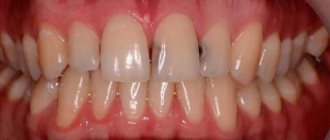
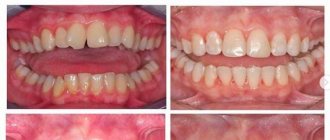
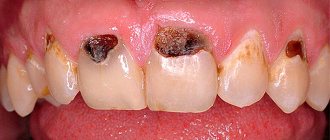
Problem: For about five years, a man suffered from food getting between his teeth. Food getting stuck meant that I constantly had to pick between my teeth to remove food debris and my gums became inflamed. Friends advised me to contact Dial-Dent to eliminate the gap between my teeth.
Solution: old crowns on the teeth were replaced (the crowns were more than 5 years old, they were done in another clinic). Using computer modeling, tight contacts between teeth were created and the anatomical shape of the chewing surface was restored. Now food does not get between the teeth, it is chewed better, and the gums do not hurt. With new ceramic crowns from Dial-Dent, the problem is completely solved.
Choosing treatment tactics for food stuck between teeth
At the consultation, orthopedic dentist S.V. Zukor discovered that between the chewing teeth on the lower jaw there is a gap where food gets clogged. Due to food getting stuck between the teeth, the gums are constantly pressed, and the use of various improvised means for picking between the teeth injures the gums even more, so the gums hurt. The teeth have crowns that do not have the correct shape, there is no close contact between the teeth, and the chewing surfaces are almost flat.
To eliminate food getting between the teeth, the dentist suggested replacing the old crowns and making new ones with tight contact so that there is no gap between the teeth.
Causes
There are many reasons why food gets stuck between teeth over and over again:
- incorrectly recreated contact points in the treatment of caries,
- low-quality artificial crown or cement residues after its fixation,
- abundant supra- and subgingival deposits,
- malocclusion.
And if the other reasons for the problematic situation are, in general, clear, then how an incorrect bite can affect food getting stuck is not obvious. Let's look at this in more detail.
Normally, the crown parts of adjacent teeth should be in close contact with each other. The places of their contact are called contact points. It is these that are so important to restore when filling a carious cavity, so that caries does not occur again in the same place. The condition of the periodontal papilla, the area of gum in the interdental space necessary to protect the neck of the tooth and the interalveolar septum, also depends on the quality of the contact points.
If the papilla disappears, food will begin to get trapped under the gum and then the roots of the teeth will deteriorate. In addition, when food gets stuck between the teeth and puts pressure on the interdental papilla, pain occurs, and the decomposition of food debris contributes to the appearance of bad breath, the development of inflammation, which ultimately can lead to consequences such as periodontitis and premature tooth loss.
Incorrect posture, the habit of holding your head low, scoliosis or any other spinal deformity causes overstrain of the neck muscles, which in turn leads to asymmetrical spasm of some and relaxation of other facial muscles. Prolonged stay in this state causes an imbalance in the facial-masticatory muscles, which ultimately leads to a change in the position of the teeth.
This process occurs slowly and often goes unnoticed. But over time, some people may experience crowding, while others, on the contrary, may have teeth that diverge. In this case, some teeth may change their position relative to the vertical axis. All these factors lead to the formation of malocclusion. Wide dental spaces or, conversely, narrow ones, are the places where food gets stuck between the teeth. Thus, it turns out that postural disturbances can cause food to accumulate between the teeth.
Dental scanning and dental crown modeling
Before modeling the new crowns, a teeth scan was performed. Dental scanning replaces traditional dental impressions, which many patients cannot tolerate due to an increased gag reflex. When taking digital impressions of teeth, the dentist runs a Sirona scanner along the surfaces of the teeth for several minutes, and a three-dimensional image of both jaws is transferred to the computer - a digital impression of the teeth.
Working with a digital impression in a specialized program, the dentist models crowns with the most tight contacts between the teeth and the correct anatomical chewing surface.
Based on the simulation results, the dental technician produced ceramic crowns from E.max ceramics. Pressed ceramics E.max has high strength and excellent aesthetic properties, therefore it is used for prosthetics of both lateral and anterior teeth.
Tooth canal treatment with a microscope
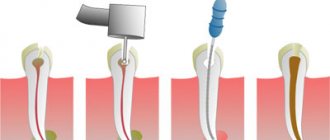
Dentist-endodontist T.I. Matienko removed the old filling, removed the pin and washed the tooth canals. Cleaning of the canals is carried out under a microscope, using special endodontic instruments that penetrate into the narrowest parts of the canals. The tooth canal is washed with antimicrobial agents, and then medicine is placed into the canal to completely destroy the bacteria. The tooth is closed with a temporary filling for 14 days.
