Tooth extraction is one of the most common operations in dentistry. It is indicated for severe destruction of the coronal part, periodontitis, inflammation with suppuration, a cyst against the background of advanced caries. After extraction of a dental unit, a hole filled with blood remains in the jaw. You need to take proper care of it to avoid complications. On average, wound healing takes 14-20 days. We tell you what you should not do after tooth extraction and what symptoms are a reason to contact your doctor.
Description of the disease
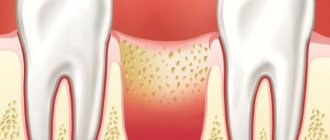
Not all dental surgeon patients know that inflammation may develop after removal, so they often ask the question: “Alveolitis - what is it, and why does it occur?” Other names for the disease: “dry socket”, “alveolar local osteitis”. The pathogenesis of the condition is based on a violation of the formation of a physiological clot or its loss from the socket after tooth extraction, which most often occurs due to a violation of the postoperative regimen or low human immunoresistance.
Inflammation of the alveoli is possible only due to removal of the segment. Alveolitis cannot develop after tooth treatment, since the hole is formed only as a result of extraction of the unit.
The main reasons for the appearance of alveolitis after tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure that is accompanied by the formation of a wound. A blood clot forms in it, protecting it from the penetration of microorganisms. Inflammation of the tooth socket after extraction occurs due to disruption of the process of formation or displacement of a blood clot. The most common causes of pathology:
- Difficult extraction. The more traumatic the operation, the more the tissue’s ability to regenerate decreases and the likelihood of infection increases.
- Wisdom tooth removal. The structure of the root system of third molars is complex, so their extraction is always traumatic. In addition, the bone in the figure eight area has increased density and is less vascularized compared to other areas, which also creates conditions for the formation of a dry socket.
- Concomitant somatic diseases of the patient (diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency states).
- History of pericoronitis (inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth).
- The presence of foci of infection in the mouth before surgery. Penetrating into the wound with saliva, pathogenic flora causes alveolitis.
- Inadequate sanitation of the alveoli. After removal, careful curettage of the wound is necessary to remove fragments of bone tissue, roots, pieces of filling, and granulations. Foreign fragments disrupt healing and lead to alveolitis.
- Exceeding the dose of anesthetic. Leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the capillaries, the development of local ischemia, which disrupts the filling of the hole with blood.
- Mechanical damage to the clot. Failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations during the postoperative period (rinsing the mouth, carelessly brushing teeth, etc.).
- Impaired hemostasis. Due to poor blood clotting, a clot does not form.
Alveolitis can be provoked by smoking, taking hormonal contraception, and insufficient oral hygiene. Age plays a certain role in the development of alveolitis after tooth extraction: the older the patient, the greater the likelihood of developing pathology. This is due to a slowdown in metabolic processes and a decrease in the regenerative ability of tissue cells.
Preventive measures in our Center
To avoid complications, our Center has developed a number of preventive measures - Uniform quality standards that all specialists follow.
- Ultrasonic formation of access to the maxillary sinus is carried out using a low-traumatic piezo installation NSK VarioSurg. The device does not injure the bone, gently softens it, and when it touches the sinus mucosa it turns off, which prevents its rupture.
- Lift-Control micro-instruments for lifting the sinus lining A coordinated set allows you to lift the mucous membrane as gently as possible, without damaging it.
- The use of barrier membranes is mandatory to prevent material from entering the sinus. First, the membrane is fixed, then bone material is introduced.
- Use of biocompatible bone materials We use bone materials based on inorganic tricalcium phosphate without the risk of allergies and rejection. We do not use donor material from other people, or synthetic substitutes that have not proven their effectiveness and reliability.
- The use of bone growth stimulants (BMP) Morphogenetic protein accelerates the maturation of new bone tissue due to the body's reserve forces. Prevents the risk of material shifting.
- Application of PRF membranes The top layer in the sinus lift sandwich technique is fixed with a PRF membrane made from blood plasma. Due to the high platelet content, it ensures the germination of all layers with blood vessels and the rapid maturation of new bone.
- Postoperative X-ray control All operations in our Center always end with a control CT scan on a high-precision 3D tomograph SIRONA GALILEOS with ENT mode settings. This eliminates the possibility of undetected perforation and penetration of bone material into the sinus.
Sinus lifting in our Center is performed only by maxillofacial surgeons
These are experienced doctors with ENT training and 7 years of work experience, excellent clinical thinking and well-developed manual skills.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Founder and Chief Doctor of the Center
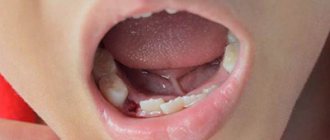
Symptoms of alveolitis of the socket
Alveolitis goes through several stages of development, each of which has its own clinical picture:
| Stage | Description |
| Serous inflammation | The first clinical symptoms appear the next day or after 3 - 4 days after surgery. Non-purulent inflammation is manifested by the appearance of episodic pain and swelling of the soft tissues around the alveoli. |
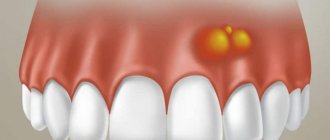
| Purulent alveolitis | If measures were not taken at the previous stage, a purulent process develops within a few days. The pain becomes constant, radiating to the auricle, jaw, and neighboring teeth. The infection spreads to nearby lymph nodes, causing them to enlarge. A gray-green coating appears inside the hole. The temperature rises. |
| Purulent-necrotic stage | The pain intensifies and becomes throbbing. A putrid odor appears from the mouth. Progression leads to disruption of microcirculation, ischemia, and the development of necrosis. The patient’s health deteriorates significantly, and signs of intoxication appear. |
| Hypertrophic tissue change | Lack of medical intervention within 14 days leads to chronicity of the process. Soreness and swelling become less pronounced. Soft tissues grow and fill the hole. When pressure is applied to the granulation, pus is released. The mucous membrane is swollen, bluish in color. |
If left untreated, alveolitis has an unfavorable outcome. The main complications after alveolitis:
- phlegmon (extensive purulent inflammation);
- acute periostitis (inflammatory process of the periosteum);
- osteomyelitis (purulent-necrotic inflammation of the jaw bone);
- sepsis (purulent-septic blood disease).
