People with dental problems often wonder whether a lymph node can become inflamed due to a tooth. Doctors have repeatedly warned that inflammatory processes in the oral cavity often lead to enlarged and painful lymph nodes. If a person experiences these symptoms, they should immediately make an appointment with a dentist. The doctor will treat the diseased tooth, after which the work of the inflamed lymph node will normalize and it will no longer cause discomfort.
Causes of pathology
If the lymph node in the neck under the jaw is inflamed, then the possible causes are:
- diseases of infectious origin that affect the ENT organs and the upper parts of the respiratory system (tonsillitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, otitis media);
- diseases developing in the oral cavity (caries, periodontal disease, periodontitis, periostitis, or gumboil, pulpitis, gingivitis, alveolitis, stomatitis);
- systemic infections (measles, whooping cough, mumps, popularly called mumps, chicken pox);
- pathologies affecting the immune system (lymphomas, leukemia, lupus, HIV);
- neoplasms (benign or malignant) of various origins (atheromas, granulomas, lipomas, cysts);
- infections caused by parasitic microflora (lymphoreticulosis, toxoplasmosis);
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system.
You should know that the above ailments are not always accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes. Quite often, the nodes remain in a normal state even if the disease is acute.
If the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed, then in 60% of cases the pathology is caused by dental problems, in 30% by diseases of the respiratory system. In 20% of cases, the reason why the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed and hurts is advanced caries, leading to the development of a purulent abscess. After tooth extraction or conservative treatment of caries, pathological processes in the lymph nodes stop.
But sometimes it is tooth extraction that can become a provoking factor and cause an enlarged lymph node. A similar situation is possible if an infection enters the hole.
The relationship between ENT organs and dental health
30.10.2017
Author: Dentist-periodontist Tamara Valerievna Kudzieva
Often, patients are faced with a situation where doctors have difficulty making a diagnosis due to the proximity of certain organs, and the patient is forced to turn to related specialists in order to avoid an inaccurate diagnosis.
Dental science is no exception. The diagnosis, etiology, i.e. is quite common. The cause of which dentists sometimes find it difficult to determine. Namely, inflammation of the maxillary (maxillary) sinus - sinusitis. Or a diagnosis whose name is more familiar - sinusitis. Patients are often confused about which doctor to see, a dentist or an ENT specialist.
Let's figure out why often an ENT doctor and a dentist cannot share this diagnosis.
First, let's give a definition and understand what the maxillary sinus is:
The maxillary sinus is a cavity formation in the upper jaw, lined with mucous membrane.
The function of the maxillary sinus is to warm and purify inhaled air. When an infection penetrates, one way or another, the mucous membrane of the sinus becomes inflamed, this process is called sinusitis (sinusitis). The patient usually complains of a feeling of nasal congestion, the presence of purulent exudate (discharged fluid), headaches, fever, pain in the projection of the sinus when tilting the head and palpation.
The reasons for the development of sinusitis can be odontogenic (due to the tooth) and non-odontogenic.
Non-odontogenic causes are most often associated with complications of colds or viral diseases, rhinitis. A specialist in ENT diseases works directly with this diagnosis.
We will dwell in more detail on the odontogenic cause of sinusitis:
As noted above, the cause of the development of this type of inflammation is an infected tooth.
This is due to the anatomical features of the structure of the upper jaw, since the roots of the teeth are located close to the sinus or even directly in it:
Thus, in the presence of a chronic inflammatory process in the canals of the teeth of the upper jaw, this infection spreads to the mucous membrane of the sinus, causing its inflammation. If there is an odontogenic cause for the development of sinusitis, it is not advisable to treat only the sinus by an ENT doctor, since this treatment will not give a long-term effect. It is necessary to eliminate the cause of inflammation - an infected tooth. And often, such unpleasant manipulations as punctures, rinsing, and prescribing antibacterial agents do not bring the desired result.
And therefore, competent ENT specialists, before starting treatment, must refer the patient to a dentist to exclude an odontogenic cause for the development of sinusitis.
