A dental lining is used to cover the bottom of a cavity if it is too close to the pulp. The gasket protects the nerve from the adverse effects that even the most careful and gentle preparation can have on it.
Such a gasket is a medicinal preparation based on calcium hydroxide, which, due to a pronounced alkaline reaction, normalizes the blood circulation of the pulp and ensures intensive deposition of replacement dentin.
What are they needed for?
Filling materials, to varying degrees, irritate the dental pulp. For multicomponent materials, the matrix can be toxic. But this does not mean that all dental treatment products contain irritating properties. Isolating pads in dentistry are used not only to remove the negative impact on loose connective tissue, but also for:
- preventing the ingress of toxins;
- protection from filling material, which can have a destructive effect on tooth tissue;
- reducing the risk of microcracks forming during shrinkage of the filling.
What are the requirements for gaskets? Here are just a few of them:
- Long-term protection of dentin from chemical attack
- Protection of enamel from high and low temperatures.
- Protection from the aggressive effects of saliva.
- Stronger adhesion to the tooth compared to a filling.
- Does not affect the pulp.
- Easy to install.
There are two options for isolating gaskets in dentistry:
- The first option is the base one (a layer of more than one millimeter). It protects the pulp from external irritants, maintains the shape of the cavity, and is also an integral part of more expensive fillings.
- The second option is thin-layer. Does not fully protect against external irritations. Provides stronger adhesion between filling and tooth.
There are several groups of gaskets.
Application area
The main purpose of any insulating gasket is to eliminate the impact of the filling material on the pulp. It also isolates the nerve of the tooth from toxins, protects against the occurrence of microcracks and marginal gaps that can form after the filling shrinks.
Requirements for insulating gaskets
The insulating gasket must:
- Protect dentin from chemical and temperature irritants;
- Easy to install;
- Withstand the most aggressive effects of saliva if the integrity of the filling is compromised;
- Withstand the maximum possible chewing load;
- Be bonded to the tooth more strongly than to the filling;
- Do not have a negative effect on the dental pulp.
Also, the insulating lining should not change the natural color of the tooth enamel.
Indications and contraindications
Medical pads are necessary in the following cases:
- deep caries (close to the pulp);
- focal pulpitis;
- if there is an accidental opening of the pulp.
Quite a lot of research has been done on the tolerability of therapeutic pads. It has been proven that therapeutic pads do not cause allergic reactions or pulp irritation.
Benefits of therapeutic pads
Therapeutic pads have both anti-inflammatory and regenerating, necrotizing and analgesic effects. The gasket material has good ductility and hardens quickly. Such a lining significantly reduces the risk of developing secondary caries and the formation of microcracks.
Flaws
It should be noted that therapeutic pads, for all their advantages and positive effects on the pulp during inflammatory processes, also have quite serious disadvantages, which, if used incorrectly, can lead to a number of problems:
- Therapeutic pads do not have the property of adhesion to dentin, which leads to weakening of the adhesion of the filling to various dental tissues;
- The healing materials of the pad gradually dissolve, dissolve, and this creates conditions for further infection of tissues;
- If the materials of the treatment lining get on the walls of the cavity formed during the treatment process, it causes microbes to enter the tooth, which will lead to secondary caries.
That is why the use of therapeutic pads for inflammation in the teeth should be trusted only to a responsible specialist who will not make mistakes and ultimately guarantees the quality of treatment and installation of a filling on the tooth.
Basic principles of therapeutic pads
The therapeutic pad can be:
- non-hardening;
- fast-hardening;
- long-hardening.
The composition of the base material is polymer, aqueous, oil or monomer. Dentists use either ready-made medicinal pads or prepare them themselves.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of deep caries is carried out using a visual examination, collection of anamnesis and complaints, as well as instrumental examination. The doctor notes visible destruction of the crown part of the tooth.
In the acute form of the disease, it reveals a deep cavity filled with light, soft dentin. Instrumental examination consists of immersing a dental probe into the cavity - its bottom is sensitive, so attempts may cause pain.
In the chronic form of deep caries, the walls and bottom of the cavity are filled with pigmented dentin of a denser structure. Its color can range from brown to black. Probing the cavity does not cause pain - this is due to the formation of secondary dentin. Tapping a tooth is also not accompanied by pain.
The doctor may also use the thermodiagnostic method. This allows you to evaluate the nature of the reaction to hot and cold. Electroodontodiagnosis allows us to identify the reaction of the pulp to the influence of a current of 2–6 μA. In some cases, a decrease in pulp excitability is observed.
