Causes of displacement Correction Possible consequences Determination of occlusion Possible consequences Methods of correction
Displacement of teeth is a change in their position after the formation of the dentition has completed, as a result of illness or injury. When teeth erupt, they also change location. This is called primary movement. All other cases are secondary movements.
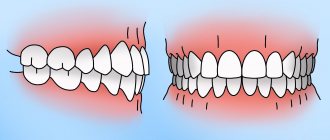
Teeth can change their position in different directions; most often the following types of movements occur:
- vertical (one-sided or two-sided);
- distal – the tooth goes back;
- mesial – the tooth moves forward;
- bends;
- rotation around an axis;
- combined.
Why is it necessary to replace extracted teeth?
When free space appears in the jawbone, bone tissue gradually begins to decrease, the alveolar ridge thins, and the teeth begin to move, trying to fill the vacant space. Due to the disappearance of lateral support, the “neighbors” of the removed tooth begin to move. The antagonist tooth located on the opposite jaw moves out and “sags”. Due to this, the patient’s bite is disturbed, and the resulting deformations cause new troubles. The more years pass from the moment of removal, the more significant the anomalies will become. Problems can even arise with the temporomandibular joint, which will cause serious pain and disruption of its functionality.
Let's look at a typical example. With a prolonged absence of the “six” and “seven” in the lower row, the last molar tooth of the upper jaw can “sag” so much that it literally rests against the lower gum. In this case, there is no longer any need to talk about conventional dental restoration
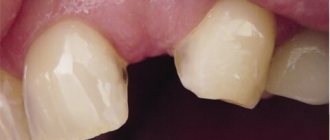
Teeth began to separate
The front lower teeth and upper teeth gradually fan out between
itself and gaps appear between the teeth? Previously, they stood in beautiful, even rows, and then suddenly, for no reason at all, they began to move. Why?
The fan-shaped divergence of the front group of teeth, or rather their position is called protrusion! Teeth pushed forward are an aesthetic flaw that changes the appearance, so you have to make a lot of effort to close your lips! Exposed tooth roots and mobility cause patients considerable discomfort when chewing and biting food. This is a characteristic sign of moderate to severe periodontitis.
Causes of teeth discrepancy.
The supporting apparatus of the teeth that holds the teeth in the bone socket is called the periodontium. The main function of the periodontium is to firmly hold the tooth with the help of an elastic ligament. The elastic ligament firmly covers the tooth and prevents
penetration of infection between the tooth root and the bone socket. The tooth is suspended in the socket and can make small movements. That is, the healthiest and most stable tooth has insignificant mobility. If it weren't for it, the teeth wouldn't last as long. Because of this mobility, the periodontium has a trophic function - it nourishes the tooth during chewing. As periodontitis progresses, the circular ligament of the tooth is damaged and over time it completely disappears! And this is due to periodontitis, which lasts for a long time in a latent form and has a chronic course. With moderate periodontitis, bone tissue is already involved in the inflammatory process. Constant destruction of bone tissue leads to exposure of the tooth root. A tooth deprived of stable support can no longer withstand chewing loads and this leads to an increase in tooth mobility. Once started, this process continues to develop uncontrollably and leads to the tilting of the teeth, their “fan” arrangement. A factor of traumatic occlusion arises, in other words, during normal chewing, the antagonists (the group of teeth opposite to it) are knocked out by their own teeth. In the absence of proper treatment for periodontitis, such a group of teeth loses their stability and eventually must be removed.
Among the main causes of a local nature in the oral cavity are:
- Incorrect bite.
- Pathological abrasion
and overload of the supporting apparatus of the tooth. - Poor oral hygiene.
- Untreated gingivitis
. - Errors in prosthetics with crowns and bridges, veneers.
- Incorrectly placed fillings when filling teeth.
What to do if your teeth start to come apart?
In such a situation, an urgent consultation with a periodontist is necessary!
Only a person can identify the cause, eliminate it and prescribe adequate treatment.
periodontist-surgeon.
Unfortunately, today, the level of training of dentists in gum diseases is extremely low. And the patient is unaware of his diagnosis for a very long time, and when the situation in the oral cavity worsens sharply, the diagnosis of periodontitis is made. The advanced stage of periodontitis not only requires considerable effort from the periodontist, but also treatment for the patient is expensive and requires large financial costs. As a rule, in such situations a full range of periodontal procedures is required, using laser technology
,
open curettage , flap operations
and after three months
the Vector procedure
. Unfortunately, as a
splinting
, this is not a treatment for periodontitis, it is simply a preparatory stage in the treatment of moderate and severe periodontitis gravity.
It is worth noting that splinting, even highly mobile teeth, allows you to connect them into a fixed block for a long time, evenly distribute the chewing load and makes it possible to carry out high-quality surgical procedures in the treatment of periodontitis. Surgical treatment
remains the leading treatment for moderate and severe periodontitis!