If the inflammation is caused by a tooth, the dentist first needs to assess the feasibility of treating and preserving the tooth. If the prospect of treatment is assessed as favorable, then the endodontist performs high-quality root canal treatment to eliminate the infection. Before permanent filling of the canals, you may need to temporarily fill them with agents that have an antiseptic effect. And then, having seen the positive dynamics, seal the tooth hermetically. If the tooth is severely damaged, or there is no possibility of passage of the canals (sclerosis, severe curvature, root perforation, false passage, broken instrument), then such a tooth must be removed.
After eliminating the cause, after a couple of months, a control CT scan is performed to make sure that the sinus has begun to recover.
It is important to note that all sinuses communicate with each other; therefore, an infection from the maxillary sinus, in the absence of proper treatment, can spread throughout the entire sinus system, which greatly complicates treatment.
Thus, a competent approach to treatment and timely redirection to a suitable specialist will prevent an incorrect diagnosis and, as a result, incorrect treatment tactics. And therefore, save the patient’s time and finances.
Stages of disease development and symptoms
Lymphadenitis in its development goes through 3 stages:
- stage
– the lymph nodes take on the appearance of mobile, compacted tubercles, when pressure is applied to them, pain appears, the temperature rises, sleep is disturbed, and general weakness is detected;
- stage (purulent abscess)
– the lymph node enlarges more and hurts even if you don’t touch it, which limits the motor activity of the jaw, pus accumulates in the lymph node, the skin around it becomes red, and the temperature is constantly elevated;
- stage (purulent phlegmon)
– the tumor spreads to the lymph nodes located in the armpits, the pain intensifies significantly, the skin turns blue, the temperature rises to 40⁰.
Prevention
To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to consume citrus fruits
Each person can prevent the re-development of cervical lymphadenitis due to dental diseases if he follows simple tips:
- In case of lesions in the oral cavity, rinsing with saline solution is required.
- It is necessary to include ginger tea in your diet.
- You should carefully monitor your oral hygiene.
Experts recommend consuming citrus fruits, natural products and honey more often. They help strengthen the immune system and improve the functioning of the lymph nodes.
Treatment methods
If the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed, how to treat it? The choice of treatment method is influenced by the cause of the pathology and its neglect. In mild cases, if the cause is eliminated, the inflammation will stop and the lymph node will return to its previous size. If complications are detected, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics or antiviral medications, painkillers, antipyretics and antihistamines. It is also necessary to take vitamins to strengthen the body's defenses. Traditional medicine will help speed up the healing process and eliminate unpleasant symptoms. The course of therapy takes a week and a half.
If a purulent infection occurs, then there will be a need for surgical intervention, during which the surgeon will open the inflamed lymph node and pump out the pus. Fortunately, this situation is extremely rare.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
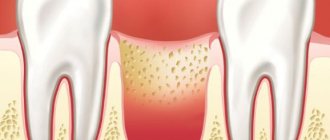
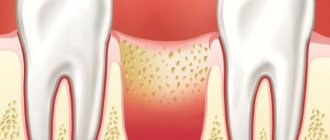
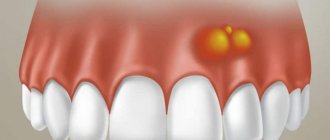
Symptoms of gum abscess
Basically, bacteria affect one tooth, but with advanced disease, suppuration can spread to several. The onset of an abscess is always noticeable, as it is accompanied by severe pain at the site of the lesion. They may decrease in intensity for a while, but then only increase. Painkillers in such cases relieve pain only for a short time.
The most common manifestations of the disease are:
- pain when pressing on the tooth, chewing;
- pain in the gum when pressing on it;
- bitter taste;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- the gums at the site of the lesion swell;
- facial asymmetry appears;
- the lymph nodes under the jaw and on the neck swell;
- Temperature may rise and headache may occur.
In the future, wounds with purulent discharge may appear on the inflamed gum skin. It should be noted that even a complete breakthrough of the abscess and subsidence of the pain does not mean a successful completion of the disease. You should definitely consult a dentist, because bacteria still remain in the tooth tissues, and in the near future the disease will manifest itself again.