If the doctor suspects secondary deep caries, radiovisiography or. The image will allow you to assess the depth of the lesion, the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in other tissues, including periodontal tissues. On a targeted image, you can see 1-3 teeth, and with the help of special computer programs, the doctor has the opportunity to enlarge the area under study for detailed analysis. On an x-ray, caries appears as a dark spot.
The basis of diagnosis in general is the differentiation of deep caries from other diseases with similar symptoms - some forms of pulpitis, chronic periodontitis, moderate caries.
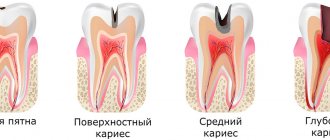
Types and purpose
In dentistry, a gasket is a layer of medicinal materials placed on the bottom and/or wall of a carious cavity prepared for filling.
Thus, the gasket acts as an additional barrier between the filling and the pulp. It performs the following functions:
- It has a bactericidal effect on pathogenic microorganisms that remained unremoved during the treatment of the carious lesion.
- Creates an obstacle to the penetration of infection into the pulp when the seal is depressurized.
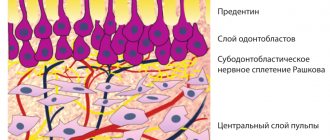
- Activates mineralization and formation of secondary dentin in the tooth. Thanks to this process, the thickness of the bridge between the cavity and the pulp increases.
- Relieves the sensitivity of the restored tooth , which can occur when the thickness of the dentinal layer between the filling and the pulp is small.
This is interesting: Why does a child grind his teeth in his sleep - the main reasons and ways to solve the problem?
According to their functions, pads are divided into therapeutic and insulating types.
Medicinal
Therapeutic pads are applied mainly in cases where the cavity is located very close to the pulp. It is believed that in order to prevent toxins from penetrating into the pulp, the thickness of the dentin layer must be at least 2 mm.
Reducing it to 1 mm prevents the penetration of microorganisms in 90% of cases, and to 0.5 mm – only in 75%. In addition, the thicker the bridge, the higher the survival rate of odontoblasts in it and the more active the reparative processes in dentin.
Therapeutic pads are indicated in the following cases:
- Deep caries, in which the thickness of the bridge between the filling and the pulp chamber is less than 1 mm.
- Acute non-purulent pulpitis.
- Accidental opening of the pulpous chamber during tooth preparation or due to injury. In this case, the gasket is placed directly on the pulp.
The healing material covers the entire bottom of the carious cavity or lies precisely in the areas of the pulp horn.
Modern therapeutic pads are made primarily on the basis of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), which has a bactericidal effect and shifts the pH of the environment in the tooth cavity to the alkaline side, which leads to neutralization of acids.
Thanks to numerous studies, it has been established that even if necrotic and infected tissues are partially left in the cavity, the carious process stops thanks to calcium hydroxide.
The main problem with Ca(OH)2 gaskets is that they have relatively little adhesion to dentin, which creates a risk of cracks and infection entering the pulp.
In addition, the material of the therapeutic pads is susceptible to dissolution and opening, resulting in a path for infection of the pulp. Gaskets perform worst when working with composite fillings.
The most commonly used brands are:
- Dycal. Chemically cured two-component material (paste + catalyst), consisting of 25% calcium hydroxide. Can be used with any filling material.
- Life. The main active ingredient of the drug is also calcium hydroxide.
- Calcipulpe. Calcipulpe. A product with Ca(OH)2, used to relieve tooth sensitivity, deep caries and some forms of pulpitis.
Insulating
Insulating gaskets are designed to solve the following problems:
- isolation of pulp and fillers from filling material;
- increasing the adhesion strength between the filling and dentin;
- increasing the impermeability of medical pads (overlaid on top of them).
The material is indicated for the treatment of moderate, deep and complicated caries, as well as for endodontic treatment. Its use is determined, first of all, by the fact that many filling materials irritate the pulp, and to avoid this, the tooth tissue is isolated with spacers.
The most commonly used insulating gaskets are made from glass ionomer cements. They are usually two-component, consisting of powder and liquid.
The first contains calcium and aluminum fluorosilicates and fluorine compounds. The liquid is a solution of polycarboxylic (polyacrylic, polymaleic, polyitaconic) and tartaric acids.
