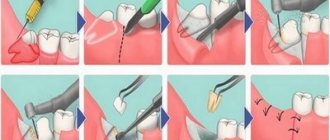
Patients often face a situation where a wisdom tooth becomes ill, or we hear that someone will have their wisdom tooth removed. Let's take a closer look at this problem. What are wisdom teeth? About how problems of wisdom teeth are solved in family dentistry - in the article by the chief physician of the center Tsukor S.V.
This article will discuss one of the problems that arises with wisdom teeth and is most often encountered in the practice of dentists - asymptomatic diseases of the wisdom tooth.
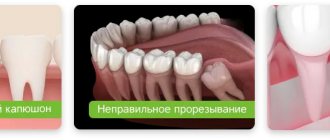
Such diseases of the wisdom tooth occur without symptoms and harm the seventh tooth. The wisdom tooth does not bother the patient in any way, but the consequences of the disease and inflammation can appear at any time and bring a lot of trouble to the person.
A wisdom tooth that does not manifest itself in any way, does not bother or hurt, often does not attract the attention of a dentist. This happens, first of all, because the doctor in most cases is focused on the patient’s complaints. In some clinics, performing a comprehensive oral examination is not standard. In many dental centers, patients are not given a panoramic photo, which helps to identify hidden dental problems.
The Dial-Dent dental clinic practices a comprehensive examination of patients using the most modern diagnostic devices. This undoubtedly improves the quality of treatment, allows you to find problems hidden from the patient and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Let's consider 3 clinical cases on the topic “Removal of a wisdom tooth” from the practice of the chief dental physician S.V. Tsukor.
- Clinical case No. 1 Asymptomatic wisdom tooth - remove the 8th tooth, save the 7th tooth
- Clinical case No. 2 Removal of a wisdom tooth before implantation of the 6th tooth
- Clinical case No. 3 An incorrectly grown wisdom tooth harms the 7th tooth
Clinical case No. 1
Number of roots in human teeth
There can only be one dental crown, but the number of roots a tooth has depends on its location and purpose. The number of roots is also influenced by hereditary factors. It is possible to determine how many roots a tooth has only with the help of an x-ray. The inner part of the tooth (root) makes up about 70% of the entire tooth.
Factors influencing the number of roots:
- Location of the tooth.
- The purpose of the tooth, its functionality (chewing or frontal).
- Genetic predisposition.
- Patient's age and race. In the European race, the number of dental roots is very different from the Negroid and Mongoloid races.
Asymptomatic wisdom tooth - remove the 8th tooth, save the 7th tooth
A young man came to the Dial-Dent dental clinic to treat a tooth with caries. Dental treatment for caries was performed on the day of treatment. Traditionally, the patient was recommended (to assess the condition of the entire dental system) to undergo Alaverdov V.P. using modern digital diagnostic equipment.
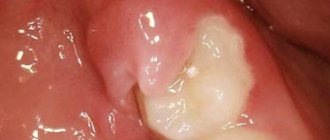
After analyzing the image, specialists drew the patient’s attention to several serious problems (see photo below):
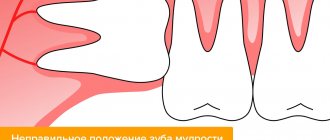
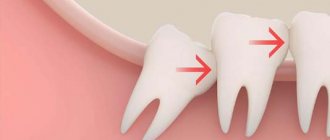
- The wisdom tooth on the lower left has partially erupted, as can be seen in the picture, but is tilted. A narrow gap has formed between the wisdom tooth and the 7th tooth. Food gets stuck in this gap, which first leads to bad breath, and later can lead to inflammation or gumboil.
- Using a panoramic photograph of the teeth, doctors were able to see a deep carious cavity on the seventh tooth.
What happens if you don't pay attention to a diseased wisdom tooth?
- Inflammation of the gums, swelling, gumboil.
- Pulpitis in the seventh tooth due to deep carious lesions. Only a panoramic photograph of the teeth will help determine what is causing the pain and inflammation in this case.
Asymptomatic wisdom tooth - solution to the problem
- Teeth cleaning. It is necessary to carry out a procedure to remove tartar and remove plaque. This is necessary in order to carry out wisdom tooth extraction in clean conditions. This approach significantly reduces the risk of inflammation after wisdom tooth removal.
