Date of publication: 04/16/2019
Should I depulp the tooth so that after the end of prosthetics I do not have to remove the orthopedic structure?
These are just a few of the questions that patients who want to restore missing teeth often ask.
One of the cornerstones of modern prosthetic dentistry is the principle of minimal invasiveness during dental intervention - i.e. minimal changes in the structure of the tooth, namely its minimal preparation.
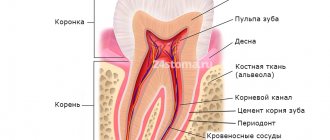
Dental organ - i.e. The tooth, as well as its surrounding structures, is created alive; inside it, in the pulp chamber, there is a neurovascular bundle that provides nutrition and sensitivity of the tooth to various irritants. The absence of pain during its operation is due to a sufficient amount of hard tissue that separates the neurovascular bundle in the pulp chamber from external temperature and chemical stimuli.
The importance of prosthetics
The main reason for refusals to install dentures is associated with the erroneous opinion of old-school dentists about the mandatory depulpation (removal of the nerve) of teeth before prosthetics. Before dispelling this myth, it is necessary to recall the importance of timely prosthetics.
Without an adequate prosthesis, neighboring healthy teeth begin to carry an unusual load, which leads to their increased wear, mobility and early loss. In addition, in the absence of even one tooth, speech defects appear, chewing functions are disrupted, bite pathologies occur, and even facial proportions are distorted.
Why is it bad to remove the nerve of a tooth?
Removing nerves is an unfavorable process for the tooth. The pulpless organ becomes dead, which entails irreversible consequences.
- The nutrition for which the pulp was responsible ceases, leading to a decrease in the level of mineral and organic components. The tooth becomes brittle and its shock-absorbing capacity decreases.
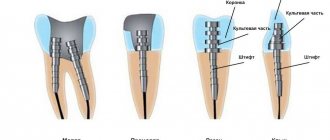
- Over time, cracks and chips appear on the dead tooth. Even if it is under a crown, the tooth can decay or break along with the installed prosthesis. To avoid this risk, before performing prosthetics, dentists often install pins that provide greater reliability.
- Teeth with removed nerves are much more likely to develop caries. After depulpation, the protective functions are reduced, so the organ becomes most susceptible to the destructive effects of bacteria.
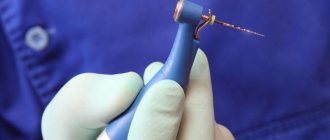
This is what a nerve removal device looks like
The process of pulp removal itself is complex and labor-intensive, requiring the specialist to have the necessary knowledge in the field of dental canal treatment. As a result of the actions of an inexperienced dentist, complications may arise due to incomplete removal of the nerve or its extension beyond the apex of the tooth, which leads to the development of granulomas and periodontitis.
Causes of frequent depulpations
Why do orthopedists so often remove pulp from teeth? The main reason lies in the desire of doctors to play it safe and avoid complications after prosthetics. The fact is that teeth have a porous structure. Pores are dentinal canals that run from the enamel to the pulp of the tooth. During grinding of teeth for a crown, mechanical irritation of the pulp may occur through these dentinal canals.
And at the last stage of fixing the prosthesis, there is a toxic effect of cement. And as a result - infection and death of the pulp. However, this does not allow us to consider depulpation as a prevention of complications, since this procedure is inevitably associated with the risk of developing periodontal pathologies. After all, no one suggests removing the appendicitis for preventive purposes. Living teeth retain their stability much longer.
Whereas teeth subjected to depulpation become extremely fragile and are more susceptible to destruction, losing their shock-absorbing function.
How to preserve a “living” tooth when installing a crown?
Someday every patient will face the question of restoring lost teeth. And one of the restoration methods can be crowns:
- metal-ceramic crowns,
- crowns based on zirconium oxide,
- crowns based on pressed ceramics (E-max).
But the essence is the same - initially you will need to grind the tooth. And with such treatment you will have to “remove the nerve.” And the question “is it necessary to depulpate a tooth when making crowns or can the tooth be kept “alive”?” was asked by every patient. I suggest you think about it together.
What is “bad” about removing the nerve of a tooth?
- Firstly, the pulp is the nutrition of the tooth from the inside; in its absence, the ratio of organic and mineral substances changes. Organic matter is elastic. Consequently, a non-vital tooth becomes more fragile over time and will be susceptible to chipping, splitting and cracking.