Professional diagnostic measures
When a lymph node becomes inflamed, you should not hesitate to see a doctor. It is better to start by visiting a dentist, who will examine the oral cavity and send you for an x-ray to obtain information about the presence or absence of hidden processes and dental pathologies.
Additionally, the patient may need the help of other specialists: an ENT doctor, a therapist, an infectious disease specialist. Be prepared that for a detailed diagnosis you may be referred for urine and blood tests (usually they reveal an increased number of leukocytes), bacterial culture, and ultrasound.
Treatment of tooth abscess at SM-Dentistry
The inflammatory process in the dental tissues will not go away on its own, and treatment at home is extremely ineffective and can only lead to the spread of infection. Therefore, we strongly recommend that at the first symptoms of tooth inflammation, you contact the nearest SM-Dentistry clinic. Highly qualified doctors, the latest dental methods and equipment, safe types of anesthesia make it possible to completely solve the problem of purulent inflammation of the tooth in the shortest possible time.
All types of abscesses are successfully treated at SM-Dentistry:
- gingival - with inflammation of the gums;
- periodontal - with a focus between the tooth and gum;
- periapical - affecting the pulp.
The treatment program depends on the extent of the infection, the nature and cause of the disease. Most often, it consists of cleaning the dental canals and pulp from pus, antibacterial therapy and tooth filling. If infection of the soft tissues of the oral cavity occurs, the intervention of a surgeon may be necessary to eliminate the source of infection while preserving the tooth. To make the treatment painless and comfortable for you, SM-Dentistry doctors use local or combined anesthesia with imported drugs.
After treatment, you will receive detailed recommendations on how to care for your teeth for effective healing. Within a day there will be significant relief.
Our specialists will also diagnose and eliminate dental diseases that caused the abscess. If necessary, you can consult doctors of related specialties.
If the abscess develops rapidly, contact SM-Dentistry at any convenient time. We work daily from 9:00 to 21:30, and on weekends until 21:00. To make an appointment, fill out an application on the website or call: +7 (495) 777-48-06.
Dentist consultation Dental filling
Why does the inflammatory process occur?
As you know, the lymphatic system is a very important component of our body. It prevents various pathogens from entering the blood and internal organs, but it itself is often the first to take the blow due to decreased immunity. Many people know that swollen lymph nodes are often the first signal that a person has some kind of disease in the body. They usually swell shortly before the first symptoms of the disease appear. Their increase may indicate a sore throat, HIV, syphilis, tonsillitis, lupus, measles, scarlet fever, arthritis and many other pathologies.
This is interesting! Scientists have found that in the human body there are more than 400 lymph nodes (they are located in small groups) and about 2 liters of lymph that passes through them. The greatest concentration is on the neck and head, under the jaw and chin, under the arms and in the groin. Each group is responsible for the well-being and protection of nearby organs.
However, not everyone knows that inflammation in this important system for the body often occurs due to dental pathologies. This means that the infection gets there from a nearby area, in this case, from the oral cavity, where a large number of different bacteria live. Naturally, staphylococci, streptococci and other harmful as well as beneficial bacteria are constantly present in the mouth, and this is normal. But the problem arises only if microbes multiply rapidly and pathogenic microflora begins to predominate. Why is this happening? Read on.
Diagnosis of submandibular lymphadenitis
You can determine that inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes has begun on your own. It is enough to simply feel the areas of the neck directly under the lower jaw, closer to the ears. Normally, the nodes are almost impossible to palpate; they are small, have a dense structure, do not hurt and move easily under the fingers. If you notice a change in the structure of the lymph nodes, or feel discomfort or pain during palpation, you should consult a doctor. It is impossible to independently identify the cause of inflammation. First, you can go to a therapist. After the initial examination, which includes examination and collection of tests, he will refer you to another specialist: otolaryngologist, phthisiatrician, surgeon, infectious disease specialist, immunologist or dentist. If caries is suspected, the doctor will diagnose using the following methods:
- Coloring. A solution is applied to the tooth enamel, which turns the areas of demineralization purple.
- X-ray. Photographs of the teeth or the entire jaw are taken, from which the location and extent of the caries process can be determined.
- Laser diagnostics. This method is the most modern. It allows you to accurately identify the extent of the spread of pathology.
