.
In pregnant women, a sweet taste in the mouth can also be caused by pathological reasons; most often it is caused by the development of gestational diabetes. The symptom is determined in the second half of pregnancy. Unpleasant taste sensations persist throughout the day. Pregnant women also notice increased thirst and an excessive increase in appetite, while their body weight increases slightly.
Pancreatitis
Complaints of a sweetish taste in the morning or during long breaks between meals are characteristic of damage to the pancreas. The disorder bothers patients most when waking up; after breakfast, the unpleasant feeling disappears. Also with pancreatitis, periodic pain in the left hypochondrium, nausea and heaviness in the abdomen are observed. Sometimes vomiting occurs, after which the sickly sweet taste in the mouth intensifies.
Gastrointestinal diseases
The symptom is detected in hyperacid conditions (gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease), which are accompanied by periodic reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus and oral cavity. The sweetest taste is most pronounced after bending the body, intense physical activity, or prolonged stay in a horizontal position. The unpleasant feeling decreases after brushing your teeth, but does not disappear completely.
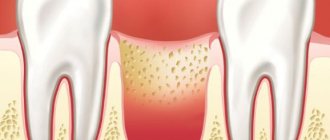
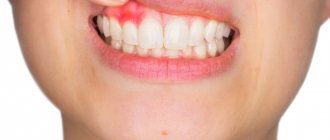
Purulent processes in the mouth
Gingivitis, stomatitis, deep caries with the addition of bacterial flora are accompanied by the formation of pus, which, accumulating in the spaces between the teeth and gum pockets, causes an irritating sweet taste in the mouth. The symptom is more pronounced in the morning. With insufficient oral hygiene, it is periodically observed throughout the day. In addition to the taste, patients are concerned about toothache that occurs spontaneously or occurs while eating.
ENT diseases
Chronic infectious processes in the paranasal sinuses or tonsils, caused by staphylococci, streptococci or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, provoke a sweetish taste. Patients with chronic tonsillitis and sinusitis note that taste discomfort does not have any visible cause and disappears after rinsing the mouth with water or eating food. The symptom often develops in the morning, when during night sleep the purulent contents of the nasal cavity drain into the pharynx.
Neurological disorders
In case of traumatic brain injury or brain damage due to intoxication, the nuclei of the cranial nerves responsible for the formation of taste sensations are involved in the pathological process. At the same time, patients lose the ability to distinguish the tastes of food and often feel a monotonous sweetish taste in the mouth for no reason. Taste disorder is combined with salivation disorders and swallowing disorders.
Rare causes
- Chemical poisoning
: pesticides, phosphorus-containing toxic substances (phosgene, etc.). - Oncopathology
: lung cancer, malignant bronchial neoplasia. - Complication of chemotherapy
.
How to treat olfactory hallucinations after coronavirus and more
First of all, it is necessary to differentiate what the smell disorder is associated with - diseases of the ENT organs or brain damage. In the first case, treatment is carried out by an otolaryngologist; it is with this specialist that the diagnostic search should begin. And in the second case, the therapeutic program is drawn up by a neurologist.
After Covid infection, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory therapy is usually sufficient. Sometimes physiotherapy may also be prescribed in combination. When polyps are identified, they are removed endoscopically. If hallucinations occur due to brain damage, then conservative treatment with nootropic, metabolic, vascular and other drugs is used.
If you are faced with olfactory hallucinations, then do not delay your visit to the otolaryngologist. Timely identification of the causes of such a disorder will allow timely initiation of targeted treatment and avoid serious complications. At the Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic, consultations are conducted by qualified specialists who regularly improve their knowledge taking into account the latest advances in the field of medicine. Make an appointment at a convenient time!
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health.
Don't delay treatment, call right now. We work around the clock. tel. (24 hours a day)
Diagnostics
To determine the etiological factor of the sweet taste in the mouth, a consultation with a gastroenterologist is required, who, after an initial examination, can refer the person to other specialists. First, the doctor collects an anamnesis and examines the oral cavity in detail for purulent processes, then prescribes specific tests and instrumental methods. From a diagnostic point of view, the most important are:
- Blood tests
. In a biochemical study, attention is paid to glucose levels; even with a slight increase in sugar, an oral stress test is performed. To determine the cause of a sweetish taste in women, the concentration of estrogen and progesterone is assessed, and the level of hCG is measured. A clinical blood test reveals leukocytosis and increased ESR. - Gastroscopy
. If the unpleasant taste is accompanied by heartburn and chest pain, an endoscopic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract is informative. The method is necessary to identify inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane, disorders of the contractile function of the lower esophageal sphincter. During endoscopy, a biopsy of pathologically changed areas is performed. - Sonography
. During a targeted ultrasound of the pancreas, the heterogeneity of the structure, the presence of hypoechoic areas, and space-occupying formations are determined. With pancreatitis, swelling and blurred contours of the organ are detected. Women are shown an ultrasound of the pelvic organs; transvaginal ultrasound is used for detailed visualization. - Neurological examination
. If the sweet taste is combined with paresthesia and swallowing disorders, damage to the central nervous system structures must be excluded. A standard examination includes checking pharyngeal and pupillary reflexes and assessing muscle strength and tone. To visualize the brain, an MRI or CT scan with contrast is performed. An EEG is sometimes recommended.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce discomfort, first of all you need to change your diet: limit the amount of sweets, white bread, fatty foods as much as possible, increase the content of protein foods, fresh vegetables and fruits. It is important to maintain an adequate drinking regime. To get rid of the obsessive aftertaste, you can eat citrus fruits and drink water with lemon juice.
Doctors recommend maintaining oral hygiene: brush your teeth thoroughly 2 times a day, and use dental floss or a toothpick after eating. To effectively clean the interdental spaces, use a mouthwash or irrigator. A sweet taste that occurs against the background of abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea or vomiting is an indication to consult a specialist.
Conservative therapy
Treatment tactics depend on the cause of the cloying-sweet sensation. Drug therapy is combined with local effects - rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions or herbal decoctions, medicinal pastes on the area of the dental canals. The treatment regimen for diseases accompanied by a sweet taste in the mouth often includes:
- Insulin
. Hormone replacement therapy is indicated to normalize glucose concentrations in type 1 diabetes. An intensified treatment regimen with a combination of short- and long-acting insulins is selected. For type 2 diabetes mellitus, oral hypoglycemic drugs are taken. - Enzymes
. Enzyme agents are effective for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. They improve digestive function and promote the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates. The drugs are prescribed in long courses; preference is given to drugs containing bile acids. - Antisecretory agents
. Medicines reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, thus eliminating the causes of the formation of a sweetish taste. The most commonly used are proton pump inhibitors, which have minimal side effects and a prolonged effect. - Antibiotics
. Purulent lesions of the oral cavity are treated with antibacterial drugs, which are used both systemically in the form of tablets and locally in the form of ointments and applications to the mucous membrane. To prevent candida infection, antifungal agents are recommended.