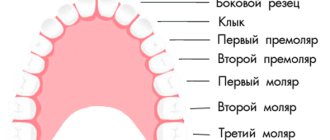
The vast majority of the adult population of the planet is familiar with toothache. It can manifest itself in different ways, including when pressure is applied to a tooth, when a person cannot bite even soft food.
| Causes of pain and accompanying conditions | Methods for eliminating toothache |
| Increased sensitivity of the tooth in the absence of external damage, pain occurs even with slight pressure | At home: rinsing with herbal decoctions, soda solution When visiting a doctor: remineralization (treatment with preparations containing calcium and fluoride), in some cases - building up new enamel |
| Damage to enamel (cracks, chips - including microscopic ones invisible to the eye), the appearance of severe pain when exposed to any factor | It is recommended to consult a doctor |
| Inflammation of the gums: pain occurs when pressing on a healthy tooth precisely because of the condition of the gums | At home: rinse with a water-soda solution, sea buckthorn oil lotions. If there is no effect, you should consult a doctor. |
| Inflammation of the upper part of the tooth (periodontitis), accompanied by independent, precisely localized pain and a general deterioration of the condition | Treatment at home is impossible; you need to see a doctor. During the first week after removal: rinse |
| Removal of the nerve: after depulpation, pain may persist due to injury to the fibers (the reason is unskilled intervention that led to tissue necrosis due to insufficient asepsis of the canals) | The persistence (especially the intensification) of pain requires immediate contact with a doctor in case of a medical error |
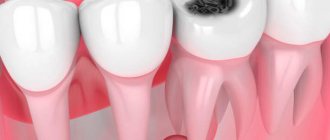
| A complication of caries is pulpitis, intense pain that intensifies when chewing, discoloration of tooth enamel (graying) | requires immediate medical attention; if delayed, tooth loss may occur |
Main reasons
Pain is a kind of “alarm” from the body, drawing attention to malfunctions in its functioning. The oral cavity is no exception: if a seemingly healthy tooth hurts when pressed, this indicates that something has happened to it. As a rule, the reason is damage to the crown, root, gums, or the presence of an inflammatory process. But provoking factors can be very diverse: injuries, infections, insufficient hygiene and even medical errors. Let's look at each case in more detail.
Treatment: when the cause of the pain is established
Having established the cause of the pain, the dentist will prescribe appropriate treatment.
The approach to treatment depends not only on the established cause of pain, but also on the neglect of the process (the degree of damage to the tooth and adjacent tissues).
- If increased tooth sensitivity is detected, remineralization or fluoridation is performed.
- The presence of chips and cracks requires composite enamel extension, or, as an option, the installation of veneers or crowns.
- In inflammatory processes, a course of treatment with antibiotics is usually prescribed with the installation of a filling after the source of inflammation has been eliminated.
- If the cause of pain lies in a poorly placed filling, it is polished or replaced with a new one.
- Detection of caries and pulpitis requires dental intervention such as preparation of the upper part of the tooth and opening of the cavity with the placement of medicine. After eliminating the infection, the dental canals are filled and the relief of the dentition is restored.
- Treatment of periodontitis is more complex; a specialist in such diseases is a dental surgeon. Drainage of the purulent cavity is performed, after the capsule is emptied of purulent contents, the canals are cleaned and the tooth is treated; in case of extensive lesions, resection of the root apex of the tooth is required.
The tooth hurts when you press on it: after depulpation (nerve removal)
The pulp is nerve fibers and vessels that provide sensitivity and nutrition to the tooth. After their removal, the tooth is considered dead, and it may seem that this is the solution to any problem, because a dead tooth is unlikely to hurt. This is wrong. A pulpless tooth can be disturbing for several reasons:
- if the dentist, while cleaning the canals, punctured the root;
- when the thin end of the endoscopic instrument breaks off and remains inside the canal;
- in case the dental canals have not been completely cleaned and an infection remains in them.
In the first two cases, the pain is quite sharp: the pulpless tooth hurts not only when pressed, but even when touched lightly. If the dentist cleans the canals poorly, pain appears after some time. In any case, a tooth without a nerve that causes discomfort is a reason for a repeat visit to the dental office.
The second group includes:
Incorrectly processed filling
Almost always, modern treatment at the dentist is carried out under local anesthesia (pain relief). In this state, not only do you not feel pain, but your other sensations may also be dulled. And when the doctor “grinds” an already placed filling to the teeth from the opposite jaw, he may, based on your dull sensations, do this not in full. The filling will come into contact with the teeth of the opposite jaw prematurely, which may cause pain.
Pain after root canal filling
Perhaps this is the only reason, most often not a sign of any big troubles. After endodontic treatment (“nerve removal”), possible pain when biting on a tooth is considered normal for 1.5-2 weeks. This happens due to dense obturation (filling) of the root canal system, the presence of microtrauma in the area of the root apex, etc.
The reasons I described above are the main ones, and there are a large number of less common diseases and situations in the oral cavity that can lead to pain when putting pressure on the tooth. In any case, when this symptom appears, the first thing to do is contact your dentist, and if a telephone consultation is not enough, then make an appointment.