What to do if bone loss occurs
If bone material comes out after a sinus lift, this should serve as an incentive for prompt action.
- The sooner the diagnosis is made and adequate treatment is started, the more favorable the further prognosis will be.
- If the start of treatment is delayed, pathological adhesions may develop with the implant being fixed in the wrong position.
In any case, a computed tomography scan is performed first . Allows you to determine the degree of “disaster” and not miss the onset of the inflammatory process:
- assess the condition of bone tissue;
- determine the quantity and placement of the remaining material;
- identify its presence or absence in the maxillary sinus.
If bone chips were released only from the oral cavity
Surgery is being performed. Sometimes it is possible to limit oneself only to plastic surgery of the bone material, filling the resulting gaps and re-applying sutures.
If osteomaterial gets into the sinus
Treatment can last for several months and will take place in several stages:
- Removal of a dislocated implant (if installed).
- Elimination of infectious complications - sinusitis, fistula (if present).
- After 1-2 months, in the absence of repeated complications and normal healing, a repeat sinus lift may be performed.
- Implantation is performed 3-6 months after the new bone is formed.
Our Center specializes in solving problems associated with complications in the maxillary sinuses
Patients often come to us after a failed sinus lift. The Center has a full-fledged ENT department to provide surgical care in complex clinical situations. A modern ENT unit includes all the necessary equipment for carrying out operations, including the removal of foreign bodies that provoked inflammation.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Founder and Chief Doctor of the Center
Alveolitis after wisdom tooth removal
Indications for the removal of eighth segments in a row can be different: deep caries, improper eruption, orthodontic correction of jaw bite, dystopia, etc. Extraction of third molars is always associated with trauma to nearby tissues, which increases the development of inflammation. The pathological process is observed in 45% of cases due to the removal of lower wisdom teeth.
Symptoms of alveolitis after wisdom tooth removal are similar to the general symptoms of the disease. However, with such localization of inflammation, a sore throat and impaired functionality of the temporomandibular joint on the affected side may occur (difficulty and painful opening of the mouth).
Diagnosis and treatment
Alveolitis can be detected by examination. If necessary, the dentist will order an x-ray. Treatment of inflammation is aimed at:
- to stop the pathological process,
- prevention of complications,
- creating conditions for wound healing.
To combat a bacterial infection, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics. With proper treatment, the symptoms of alveolitis disappear after two to three days. Residual pain may persist for several weeks.
Methods for diagnosing alveolitis
How long the alveolitis will take to heal depends on timely diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, at the first signs of illness, you should consult a dentist. Identification of pathology occurs after listening to complaints, collecting anamnesis (where there is recent tooth extraction) and examining the socket cavity.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes an x-ray examination, which helps to detect tooth fragments and other foreign fragments in the alveolus. In rare cases, when alveolitis of the tooth socket , computed tomography is prescribed for the purpose of differential diagnosis of other diseases (trauma, tumor, etc.).
Dentists' recommendations
After surgery, it is important to monitor the condition of the wound and follow the doctor's instructions. The hole filled with blood gradually overgrows and is completely covered with granulation tissue 14-20 days after the operation. The first three days after tooth extraction you cannot:
- rinse the mouth,
- eat solid food
- drink through a straw
- smoking and drinking alcohol,
- use a brush with stiff bristles,
- take a hot bath and go to the sauna.
If possible, you should avoid physical activity and stop taking medications that prevent blood clotting. Compliance with the listed recommendations contributes to the speedy healing of the wound.
How to treat alveolitis after tooth extraction
The main task of correction is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused the pathology and stopping the inflammatory process. The doctor decides how to treat alveolitis after tooth extraction. Treatment tactics depend on the stage of the pathological process. It may include revision (if necessary, curettage) of the hole, drug treatment, physical therapy (laser, magnet, fluctuarization, ultraviolet radiation). All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia.
Treatment program:
- Local anesthesia.
- Antiseptic treatment of the wound (removal of saliva, food debris, pus).
- Freeing the cavity from a disintegrated blood clot, foreign inclusions (tooth fragments, root remains, etc.), granular tissue.
- Repeated treatment with an antiseptic, application of a turunda soaked in an anesthetic drug.
- Applying a medicated antiseptic bandage.
When treating alveolitis, the doctor can use proteolytic enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin), which break down necrotic tissue, thereby helping to cleanse the socket. To reduce pain, a blockade is made with local anesthetics, which are injected into the soft tissue near the inflamed alveoli. To suppress the infectious process, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Causes
Tooth granulation can lead to the formation of granuloma for various reasons:
- Unsuccessful removal, after which a necrotic area of the apex of the tooth root remains in the gum.
- Chronic jaw diseases in which sequestration is formed. In this case, gum granulation forms around them.
- Pulpitis and a rapidly spreading infectious process in the gums.
- Injuries that provoke the development of a focus of inflammation, resulting in the formation of a granuloma.
Since granulation tissue grows rapidly, it begins to replace cells that have died as a result of injury or inflammation. Therefore, it is very important not only to stop the infection, but also to carefully scrape out the cavity.