Another combination of materials is possible, in particular, distilled water and powder containing, among other components, polycarboxylic acid.
Depending on the type of curing, insulating glass ionomer gaskets can be chemically or light-cured. The most famous and in demand are the following types:
- Ionoseal . Contains fluoride, which reduces the risk of secondary caries. Durable, light-curing, acid-resistant, has good adhesion to composites and dentin.
- Fuji Lining . Photocurable. Low shrinkage during hardening.
- Fuji IX . The chemically cured material has the properties of a classic glass ionomer cement.
- Ionosit Baseliner. Compomer (hybrid) dual curing - light and chemical reaction. Hardening is accompanied by slight expansion (1-2%), which compensates for polymer shrinkage. Very durable.
- A universal preparation used for gaskets and temporary fillings.
- Time Line. Light cured.
Symptoms of deep caries
Symptoms of deep caries depend on the type of disease. All forms are characterized by pain. It is sharp, but short-lived. This is how it differs from pain during pulpitis, when the tooth “pulsates” and can hurt without irritation, including at night.
In acute deep caries, the tooth hurts mainly as a result of thermal, chemical effects: ingestion of hot or cold, sour, sweet foods, drinks. In chronic cases, pain is added to this symptom during mechanical action - chewing, food particles entering the cavity. As a rule, after the impact on the tooth stops, the pain subsides.
If food particles continue to remain in the cavity, aching pain may persist until the irritant is removed.
Another symptom is bad breath, but this does not occur in all cases. Halitosis is observed with multiple deep caries or a large cavity of a decayed tooth.
A carious cavity can take quite a long time to form. This is especially true in cases of a previously filled tooth. There may be no symptoms at all; painful signs appear only when the pathological destruction of dentin reaches the bottom of the tooth. In this case, the filling may be movable, have cracks and chips, or fall out entirely.
Materials used
Padding materials contain various active components - zinc compounds, eugenol, calcium hydroxide and glycerophosphate, steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.
They are produced in different forms - aqueous suspension, ionomer cements, varnish, zinc-eugenol and combined pastes, light-curing polymer materials.
This is interesting: Bleeding after tooth extraction: how to stop it yourself, without seeing a doctor
Aqueous suspensions
They are a powder containing calcium hydroxide mixed with water. It is possible to add other components, in particular, radiopaque agents. An example of the composition of Calcesept material: calcium hydroxide + barium sulfate + isotonic solution.
The gasket is applied in a thin layer, dried and closed with a temporary filling. After 1.5 months the gasket is changed.
Disadvantages of the material:
- the need to avoid contact with air due to loss of medicinal qualities;
- resorption, necessitating repeated applications to ensure the formation of secondary dentin;
- cannot be used simultaneously with filling mineral cements that contain acids that react with calcium hydroxide.
Ionomer cements
Ionomer cements based on calcium compounds with chemical curing are the most successful materials, superior to other types of gaskets. Hydroxide and ether are mixed in a 1:1 ratio before application and cure in the mouth.
Advantages of gaskets made from glass ionomer cements:
- strong chemical adhesion to dentin and filling material, which increases due to the slight volumetric expansion of cement during hardening;
- no negative impact on the pulp (the molecules of the material are larger than the dentinal tubules);
- the presence of fluoride compounds that strengthen dentin;
- resistance to oral fluid;
- good strength properties;
- acceptable aesthetics (when using the material as a filling);
- compatibility with composite filling materials;
- ease of use;
- low price;
- low solubility, no need to reapply.
Disadvantages of glass ionomer cements:
- duration of hardening (about a day), during this time the tooth should not be subjected to stress;
- dependence of the strength of the hardened material on environmental parameters - for example, excessive dryness of the filling;
- cracking if overapplied.
Insulating gaskets based on polycarboxylate cements
It contains powders of magnesium and zinc oxides with the addition of polyacrylic acid. Sometimes water is used instead of acid in such gaskets. Polycarboxylate cements do not cause irritation to the pulp, harden very quickly (literally within three minutes after preparing the mixture), and adhere well to tooth tissue. The disadvantage of these mixtures is that they can completely dissolve under the influence of saliva after a certain time, and they are also difficult for the dentist to work with due to their rapid hardening.
Insulating varnishes
These products are also used in dental practice. They belong to insulating gaskets. Consists of one component. Its composition: polymer resin, solvent, filler and very rarely - a medicine.