Tooth hurts when pressed after filling
Slight pain after the doctor has given a filling to the patient is normal: during the sanitization of cavities affected by caries, the tissues receive microtrauma. The condition is easily treated with analgesics and goes away on its own in 2-3 days. But if a filled tooth hurts when pressed hard enough, then the problem is one of five reasons:
- high filling - the occlusion is disrupted, the tooth experiences excessive pressure and becomes painful;
- the dental pulp was burned when the filling was treated with a photopolymer lamp;
- a gap has appeared between the filling and the enamel, into which bacteria and food particles have entered, causing inflammation;
- the cavities affected by caries were not drilled out thoroughly enough, and it reappeared;
- I developed an allergy to the filling.
If the tooth under the filling hurts when pressed, this means that you need to make an appointment with the doctor again and have it filled again.
What you can do yourself
If the tooth hurts severely, and for some reason it is impossible to get an appointment with a doctor today, you should rinse with a saline or soda solution. Warming compresses should never be used - they often aggravate the inflammatory process and provoke blood poisoning.
For unbearable pain, you can take an over-the-counter analgesic available in your home medicine cabinet. But this should be a “one-time event”. As soon as possible, the patient should see an experienced dentist.
The treated tooth hurts when pressed after canal filling
Working with roots requires precision and accuracy from the doctor. If he incorrectly assessed the depth of the canals, then the following complications cannot be excluded:
- a tooth without a nerve hurts when pressed if the filling material extends beyond the apex of the root, gets into the gum and puts pressure on it;
- when the channels, on the contrary, are not completely filled, inflammation may begin in the voids over time. If a lot of time has passed after visiting the doctor, and the tooth aches and hurts, then the problem is the unsatisfactory filling of the canals.
Treatment
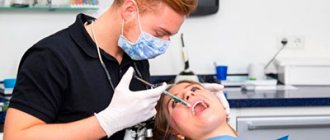
For an experienced specialist, a visual examination of the oral cavity is sufficient to make a correct diagnosis. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor resorts to instrumental examination methods, such as x-rays.
If it is painful for the patient to touch the tooth, the treatment will be carried out under anesthesia
After the effect of the drug, the jaw becomes numb, and the person ceases to feel discomfort during the intervention. Before administering an analgesic, the doctor is warned about pregnancy, the presence of allergic reactions to drugs, and breastfeeding.
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the situation. Light caries, which causes teeth to hurt when chewing, can be eliminated in one visit to the dentist. Pulpitis is treated in 2-4 visits. Treatment of periodontitis and periostitis will require more than 2 weeks. After treatment, it will be painful for the patient to bite food and press on the problem area for another 2-4 days. Untimely intervention causes the tooth to become loose.
Drugs
What to do after filling? To reduce acute pain after dental work, it is recommended to take the following medications:
Why does a tooth hurt when pressed after filling?
- Analgin. Suitable for eliminating mild pain that occurs after dental treatment.
- Baralgin. Contraindicated in children under 15 years of age and pregnant women. The effect of the drug lasts for 6 hours.
- Ketanov. A drug with a powerful analgesic effect. The effect lasts up to 6 hours.
- Nalgesin Forte. The most powerful pain reliever, which is taken when the above drugs are ineffective. Has many adverse reactions.
Folk remedies
Natural ingredients help soothe toothaches when chewing. Their effectiveness has been tested by generations of people. To relieve symptoms, use alcohol rinses. Alcohol-based tinctures are made from herbs (elderberry, strawberry leaves and St. John's wort). The product is prepared from 1 tbsp. l. vegetable raw materials per 150 ml of vodka.
To prevent pain in the problem area, use cold compresses with ice. The duration of the procedure is no longer than 15 minutes
Onions and garlic relieve pain and relieve inflammation. It is enough for the patient to chew a small piece of vegetables on the problematic side. If a tooth aches when chewing, you can apply a paste of onion and garlic to it and cover it with a gauze pad.
Homeopathic treatment
Homeopathic remedies cannot replace treatment with a specialist. They are used for emergencies or after dental surgery. The analgesic effect after taking such drugs is not as fast as after using analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. However, homeopathic medicines have fewer side effects and can be used if touching and pressing on the tooth hurts.
The following medications help with the problem:
- Staphysagria – for tooth pain after treatment;
- Lycopodium - to eliminate discomfort when it hurts to bite food;
- Plantago – to reduce the sensitivity of tooth enamel.
For the same symptoms, patients may be prescribed different homeopathic medicines. In this case, the consultation is carried out by a homeopathic doctor.
The tooth under the crown hurts when pressed
Crowns and bridges can also cause many unpleasant moments for their owner. Normally, you may feel discomfort under the crown for several days after installation, but as you adapt, the pain gradually goes away. If a month later the tooth still aches a lot and hurts when pressed, and also if the pain under the crown appears suddenly, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
There are four main reasons:
- the crown became loose, food particles and plaque accumulated under it, and inflammation began;
- the crown is cracked or split;
- the tooth is poorly ground under the crown;
- The shape of the crown is chosen incorrectly; it puts pressure on neighboring teeth or gums.