Based on the results of the examination, treatment is prescribed. First, we will describe the general features of the treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis, after which we will tell you what to do if the lymph nodes become inflamed due to caries.
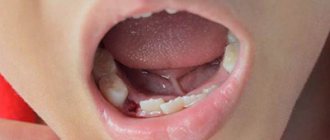
Teething and enlarged lymph nodes
The problem is typical mainly for children whose first milk units are being cut. Babies have a weak immune system, and during this period it weakens even more, since the body is under a serious load. Often, teething itself is very difficult, accompanied by alarming symptoms (moodiness, cough, fever, runny nose) and even the addition of bacterial and viral infections.
This pathology does not always escape adults. For example, when a wisdom tooth is cut and the submandibular lymph node increases in size, this is a fairly common occurrence. The third molars pass through the jawbone, and this process takes a long time, plus it is often associated with disturbances. “Sages” can compress and touch the branches of the trigeminal nerve, rest against neighboring elements of the row and destroy them. Their eruption may be accompanied by a decrease in immunity and an increase in body temperature, to which all the defense systems of our body react very sensitively.
Sometimes growth pathologies of the “eights” lead to the development of a purulent-inflammatory process such as pericoronitis. The problem arises when a kind of hood forms between the gum and the not fully erupted “figure eight”, where bacteria and food debris get trapped.
On a note! If your wisdom tooth hurts and the lymph node is swollen, then the symptoms may indicate damage to the third molar by caries, pulpitis, or periodontitis. If the cheek is also swollen, then, most likely, gumboil has developed.
Inflammation of the lymph node
Inflammation of the lymph node can cause neck pain
The lymphatic system and nodes belong to the body's immune defense system. The nodes are a kind of filter for infection and a sensor that shows the presence of inflammation.
Lymph nodes enlarge and hurt when performing their function - retaining microbes, infections, foreign cells.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs:
- Due to other diseases (most common).
- An independent disease (in the absence of diseases of other organs, lymphoma, metastases).
According to the nature of inflammation, lymphadenitis occurs:
- Serous. Symptoms will be enlarged, painful lymph node. Treatment will include searching for the underlying cause and conservative therapy.
- Purulent. It is characterized by an enlarged lymph node, severe pain, redness of the skin, increased temperature, and a disturbance in the general condition. Surgical and medical treatment is necessary.
Treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis with caries
Caries is treated with various methods depending on the stage. At the first stage, in which you only need to eliminate the white spot, remineralization of the tooth surface is carried out. With the help of special preparations, the enamel is saturated with minerals - calcium and fluorine. Therapy is prescribed in a course lasting 5-15 procedures. For home use, the patient is prescribed hygiene products that help restore enamel and the balance of microelements in the oral fluid. Such means include:
- toothpastes: Marvis Orange Blossom Bloom, Dentissimo Complete care, Apadent Perio;
- gels: Stomysens® Desensitizing Repairing Treatment 4, DRC ROCS (ROCS) Medical Minerals, Dental Resources Inc Sorbet Revive;
- rinses: Vivax “Remineralization”, CURAPROX Perio Plus Forte chx 0.20%, Biorepair Delicate Gums Mouthwash.
If a carious cavity has formed on a tooth, then remineralization will not help; filling is necessary. First, the dentist cleans the hole from necrotic tissue and food debris, after which he places a protective gasket and fills the cavity with filling material. If caries is complicated by pulpitis, the nerve has to be removed.
After treatment of the carious process, the inflamed lymph node should return to normal. If this does not happen, it is necessary to re-diagnose. Perhaps the inflammation is not a consequence of caries, but of another disease.
More often, the submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed during the chronic course of the carious process, in which slow tooth destruction is observed. It is not accompanied by severe symptoms, but with exacerbations or the presence of certain factors, inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs.
Stages of caries
There are 4 stages of carious lesions, each of which differs in the number and intensity of symptoms. The first (initial) stage is called the chalky (or white) stain stage, in which an area of demineralization forms on the tooth surface. Outwardly, it looks like a white speck, lacking shine. Under a microscope, you can see that in this area the enamel is rough, loose and porous. However, there is no carious cavity yet, so it is possible to cure the tooth without filling. The person is not bothered by any symptoms. Caries can be detected at the initial stage only during an examination.