Varnishes are used to protect the pulp from toxins of filling materials; they are recommended for deep and medium caries. Dental practice shows that the product can be combined with other pads. It is applied to the bottom and walls of the cavity. Only after this a gasket made of a different type of material is applied.
Positive sides:
- has bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects;
- reduces edge sensitivity;
- stimulates the process cell of the pulp;
- resistance to moisture and “chemistry”.
Negative points include:
- The thermal insulating effect is weak. This does not allow varnish to be applied to the bottom of a cavity with severe corrosion.
Application. The varnish is applied to the damaged tooth with a thin brush or cotton swab. The walls are evenly coated with the product and dried with air. The varnish is applied in two or three layers. The next layer is applied after the previous one has dried. One layer is not enough - the varnish shrinks and cracks form.
Zinc - eugenol cements
Contains eugenol - a natural antiseptic. The cement reaches its final hardness in 10 hours. Not used with composites due to the action of eugenol. Preparations: Cavitec, Kalsogen Plus.
Light-curing polymers
The disadvantages of gaskets in the form of light-curing polymers include the possibility of pulp burns. This limits their use for medicinal purposes. If they are used, it is rare, subject to the obligatory condition of precise and careful application. The advantages include high strength.
Combined products
The paste is prepared by a doctor, depending on the availability of ingredients, the doctor’s experience, and the clinical picture.
- Odontotropic drugs stimulate the formation of replacement dentin (fluorides, calcium glycerophosphate, collagen, hydroxyapatites)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (prednisolone, hydrocortisone) and NSAIDs (salicylates)
- Antiseptics (chlorhexedine and metronidazole)
- Enzymes (proteolytic)
- Other products (EDTA, novocaine, dimexide, vitamin solutions)
Preparations: Dycal, Life, Pulpomixine, Calcipulpe.
Dycal, Life - cements that harden by the interaction of two pastes. They are in demand.
Pulpomixine is a mixture of antibiotics and corticosteroids. Normalizes blood circulation, suppresses pathogenic microflora. “First aid kit” for acute processes in the pulp. Does not help form dentin, used within a couple of days. After removal, odontotropic preparations are applied.
This is interesting: Classification of glass ionomer cement for filling and technique of use in dentistry
Calcipulpe consists of filler, hydroside and barium sulfate. Easy to apply (a syringe is included in the kit) and stimulates the growth of replacement dentin. It is used for deep caries and accidental opening of the pulp.
Using combination pastes
Combined cushioning pastes may contain components with different therapeutic effects. They are selected by the doctor depending on the clinical picture and the problem being solved; their content can vary greatly.
Main components of combined pastes:
- substances that stimulate the formation of secondary dentin (bone powder, calcium hydroxide and glycerophosphate, etc.);
- anti-inflammatory drugs of hormonal and non-hormonal nature; (prednisolone, hydrocortisone, indomethacin, salicylic acid derivatives);
- antiseptics (sodium hypochloride, dimexide, chlorhexidine);
- drugs used in chemotherapy (metronidazole and other antibacterial agents), currently antibiotic pads are rarely used;
- proteolytic enzymes (imozymase, stomatozyme), used for caries and acute pulpitis;
- painkillers (Novocaine);
- oil and vitamin-containing products (clove and peach oil).
Due to the weak strength of gaskets made from combined pastes, they are usually used as temporary materials , after which it is recommended to use other means.
In the video, a practicing dentist will talk about the features of materials created on the basis of calcium hydroxide.
Properties of the drug Dycal (Daykal)
Dycal is a calcium hydroxide-based cushioning material. The material is used to protect the pulp. The substance promotes the formation of secondary dentin.
The material has the following properties:
- clinically effective;
- hardens quickly;
- differs in strength in the early period;
- does not dissolve in oral fluid, is resistant to saliva;
- has a natural dentin shade or ivory color (Dycal Ivory);
- easy to apply, filling the necessary areas;
- does not affect the color of the final restoration.
The base composition includes calcium phosphate and tungstate, zinc oxide, iron oxide. The catalyst contains calcium hydroxide, zinc stearate, zinc and iron oxides. The cushioning material Daikal is characterized by high strength.
Instructions for use
Dycal is used as a therapeutic lining material before using the main filling material. The base and catalyst are mixed in equal proportions. The finished mass should have a homogeneous consistency, without streaks. Mixing is carried out within 10 seconds.