- Secondly, non-vital teeth are more often subject to carious lesions - caries. Since bacteria penetrate deeper and are not prevented by the resistance of the pulp.
- Thirdly, high-quality pulp removal is a complex procedure: there is no direct visibility, a large set of instruments and medications are required to ensure comfortable treatment, and the doctor’s high-quality knowledge in the field of root canal treatment is required.
Why is tooth depulpation required?
The answer lies in the amount of treatment of the tooth walls before installing the crown:
- in the manufacture of metal-ceramic crowns - from 1.7-2.2 mm,
- based on zirconium oxide and all-ceramic - from 1.1–1.5 mm, while the thickness of the residual dentin should not be less than 0.8 mm, preferably 1.5 mm.
If we translate into “human language”, then when processing a tooth, its walls become very thin, and as a result of the friction of the bur on the dentin, heat is released, which leads to “overheating” of the pulp.
Conditions under which “overheating” of the pulp does not occur will be maintained only when treating vital teeth under a zirconium and all-ceramic crown (without additional layers of ceramic). In this case, the tooth must be free of tilting, protrusion and disruption of the development and position of the pulp chamber. In this case, the crown will preserve the natural color of the tooth, and the risk of damage to the pulp will be minimal.
When processed under a metal-ceramic crown, the thickness of the tooth wall remains 1.0-1.5 mm. As we already know, any tooth treatment causes an increase in temperature. And when tissue temperature increases by more than 11°, changes occur in the pulp, which cause pain or the formation of granulomas.
To keep the tooth alive and not damage the pulp, our clinic pays great attention to:
- technical equipment of the doctor’s office - sharp bur, abundant cooling, work with a handpiece that has stable speed (increasing handpiece)
- tooth processing technologies - increased processing time, since reducing the processing speed reduces the amount of heat generated by the friction of the bur on the tooth tissue. Compliance with the sequence of processing stages. Carrying out manipulations under anesthesia. Coating teeth with protective varnish. It is mandatory to make temporary crowns and fix them on the first visit.
- taking into account the reactivity of the body. This is the most unpredictable component - the body's response to tooth treatment. In 96% of cases, after the end of anesthesia, a feeling of discomfort or pain persists until the end of the day. 2% - pain persists for more than 48 hours and 2% develop pulpitis (inflammation in the pulp) - requiring root canal treatment. This happens even when all precautions are taken, so the patient is informed about this before treatment begins.
The technique of treating teeth while preserving the pulp when making crowns is not often practiced by orthopedic doctors, since complications from overheating of the nerve during treatment led to inflammation and the teeth began to hurt under the crowns. This happened after some time, which required the removal and alteration of an expensive structure. However, at present you have the right to demand the best treatment for yourself and the opportunity to preserve living teeth under crowns. To do this, you need to choose a doctor and a clinic that takes a comprehensive approach to dental restoration and uses the capabilities of all specialists in a narrow profile. For example, the ability of an orthodontist (installation of braces) to move his teeth or correct the tilt of his teeth, which will provide the possibility of gentle treatment in the future.
At the Grandmed Dentistry Clinic, our specialists will offer several methods for restoring teeth, based on their experience in gentle tooth treatment. Technical equipment will allow a team of specialists to plan treatment taking into account all your wishes and condition. And the treatment will be as high quality and comfortable as possible.
Knowledge and experience of orthopedists
Of great importance in the issue of prosthetics without depulpation is the knowledge of orthopedic doctors about the safety zones of the crown parts of teeth. Safety zones are those areas of the tooth within which you can safely grind the tooth tissue without damaging the pulp.
The canines have slightly more such tissue than the lateral incisors. The age of the patient is also important: the older the person, the less likely the pulp is to be damaged.
Contact our clinic for a consultation on prosthetics without depulpation, and we will definitely find the right solution for you!
Dental prosthetics in our clinic. Types of dental crowns and methods of their manufacture
Prosthetics on “living” teeth
However, with a sufficiently preserved volume of the coronal part of the tooth and an intact nerve, if it is necessary to make a bridge structure, as well as if it is necessary to correct the shape of the tooth, it is possible and necessary to keep the teeth vital (alive).
The classic metal-ceramic crown, widely used in practice by orthopedic dentists, is a combined two-part crown - the frame (cap) of the crown consists of a metal alloy, onto which ceramic mass is applied layer by layer. The technology requires abrasion of a sufficient amount of hard tissue, which is an extremely invasive technique.