Three golden rules that will save your teeth.
Necessary:
- Professional examination every six months by a periodontist.
- Consultation with a periodontist before installing crowns, bridges, veneers and
orthodontic treatment. - After prosthetics and fillings.
Here are three simple rules that do not require any financial costs from the patient, but will allow you to identify periodontitis at the initial stage and monitor the work of the orthopedic dentist, therapist and orthodontist.
IMPORTANT:
It is always easier to prevent and eliminate the causes than to deal with their consequences.
With timely and competent treatment of periodontitis, you can preserve your teeth and the beauty of your smile for a long time. Do not forget to visit a periodontist once every six months for the purpose of prevention and periodontitis will not overtake you!
How can you solve the problem?
A layman will immediately name two obvious solutions:
- remove protruded tooth;
- file down its coronal part.
Removing a tooth without pain can only be justified by its severe destruction, and even accompanied by the patient’s complete reluctance to seriously engage in dental treatment.
Filing the crown does not seem rational either. After all, for this you will have to remove the nerve of the tooth, since it will have to be “shortened” by more than half, and then covered with an artificial crown. It is difficult to call the formed “formation” a full-fledged tooth. “Grinding” is not required only when the molar is slightly advanced, when you can limit yourself to grinding its cusps to the existing bite height.
The best option is orthodontic treatment, since it is the orthodontist who deals with problems of tooth displacement. Modern technologies make it possible to return a “failed” upper molar to its place.
Cost of correcting diastema
It is easy to guess that the cost of correcting a diastema depends on the chosen method and the need to use certain materials. The severity of the defect also matters.
In general, the most affordable way to achieve a beautiful smile is cosmetic correction or surgical plastic surgery. Artistic restoration, braces and other methods of correcting the position of teeth will be more expensive, but the cost of these methods remains affordable for most patients. When it comes to mouthguards, their production will be the most expensive.
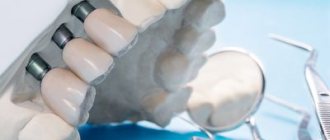
Mini-implants - as a basis for orthodontic treatment
The procedure for installing mini-implants is carried out under local anesthesia and does not require any incisions or sutures. A puncture is simply made in the tissue through which the surgeon implants a titanium implant. But simple and low-traumatic manipulations should be performed by a highly qualified specialist who can take into account the peculiarities of the location of the dental roots so as not to injure the tooth.
- In this example, small orthodontic dental implants will be installed next to the lowered upper “seven” - one each on the vestibular (external) and lingual (internal) sides.
- The orthodontist will glue special hooks to the molar on both sides, which will be connected to the heads of the implants using elastics. This way, the doctor will create a constant force, supported by the implants, pulling the sagging tooth back into the jaw bone.
- As with treatment with braces, stretchable elastic bands will need to be replaced periodically, for which you will have to visit the clinic. At the same time, the orthodontist will monitor the process, correcting the movement of the problem tooth.
As a result, a place for prosthetics will be obtained without removing, depulping or grinding the molar.
What will be the consequences if the gap between the teeth is not corrected?
Will the child face consequences if the gap between the teeth is not corrected? It is impossible to answer unequivocally. During the consultation, the dentist will assess the degree of development of the diastema and correlate this with a number of other factors. However, it is impossible to accurately predict the consequences. The gap may not manifest itself in any way throughout life, but serious consequences cannot be ruled out. The diastema can expand and cause problems with bite and diction. If your child is already burring, then it makes sense to work on eliminating the diastema instead of trying to solve the diction problem with a speech therapist.
With age, the load on teeth increases, especially if they are incorrectly positioned in a row. This easily leads to caries and can cause periodontitis. An incorrect bite often results in teeth that are loose, painful, worn down, and at risk for infection and inflammation.
Therefore, in order to protect your child from frequent visits to the clinic in the future, take care of the position of his teeth today.
Causes of dislocations
Dislocation always occurs under the influence of a directed force, the source of which is:
- a blow to the tooth during a game, a fall, a fight, an accident, an industrial accident;
- the load acting on the tooth when chewing bones, unshelled nuts, or opening beer bottles with the teeth;
- incorrect tooth extraction technique;
- pressure on a moving tooth when biting hard food.
When dislocation occurs, the position of the tooth root in relation to the walls of the socket changes, periodontal fibers are completely or partially torn, and the neurovascular bundle is damaged; often a dislocation is combined with a fracture of the tooth crown or maxillofacial injuries. Based on the nature of tooth displacement, incomplete, complete and impacted dislocations are distinguished.
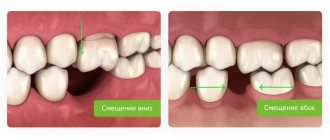
Basic types of offset:
- Mesial displacement - the tooth is located in front of its natural position in the jaw arch.
- Distal displacement - the tooth moves back from its optimal position in the jaw row.