At the second (superficial) stage, the carious process penetrates into the deep layers of the enamel, but remains within its limits, without spreading to the dentin. The white spot darkens and becomes brownish. The pathology can already be noticed independently if it develops on the outside of the tooth or fissures. Complaints appear: tooth sensitivity to sweets increases, sometimes to hot and cold, and there is discomfort when chewing food. However, it disappears as soon as the irritating factor is eliminated.
The third (middle) stage of caries is characterized by the penetration of the carious process into dentin. A brown or dark yellow cavity is formed, which is easy to see with the naked eye. Discomfort while eating is an almost constant concern, especially when a diseased tooth interacts with sour or sweet foods. The sensitivity of dental tissues to temperature changes also increases. The pulp is not yet involved in the pathological process, but this stage of caries can already be considered complex. At this stage it will not be possible to avoid preparation and filling. There is a risk of complications, possibly inflammation of the lymph nodes.
The fourth (deep) stage of caries is considered an advanced form of the disease, in which the carious cavity covers almost half of the tooth. It usually looks like a black hole with sharp edges. Pain occurs not only when eating, brushing teeth or temperature changes, but also at rest. The likelihood that caries will spread to nerve tissue and cause pulpitis is quite high. Moreover, the tooth may break into several parts, resulting in the need to remove it. This happens in cases where there is no treatment for the disease.
You can cure caries and save your tooth at any stage. But its loss is not the only complication of the carious process. There is a risk of developing other pathologies that are not dental.
Stomatitis and inflammation of the lymph nodes
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa that occurs against the background of infectious diseases, after burns, as a result of trauma, due to an allergic reaction, etc. Traumatic stomatitis is often diagnosed, for example, when the mucous membrane is injured by crowns or braces.
After an injury, bacteria enter the wound and cause inflammation, which is accompanied by:
- painful sensations;
- the appearance of rashes and ulcers on the mucous membrane;
- release of translucent exudate;
- the formation of a white film on the surface of the wound;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- high temperature, chills and fever;
- hyperemia and swelling of the gums.
As a rule, stomatitis goes away without consequences. However, it can be complicated due to weak immunity, alcoholism or smoking. There is a risk that the disease will cause inflammation of the lymphatic system.
Pulpitis and inflammation of the lymph nodes
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the pulp - the nerve tissue inside the tooth. It often occurs in people with advanced caries at a deep stage. The following symptoms are characteristic of pulpitis:
- Acute pain that occurs both at rest and when the tooth is exposed to various irritants: food, brushes, water, etc. After eliminating the factor that provoked the pain, the symptom persists for some time, but gradually subsides. The pain is usually sharp and intense; it cannot be eliminated with analgesics.
- Headaches, pain in the ear area from the affected tooth, general malaise and increased fatigue. The pain may radiate to the temple and eyebrow.
- Increase in local and general temperature. In adults it can rise to 38°C, and in children even higher.
- Swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes, pain when swallowing and chewing food.
With pulpitis, as a rule, it is necessary to remove the diseased nerve, after which the tooth becomes dead and noticeably darkens.
What are the symptoms of inflammation of the lymph nodes?
The submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed against the background of other pathologies, each of which has its own specific symptoms. We list the most common signs of lymphadenitis:
- sudden enlargement of the lymph nodes under the lower jaw, their pain when pressed and hardening;
- first slight and then severe redness of the inflamed areas, they become burgundy and sometimes bluish;
- swelling at the site of inflammation on one or both sides, depending on the etiology of lymphadenitis;
- sharp and short-term attacks of pain that radiate to the ear, temple or eyebrow;
- discomfort when chewing food, increased pain during swallowing;
- inflammation of the oral mucosa, which is accompanied by redness and increased sensitivity;
- increased body temperature, general weakness, sleep disturbance, fatigue.
To make a diagnosis, it is important to determine not only the cause, but also the type of lymphadenitis, since the clinical picture of each of them may be different.