- Wisdom tooth removal. In dental dentistry, the removal of wisdom teeth is performed by qualified maxillofacial surgeons Alaverdov V.P. and Yakimenko I.I. There is the necessary equipment and anesthesiologists to remove teeth under anesthesia.
- Healing of the gums after wisdom tooth removal usually lasts 2-3 weeks. After this, you can begin treatment and restoration of the 7th tooth. Without removing tooth 8, quality treatment of tooth 7 is impossible.
- Treatment of the 7th tooth. Note that it is extremely difficult to treat a distant tooth due to its location. For high-quality treatment, it is necessary to have high-quality equipment at the workplace and qualified assistance from a medical assistant. It should be added that it is not recommended to restore a tooth with a light-curing filling. The best restoration method in this case is a ceramic inlay.
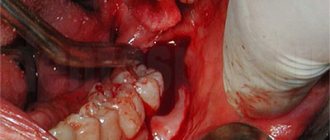
The 8th tooth socket is covered with a special material
Advantages for patients of the treatment and diagnostic tactics offered by the Dial-Dent clinic:
- Comprehensive diagnostics - identifying hidden problems at an early stage.
- Saving the 7th tooth, the health of which is very important for the bite.
- Identifying a problem in the 7th tooth before the onset of predicted pulpitis allows you to save money on treatment, since pulpitis is more difficult to treat and therefore more expensive.
Clinical case No. 2
Teeth numbering system
Dentists have developed a system in which all teeth have their own serial number. The numbering system for the teeth of the lower and upper rows will not allow you to “get confused” in the teeth.
The first number is the incisors - the frontal teeth of the upper and lower rows. There are two teeth on each side (left and right): No. 1 - central, No. 2 - lateral, behind which there are fangs, numbered No. 3. The small molars have numbers 4 and 5.
All of the listed teeth have one cone-shaped root.
Teeth No. 6, 7, 8 - large molars have three roots, and tooth No. 6 of the lower row has one root, with the exception of tooth No. 8, which can have 3 or even 4 roots.
Causes and consequences of removing the seventh teeth
The functions, structure, and location of the sevens create favorable conditions for the development of pathology:
- Molars are responsible for chewing food and are exposed to stress every day.
- Sixes and sevens are difficult to access for hygiene procedures. The accumulation of food debris leads to the formation of plaque and carious lesions.
In addition, tooth trauma and destruction due to a deficiency of vitamins and minerals that maintain normal bone density lead to removal.
The long-term absence of seven leads to undesirable consequences for health and appearance:
- the quality of grinding and digestion of food deteriorates;
- the bite is disturbed;
- jaw atrophy develops;
- the facial muscles rest on the crown of the tooth;
- if there is no tooth, deep nasolabial folds appear and the cheeks sag.
How many canals are there in teeth?
The number of tooth canals does not always coincide with the number of roots. The number of channels can only be determined using x-rays. The upper incisors usually have two or three canals. Some teeth have only one canal, which branches into two parts.
Number of canals in teeth:
- Upper Lower four – 1, less often 2 channels;
- Upper second – 1, less often 2 and even 3 channels;
- Bottom five – one channel;
- Upper first molar 3, 4 canals;
- Lower first molar – 3, less often 2 canals;
- Upper and lower seven – 3, 4 channels.
Removal of a wisdom tooth before implantation of the 6th tooth
The patient went to the Dial-Dent clinic to see dentist S.V. Tsukor. with the desire to carry out prosthetic replacement of one missing tooth in the jaw.
The patient was offered implantation to replace 1 missing tooth. During diagnosis and preparation for dental implantation, the patient was given a panoramic image, which showed the presence of a hidden problem - a wisdom tooth. The treatment plan was changed: first, the patient had to remove the wisdom tooth, then treat the 7th tooth, and only then proceed with dental implantation.
In this case, correct diagnosis (panoramic image of the teeth) helped specialists correctly plan treatment and dental implantation.