Before use, the dental cavity is washed and dried. The substance is applied in a thin layer: from 0.8 to 1 mm. You should not use very thin pins in your work. Remaining material is removed. Next, an adhesive or restorative material is applied. The working time of the material is 2 minutes 20 seconds, hardening occurs within two to three minutes.
Special information
When working with the drug, avoid contact with the skin and mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes. Upon contact, irritation, an allergic reaction, and a rash may occur. Ingestion of the product is prohibited. During restoration work, you should wear gloves on your hands and protective goggles on your eyes.
Gasket material Daikal
At high temperatures and humidity, the working time is significantly reduced, since the mass begins to harden much faster. In this connection, work is carried out at an air temperature of about 21 degrees, air humidity should not exceed 50%. After each use, the tube of material should be tightly closed. It is prohibited to use products that have expired.
The price of the drug ranges from 1,700 to 2,000 rubles.
Analogs of material:
- Vitrebond
ENDOFIL (Endofill) - filling material for root canalsViedent VladMiVa: instructionsPulposeptin in dentistryZincoxide eugenol paste for filling root canalsSilidont 2: instructionsCemfil 15 Stomadent
Treatment of deep caries
The main goal of therapy is to preserve the functionality of the tooth and prevent complications of the disease. Treatment of deep caries is carried out in one or two visits to the doctor. Two visits may be required if the dentist is not sure that the pulp is not affected by an infectious process. He carries out treatment in several stages:
- Pain relief - using a local anesthetic is sufficient.
- Cavity treatment - removal of tissue softened by caries, preparation.
- Rinsing the cavity with antiseptic solutions, drying.
- Application of medications and installation of temporary filling.
Next you need to wait a few days. If after 3-4 days no painful symptoms are observed, the doctor replaces the temporary filling with a permanent one. If, during observation, increasing pain is detected, most likely, we are talking about damage to the pulp - this requires treatment for pulpitis.
If there is no suspicion of possible infection of the pulp, treatment of deep dental caries is carried out as follows:
- Anesthesia.
- Preparation of the tooth cavity - removal of affected tissue.
- Drug treatment - washing with antiseptic agents.
- Drying the cavity with a stream of air.
- Applying a gasket to the bottom of the cavity (gasket with impregnations - calcium hydroxide, eugenol, etc.).
- Installation of a seal.
- Grinding, polishing.
The peculiarity and main difference between the treatment of deep caries is the need to isolate the pulp. The gasket is necessary so that through the thin layer of dentin the pulp is not irritated by the filling materials. Such pads not only mechanically protect the tissue from irritation, but also stimulate recovery and help destroy bacteria.
In some cases, if the walls and bottom of the cavity are sufficiently thick, only a filling is used. But often applying a gasket is a necessary measure. It is also worth noting that a gasket is often installed under a temporary filling - for a period of 4 weeks to six months. This is necessary for the development of replacement dentin. It is imperative to visit a doctor after the appointed time - he will install a permanent filling without a special layer.
How to apply a therapeutic pad
The first step in applying a medical pad is preparing the patient's mouth. Anesthesia is performed, then the defect is prepared and necrotic tissue is removed. After this, the doctor applies a gasket and seals it. The gasket is moistened with distilled water.
The treatment spacer must completely cover the carious plane and reach the base of the junction of enamel and dentin. To prevent the chewing load from damaging the gasket, its layer must be at least 2 mm. In this case, the process of applying a medical pad has two options:
- Direct application (applied to the exposed pulp, used to treat acute pulpitis);
- Indirect application (used to treat caries, applied to a thin layer of dentin).
A temporary filling is placed on the lining, since an oil- or water-based dentine dressing alone cannot provide long-term insulation and protection from irritants.
After ten weeks, using electroodontodiagnostic data, the viability of the pulp is checked, reactions to temperature stimuli are tested, and an x-ray is taken (if necessary). The temporary filling is removed, the lining is replaced and a permanent filling is applied.
Reviews
In most cases, patients in dental clinics do not know whether they have had a gasket installed.
This operation is part of the treatment of caries or pulpitis, and doctors do not consider it necessary to tell the patient the details of the technology being performed.
But if you still have something to say about this, leave your comment at the bottom of this page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: toothache, caries
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet
Treatment of deep caries with pulp damage
If, after installing a temporary filling or even at the diagnostic stage, the doctor determines that the pulp is infected, a more complex multi-stage treatment is planned.