Pulpitis
Inflammation of the neurovascular bundle of the tooth is one of the most common diagnoses with which patients come to the dentist. Most often, pulpitis occurs due to untreated caries, which destroys the hard tissues of the tooth and reaches its core. As already mentioned, pulpal pain when pressed is very sharp, they are characterized as a “lumbago”. Nerve endings give the most severe symptoms, so it is very difficult to tolerate this phenomenon. You should not rely only on painkillers. It is better to consult a dentist to get timely help for your tooth.
A healthy tooth hurts when pressed
What should you do if, when pressed, a tooth that has not been sanitized, depulped, drilled or loaded with a crown hurts? Yes, this happens too. Here are a few reasons why a seemingly healthy tooth can be painful.
- Periodontitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the tissues around the teeth. When pressed, both the gums and the tooth hurt at the same time. If no action is taken, progressive periodontitis will lead to a reduction in the volume of the gums and even bone, and then the tooth will become loose and may fall out.
- Excessive enamel sensitivity. It is provoked by chemical teeth whitening, after which even a tooth with a nerve can ache when biting or drinking cold and hot drinks. Teeth with filled canals do not have this problem. You can make your enamel less sensitive at home by using remineralizing gels and toothpastes.
- Removal of a tooth. After surgery, the adjacent healthy tooth may hurt. This is due to damage to soft tissues and does not require any additional therapy other than that prescribed by the doctor.
Why complications arise
Deformation of tissues (even minimal chips of enamel) causes various complications, which is associated with the penetration of infections into the depths of the tooth. Among the most serious complications:
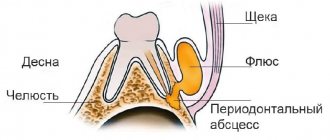
- abscess (can spread to several teeth or cover half the jaw);
- sinusitis, pharyngitis, sepsis;
- inflammation of the jaw bone;
- development of phlegmon (with damage to the facial muscles).
All these infections are fraught with penetration into the blood and disruption of the general condition of the body.
The most common complication is the development of caries, which, in the absence of adequate treatment, leads to complete destruction of the tooth with the need for its removal.
What should you do if your tooth hurts when you press it?
Pain almost always accompanies the rehabilitation period after dental surgery. If the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, the discomfort disappears on its own after 2-4 days, however, in some cases, pain can signal complications. The patient should return for a follow-up appointment if:
- immediately after the anesthesia wears off, severe and sharp pain appears;
- More than a week has passed after treatment, but the toothache does not go away;
- The rehabilitation period went well, but after 1-3 months pain appeared again.
The most important thing is not to endure, but to figure out where the pain comes from.
Rinse for painful sensations
Rinses are also widely used - both homemade and pharmacy. For example:
- 100 ml of water, a teaspoon of soda, a teaspoon of soda, iodine - 5 drops. Used to relieve swelling and remove purulent contents
- 1 spoon of sage per glass of boiling water (decoction), anise - 10 drops. Provides pain relief and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- 1 glass of warm water, 1 tablet of furacillin. Powerful antibacterial effect, reducing swelling.
The drug chlorhexidine has a good aseptic effect; so-called dental elixirs can be used to relieve pain.
It is important to understand that all the methods listed above are only first aid for toothache; if you stop there, you will soon inevitably need tooth extraction!
To eliminate pain, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of the problem. This can only be done in a dental clinic, where modern equipment ensures comfortable and painless treatment.
When to see a dentist
If the pain syndrome, which should last no longer than a few days, does not go away within the specified period, you should immediately go to the doctor. Why do you need to consult a doctor: if you do not treat the “damaged” tooth, then not only will the pain intensify, but a lot of other serious complications will also develop. To determine the cause of the discomfort, a specialist will conduct a palpable examination, tap the tooth (so-called percussion), determine how viable the pulp is, and send it for an x-ray.
If the diagnosis reveals medical errors, the tooth will need to be treated again. In emergency situations, if conservative methods are ineffective, the “affected” unit will be removed and a crown, bridge or other suitable prosthesis will be installed in its place.
Important! When, immediately after the filling has been installed, the gums become swollen and the pain rapidly increases, you should immediately contact a dentist.
So, the fact that a tooth hurts after canal filling is a variant of the norm, but it may also indicate the development of a pathological process. It all depends on how long the unpleasant sensations last and what nature they have. If a tooth hurts when pressed immediately after installing a filling, the discomfort persists for longer than three days and the pain increases, this is a reason for an immediate consultation with a dentist.
How is inflammation of the trigeminal nerve treated?
Correct treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can only be prescribed by a neurologist. Depending on the complexity of inflammation, the following agents are included in therapy:
- Drugs to combat symptoms (pain);
- Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants of central action;
- Alcohol blockades (for severe inflammation);
- Metabolic drugs;
- Anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, finlepsin);
- B vitamins;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
The measures are aimed at relieving inflammation and completely eliminating pain symptoms. Properly prescribed treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can not only restore excellent health, but also prevent relapses.
This information is for informational purposes only. Only a professional specialist can prescribe treatment after examination and diagnosis.