Situation at the time of application
Clinical case No. 3
Ways to restore sevens if they are lost
In dental practice, to replace a lost molar, the following is used:
Temporary prosthesis "butterfly"
“Butterfly” is a removable structure that imitates a living tooth and masks a defect in the dentition. Includes an artificial crown made of plastic and a gum made of nylon or acrylic. The denture is attached to adjacent molars without grinding.
The advantage of removable prosthetics is efficiency and efficiency. The disadvantages of the “butterfly” include rapid wear and the need to regularly take it off and put it on. If a breakdown occurs, the prosthesis is replaced with a new one. The design is too small and does not create a physiological load on the jaw. This leads to its atrophy, which further complicates implantation. Recommended as a temporary option for replacing a missing row unit.
Dental bridge (bridge prosthesis)
Bridges are a type of fixed prosthetics, a traditional way of restoring a molar after removal. Externally, the prosthesis resembles an arch with combined crowns. When restoring one tooth, the number of crowns is three - the two outer ones rest on adjacent teeth on both sides of the defect, the middle one replaces the missing seven. The design hides aesthetic defects and lasts for a long time - up to 10 years. Before installing a bridge, preparation of the supporting teeth is required - root canal treatment, grinding of tissue for crowns. If the preparation is poor, the orthopedic structure will have to be removed and the teeth re-treated. In addition, extensive preparation leads to loss of enamel, which makes adjacent teeth fragile. The bridge increases the load on them and accelerates destruction.
The advantage of a dental bridge is its reliable fastening and ability to withstand chewing loads. The patient does not need to remove the structure: only a doctor can remove it. Crowns imitate the color of natural enamel and are made of metal-ceramics, porcelain, and other materials. The disadvantages of the method include the inability to stop bone resorption. Atrophic processes continue in the defect area, because the chewing load falls only on the neighboring units of the row.
Implantation
Installing an implant is the most progressive method of restoring the seven. The treatment does not affect adjacent molars and preserves healthy tissue. The doctor implants a titanium root in place of the extracted tooth. With the classic two-stage technique, the patient is implanted with an implant and a plug is placed. The abutment is installed 4-6 months after the root has grown into the jaw, and a permanent crown made of metal ceramics or zirconium is attached to it.
Seven implants restore chewing functions and create a physiological load on the jaw. This is the only way that stops the process of bone resorption after tooth loss and prevents sagging of soft tissues. Bridges and butterflies lack this ability. In addition, in the absence of a figure eight (wisdom tooth), it is impossible to install dentures, since an end defect occurs and there is no support for fastening.
Mandibular canine
Average age of teething: 9-10 years
Average age of root formation: 13 years
Average length: 25.6 mm
The canine of the lower jaw is more powerful and significantly wider than the incisors in the mesial-distal direction. It rarely causes treatment problems. The atypical form with two roots can be problematic, but is rare.
The access cavity is oval and can be expanded in the incisal direction to facilitate vestibular-lingual access. In the cervical region the canal is oval, in the middle third it is rounded. To completely clean its walls, directed instrumental action is necessary.
If there are two roots, one of them will always be easier to instrument. The other canal must also be opened and funnel-shaped in accordance with the first to prevent dentine filings from entering it and impairing access. Pre-bending the instruments during the initial approach will allow the clinician to walk along the walls of the buccal or lingual root until the tip of the instrument enters the orifice. Once a difficult-to-reach canal has been identified, every effort must be made to shape and create a funnel-shaped orifice to keep access open.
Installation of a lower tooth implant
Below, the jawbone is denser and stronger. Its volume is higher than that of the upper jaw. This allows for better fixation of the implant, increases the survival rate of titanium roots, and accelerates fusion - the process lasts 2-4 months.
If molars are missing for a long time, there is a need to build up the jawbone. The procedure will eliminate the volume deficit due to resorption and create conditions for reliable fixation of the titanium support.
Osteoplastic surgery on the lower jaw is performed in several ways:
- Splitting of the alveolar ridge.
The alveolar process is sawed in two, the inside is filled with synthetic material, and an implant and barrier membrane are installed. Sutures are placed on the gum. After 4-6 months, the artificial root is loaded with a crown. - Autotransplantation of bone blocks.