Currently, all-zirconium crowns, the so-called, have become widespread. prettau technology (one-piece, without ceramic lining). The advantages of such crowns over classic metal-ceramic crowns are that during preparation a minimum amount of hard tooth tissue is ground off, which, in turn, allows the orthopedic dentist to carry out minimally invasive intervention, does not take the patient out of the comfort zone, and also allows the tooth to be kept vital ( alive).
Doctor of Medical Sciences orthopedist dentist Leonid Yakovlevich Koussevitzky
Sources:
- Samoilenko L. A. Depulpation of teeth in some diseases of the dental system, 1970
- Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology. Patient management protocol. Partial absence of teeth (partial secondary adentia), 2009
Expert author:
Avdeeva Tatyana Dmitrievna
Dentist-therapist
The information presented in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace the advice of a qualified specialist.
At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Tell us about us:
Indications for depulpation
Despite all the disadvantages of tooth depulpation, in some cases it is impossible to do without this procedure. Indications for nerve removal may include:
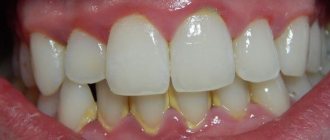
- advanced caries affecting the deep tissues of the tooth;
- the appearance of caries on one or more roots;
- incorrect anatomical position of the tooth;
- low landing of crowns;
- inability to prepare a tooth without opening the pulp chamber;
- inflammation of the pulp or periodontium;
- uncharacteristic anatomical features of the organ (for example, significant tilt of the tooth axis or large size of the pulp chamber).
If the dentist identifies at least one of the listed reasons in the patient, depulpation will be justified.
If caries or pulpitis is present, depulpation is necessary
How to treat a tooth under a crown
Not every therapy method can be applied to a dental unit covered with a prosthesis. In many cases, it needs to be removed, and only then can the problem be fixed. Filled canals, installed pins, and inlays are also difficult. If there is serious inflammation and complications, treatment can take up to several months.
First aid
What to do if your tooth suddenly hurts:
- take medications that relieve pain and inflammation (painkillers, non-steroidal drugs);
- every three hours, rinse your mouth with a solution of soda, antiseptics, pharmaceutical herbal tinctures or homemade herbal decoctions;
- Contact your dentist as soon as possible.
It is strictly forbidden to make hot compresses or heat the site of inflammation, or take antibiotics. It is not recommended to sleep without a pillow, as unimpeded blood flow is necessary.
Medicines for pain relief
Even severe toothache can be relieved with painkillers. This can be any product from the first aid kit. Dentists recommend using Ibuprofen, Ketanov, Tempalgin, Ketofril or Ortofen. There is no need to suffer from a painful symptom if there are medications available. Take strictly according to instructions.
Safe folk remedies
Immediately after dentures, many patients experience minor pain and swelling of the gums. During this period, it is possible and even recommended to rinse the mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs. It is important to coordinate traditional medicine methods with your dentist in advance.
Can be used:
- Sage. Stops bleeding, kills germs, relieves pain. Rinse your mouth with warm infusion every 4 hours. To prepare a therapeutic rinse, place one tablespoon of dry raw materials in a container and pour 250 ml of boiling water.
- Calamus root. Perfectly relieves pain and disinfects. The decoction is prepared similarly to sage. Can be used for rinsing and application. The dry root is applied to the inflamed area and left until the fibers soften.
- Oregano. It has antiseptic, antifungal properties and relieves pain. The decoction is prepared at the rate of 2 tablespoons of dry raw materials and 250 ml of boiling water. You can rinse your mouth up to eight times a day.
- Soda. The simplest remedy that is in any kitchen. Dilute a heaping teaspoon in a glass of warm water. Rinse every 2 - 3 hours until acute symptoms subside.
Long-term consequences after treatment
Patients often experience complications after nerve removal. This is due to many factors: lack of diagnosis, poor quality treatment, incorrect diagnosis, etc. Main consequences:
- poor canal filling. A loose filling leads to the re-emergence of bacteria that extend beyond the tooth root. A cyst forms, due to which the tooth is often removed;
- tool fragments. The complex anatomy of the canals and low-quality instruments can lead to its failure.
- removal of material beyond the root apex. If the filling material is chosen incorrectly or there is too much of it, it extends beyond the root.
- Tooth perforation occurs due to aggressive processing.
To avoid such complications, doctors at the SDent clinic recommend contacting us for medical help, as we have a staff of highly qualified doctors, an equipped X-ray room and advanced equipment!