Most often, the pulp is removed, and the root canals are cleaned and processed. However, if the inflammatory process occurs at the initial stage, the doctor may recommend complete or partial preservation of the pulp - antibacterial therapy will be required.
If there are indications for beam removal, further tactics are determined taking into account the individual characteristics of the course of the disease and the extent of destruction of the coronal part. The doctor can fill the canals, and then the coronal part, or install a stump inlay or a crown if your own is badly damaged. The last option requires accessing .
After treatment for deep caries, pain may persist for some time. As a rule, we are talking about a time of no more than 1–2 days, and the pain is moderate, observed only when chewing. If the pain does not subside or intensifies, it is important to return to the dentist - especially if the pulp is intact.
Stages of treatment
Stages of treatment of deep caries
The stages of treatment of deep caries are an important sequential technique that requires planning.
Much depends on the initial condition of the dental crown and how seriously it is damaged. The doctor conducts a visual analysis of the density of the walls, looks at how deep the caries is, in order to determine the correct treatment.
Inspection and diagnostics
When a patient comes to the clinic with deep caries and consults a specialist, the first thing the doctor will do is an examination. One of the important stages in the examination. With a thorough examination, you can easily see deep dental caries and how serious the damage is. It is carried out sequentially, using a dental mirror. It helps identify inaccessible areas. The mirror also provides additional illumination and helps retract the tongue and cheeks for better visual diagnosis. A thorough examination is necessary to prescribe adequate treatment.
Using a dental mirror
Anesthesia
The anesthesia used depends directly on the stage of deep caries, and at what stage of treatment the patient is. To avoid pain, dentists recommend injection local anesthesia. The anesthetic should be chosen correctly, taking into account the patient's current condition and other factors, such as a tendency to high blood pressure or a history of allergies. The following drugs are often used: Novocaine, Dicaine, Lidocaine, Articaine.
The injection is made with a needle. The anesthetic drug is injected first under the mucous membrane, and after a few minutes subperiosteally - this relieves pain from the injection. Modern anesthetics can cope with any pain when treating deep caries.
Preparation - removal of carious tissue
The next step in the treatment of deep caries is grinding. The main task of the dentist is to rid the oral cavity of necrosis, remove pigmented areas, and remove dentin that has exfoliated. An invasive method is used. This prepares the patient for the upcoming procedure. If this procedure is skipped, the symptoms will increase and complications will arise due to infection of the cavity affected by deep caries. In this case, the treatment will be more serious.
Preparation of carious cavities
Medical pads
Therapeutic pads play an important role; in case of deep caries, their use is necessary. It is placed on the carious cavity, or rather on the bottom. The composition of the gasket is calcium preparations that have bactericidal properties. This is an indispensable condition when eliminating deep caries, since during surgical intervention there is a risk of infection of the pulp with pathogenic microorganisms. This will lead to subsequent infection and suppuration.
How deep caries is treated in dentistry and how to choose the right filling
Today, perhaps, there is not a single person who has not encountered caries. This is often accompanied by severe pain. In dentistry, four types of uncomplicated caries are distinguished: carious stain stage, superficial, medium, deep. A term such as “deep caries” shows how severe the changes in the tooth are. This is a pathological process in which hard tissues are destroyed under the influence of microorganisms. The pain is severe and cannot be relieved by analgesics. Not everyone thinks that if treatment for deep caries is not started in time, then serious complications in the form of periodontitis and pulpitis cannot be avoided.
Prevention of deep caries
In order to prevent complications, it is important to visit the dentist in a timely manner, pay attention to proper oral hygiene, and limit the consumption of sugar-containing foods and drinks. Timely treatment of the disease at the initial stage, as well as moderate caries, can prevent the formation of a deep cavity - such treatment is comparatively simpler and less expensive.
Prevention of deep caries consists of following the following recommendations:
- visits once every 6 months, professional cleaning of the oral cavity, examination;
- maintaining hygiene at home - brushing teeth, using dental floss, mouthwash;
- rational nutrition - avoiding deficiency of vitamins and minerals.
Treatment prognosis
With the right professional approach, it is possible to save the tooth, prevent pulpitis and periodontitis, and eliminate the need for tooth extraction. Recovery is possible even with severe destruction of the coronal part. If it is completely destroyed, it is possible to install an artificial crown, preserving the aesthetics and functionality of the tooth. If you do not resort to dental care in time, there is a high probability of pulp damage, further severe destruction, inflammation of the periodontal tissues - periodontitis, and complete tooth loss.