The bone is grown with natural donor material. It is borrowed from the thigh, chin or jaw in the area of the patient's wisdom teeth. The blocks take root well when installed correctly. The disadvantage of this method is the need for two interventions in the area of sampling and installation of the material. - Guided bone regeneration.
Granules made of synthetic material are placed in the well and covered with a membrane. Depending on the clinical case, the procedure is compatible with implantation. This technique is the least traumatic. After six months, the bone chips and artificial root are integrated into the jaw.
To replace sevens, implants are used that are as close in size as possible to the natural root in order to withstand chewing loads.
The main method of implanting sevens is a classic two-stage protocol with delayed loading of the prosthesis. Single-stage with immediate loading is not recommended. This is due to the location of the tooth, which is actively involved in chewing, and is at risk - the implant may move.
Stages of implant installation
- Preparation and diagnostics.
A diagnosis is carried out, the doctor draws up a treatment plan, and selects an implantation system. Carious lesions and gum disease are eliminated. Before implantation of the upper jaw, it is necessary to cure inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. - Bone tissue augmentation.
If there is a lack of volume, the bone is increased with osteoplastic material. Engraftment lasts 2-6 months. If the clinical situation allows, this stage is combined with implantation. - Implant installation.
The artificial root is introduced under local anesthesia through an incision, a plug is placed, and the soft tissue is sutured. Osseointegration lasts 2-6 months. - Gum formation.
After the implant has fused with the bone, the gum above it is cut, the plug is removed and a gum former is installed for 10-14 days. - Prosthetics.
The former is replaced with a permanent abutment. A crown made of metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide, created from impressions in a dental laboratory, is attached to it.
First lower molar
Average age of teething: 6 years
Average age of root formation: 9-10 years
Average length: 21.0mm
The mandibular first molar erupts earlier than other permanent teeth and most often requires endodontic treatment. It usually has two roots, but sometimes three roots are found, with two canals in the mesial root and one or two canals in the distal root.
The distal root is easily accessible for endodontic cavity preparation and mechanical treatment.
The doctor can directly see the opening(s) of the canal. The distal root canals are wider than those of the mesial root. Sometimes the mouth is wider in the buccolingual direction. This indicates the presence of two channels or a slit-like channel with a complex network-like configuration that can complicate cleaning and shaping.
The mesial roots are usually curved, with the greatest curve in the mesiobuccal canal. The orifices of the canals at the bottom of the pulp chamber are usually clearly separated from each other and located buccally and lingually relative to the upper tubercles.
The tooth often undergoes extensive filling. It almost always experiences a strong chewing load, so the coronal pulp cavity can be obliterated. It is easiest to identify the mouths of the distal canals.
Then the mouths of the mesial canals are found, which will be located in the above locations in the same horizontal plane.
Since the mouths of the mesial canals lie under the mesial tubercles, they may not be detected during normal cavity preparation. In this case, to determine their location, it is necessary to remove the hard tissue of the tubercle or filling. During access preparation, overhanging molar cusps need to be ground down [15]. Remember that this tooth, like all other lateral teeth, after endodontic treatment requires complete restoration of the entire occlusal surface area. Therefore, to identify anatomical landmarks and orifices, it is better to make a wider access cavity than to skip one or more channels for the sake of “sparing” preparation, which may cause failure.
Skidmore and Bjoradal [11] found that approximately one third of the mandibular first molars examined had four root canals. If there are two canals, “they either remain separate with separate apical foramina, or unite and form a common apical foramen, or communicate with one another by transverse anastomoses partially or completely... If the tooth, instead of the usual triangular shape, had a more rectangular shape, this would allow better vision and explore a possible fourth canal in the distal root.”
In the area of bifurcation of the roots of the lower molars there are several orifices of additional canals [9]. They are usually impossible to clean and shape, and are rarely visible except incidentally on radiographs when they are filled with root cement or heated gutta-percha during treatment. It would be correct to assume that if irrigation solutions tend to clean the canal from protein decomposition products, then the area of root bifurcation in the pulp chamber must be thoroughly cleaned (remove denticles, etc.) so that the solutions can reach the small mouths of the canals.
All infected dentin, leaking fillings, and pulp denticles must be removed before endodontic treatment begins. It is recommended to completely cover the cusps with a restorative structure after endodontic treatment.