- Vestibular displacement - most often the anomaly affects the fangs, the teeth move towards the vestibule of the oral cavity.
- Oral displacement - classified into lingual and palatal.
- Palatal anomaly is characterized by movement of the elements of the upper jaw towards the palate.
Causes and consequences of dental pathology
Abnormal two-row growth is possible for many reasons:
- heredity;
- chronic colds and decreased immunity;
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of soft foods and purees;
- lack of vitamins and useful elements;
- premature removal of milk units;
- disturbance in the location of tooth germs.
With timely treatment, the orthodontist will easily straighten the bite and place each tooth in its proper place. If you delay visiting a doctor, the consequences can be serious:
- malocclusion;
- problems with hygiene and the development of caries;
- facial deformation due to jaw imbalances;
- ugly smile.
A sign of a potential shark jaw is the absence of gaps between the teeth in a 4-6 year old child. Insufficient space is the first prerequisite for the appearance of a second row of teeth in children and a signal for an attentive parent.
It is easy to see an incorrectly growing tooth, especially in the lower jaw. During the period of change in bite, dentists recommend monitoring the process - periodically conducting home or professional examinations and listening carefully to the baby. Complaints of discomfort in the mouth, inconvenience of chewing and pain indicate the need to visit a dentist to assess the condition of the oral cavity.
The first stage of treatment for tooth transposition
The first step was to move the crown of permanent canine 1.3 into place. Naturally, primary canine 5.3 was removed before installing braces at the stage of sanitation of the oral cavity. For this, a NiTi spring was used to open from the bracket on the second premolar to the canine crown on one side, and light traction with an elastic chain on the other.
Anomalies in the closure of teeth
Dental rows are not always placed correctly. How do you know when treatment is required? Depending on the type of malocclusion, the following signs of violations are distinguished:
- Distal - the upper jaw is more developed when compared to the lower jaw. She comes forward significantly.
- Mesial. The situation is the opposite of the previous case - the lower jaw is more developed. It may bulge forward slightly or strongly.
- Cross. With this pathology, there are interdental gaps. Part of the upper front teeth is behind the lower ones, and the other part is in front of them. Such a smile looks unaesthetic. As a rule, teeth grow in different directions.
- Deep – the upper row of teeth almost completely overlaps the lower one. If even more than 30% of the teeth are blocked, this is considered a pathology. But visually such a violation may not be visible.
- Open. When the jaws close, only the chewing teeth come into contact; pronounced gaps are visible between the front teeth. In some cases, it looks like an open mouth.
Whatever the diagnosis, any pathology must be treated.
Methods for diagnosing dislocations
When diagnosing dislocations, the following methods are used:
- Questioning the patient - the circumstances of the injury and the time when it occurred are clarified. The patient describes his feelings and complaints.
- External examination - the doctor assesses the general appearance of the patient, notes damage to the soft tissues of the face that occurred as a result of injury. The dentist may be the first to notice signs of a traumatic brain injury in a patient: pallor, sluggish reaction, weakness, respiratory rhythm disturbances.
- Examination of the oral cavity using a dental probe and a dental mirror. The mirror allows you to see areas that are not accessible to direct visual inspection. With the help of a probe, in case of incomplete dislocation, the depth of the periodontal gap is determined.
- Percussion - tapping on the tooth, helps determine the condition of the periodontium. In case of incomplete dislocation, percussion of the injured tooth causes acute pain; with impacted dislocation, percussion is painless or slightly painful.
- Palpation - feeling. Palpation of the gums with impacted dislocation is painful; Using this method, the dentist distinguishes incomplete dislocation from a root fracture.
- EDI – electroodontodiagnostics – determines the electrical excitability and conductivity of the pulp. A current of a certain strength is passed through the tooth using a special apparatus, and the patient is asked to report the tooth’s reaction to electrical impulses. If the pulp is viable, a slight feeling of pain appears in the tooth; When the pulp dies, there is no pain, the patient will feel a push in the tooth. During diagnosis, the threshold response of the tooth to current is recorded; in the normal state of the pulp, it is within the range of current readings from 2 to 6 μA.
Immediately after the injury, the pulp may not react to the action of the current, so tests are carried out 2-3 days after it, then every week for 4 weeks, sometimes longer. This is explained by the fact that while maintaining the viability of the pulp in case of dental trauma, its electrical sensitivity can be restored for a long time.
- X-ray examination - allows you to assess the condition of the roots of the tooth, periodontium, alveolar walls, jaw bone after injury; see the degree of tooth displacement after dislocation. It is preferable to carry out 3D computed tomography, since this method allows you to view the tooth and jaw bones in three projections, eliminating the effect of overlapping images.
- Transillumination diagnostics - transillumination of the tooth with a beam of cold light. Used to detect enamel cracks that cannot be detected with the naked eye. The method helps to maintain the health of teeth adjacent to the injured one, and at first glance not damaged during the injury.