During the second visit to the endodontist, the filling was removed, the canal was again washed and dried, and then sealed with gutta-percha along its entire length. Since the tooth on top was badly damaged, a fiberglass pin was installed in it to strengthen it, and then the cavity in the tooth was closed with a light-rejecting filling made from the most modern Estelite material.
A filling is only an intermediate stage in tooth restoration. Next, an orthopedic dentist worked with the patient.
The result of replacing crowns is that food does not get stuck between the teeth
Tight contacts between teeth ensure that food does not get stuck and gums remain healthy.
The cost of ceramic crowns is 55,000 rubles per unit.
Of course, it is possible to make dental crowns cheaper (cheaper material, lack of computer modeling, etc.), but this will invariably affect the quality. The use of computer technology makes it possible to more carefully work out the shape of the crowns, provides additional convenience when taking impressions - all this is reflected in the price, so good dental crowns cannot be cheap. In addition, Dial-Dent uses the highest quality and most modern materials both for the crowns themselves and for their fixation, which increases the service life of dental restorations.
Video about how teeth are scanned with an intraoral scanner:
What is oral microflora?
Surprisingly, according to scientists, there are from 43 million to 5.5 billion cells per 1 milliliter in saliva. The concentration of microbes in the gingival groove and dental plaque is 100 times higher, reaching 200 billion per 1 gram of deposits.
During birth, the baby's skin receives the most important microflora for his health from the birth canal. But, despite the fact that the baby receives micrococci, lactic acid bacteria, a-, b- and anaerobic streptococci, fungi, enterobacteria and even simple viruses on the skin, his oral cavity remains sterile. The rapid increase in microbes in the oral cavity begins only 8 hours after birth.
After teething, a change in flora also occurs. Various anaerobes can grow in the folds of the oral mucosa. Each person has his own unique microflora on his tongue, saliva and teeth. Microbes accumulate on the smooth surface of teeth, as well as in various fissures and plaques.
What happens when you lose teeth?
With tooth loss, the natural flora changes. The number of lactobacilli, spirochetes and some types of streptococci decreases. When wearing dentures, even greater changes occur. Like any therapeutic agent, these structures, in addition to the therapeutic effect, provoke unwanted and inevitable side effects.
Dentists conventionally distinguish three levels of interaction between the prosthesis and the body:
- Local, tissue, determined directly by the contact of the structure with the tissues of the prosthetic bed.
- Systemic, affecting all components of the masticatory-speech apparatus, as well as parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Some scientists also note the effect of prostheses on the body's immune system.
- Organismal, in which prostheses directly or indirectly change the psychology and autonomic functions of the patient.
Very often, when wearing dentures, not only the microflora of the oral cavity changes. Various forms of inflammation may also appear:
- local;
- diffuse;
- granulating.
How to maintain healthy teeth and gums for a long time and extend the life of dental crowns
The dentist said that to maintain healthy teeth and gums, it is necessary to undergo professional teeth cleaning at least once every six months. Dial-Dent understands the importance of prevention and oral hygiene, so they have developed the “Teeth for Life” program. Professional oral hygiene helps remove plaque not only from your teeth, but also from crowns, veneers, implants, thereby extending their service life, and prevents the occurrence of caries, periodontitis and other diseases.
See other examples of the work of Family Dental specialists here.
Make an appointment for a consultation by phone +7-499-110-18-04 or through the form on the website. You can ask questions about dental prosthetics to the chief doctor of the clinic, Sergei Vladimirovich Tsukor, at
Possible diseases
Constant pain in the gums is one of the main symptoms of the following oral diseases.
- Gingivitis. Acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane. Develops due to the accumulation of plaque. Soft deposits mineralize and turn into tartar, which cannot be removed with a regular brush. Pain occurs in the gums between the teeth.
- Periodontitis. Periodontal inflammation, in which the dentogingival joints are destroyed. Develops due to advanced gingivitis. The risk group includes patients with a hereditary predisposition to the disease.
- Stomatitis. An inflammatory process accompanied by the formation of blisters or ulcers. They cause burning and pain in the mouth when eating and brushing teeth. Stomatitis can be triggered by injuries, burns, as well as pathogens - herpes simplex virus, Candida fungi.
How is the problem corrected in the clinic?
The main thing in treatment is the correct formation of the contact point. A wide variety of matrix systems and filling materials will help to successfully treat caries. The filling must not only be placed, but also given the correct shape in order to achieve tight contact with the adjacent tooth. If the problem of food getting stuck is caused by an overhanging edge of the filling because the previous dentist gave it the wrong shape, then the filling will be changed. Dentures of unsatisfactory quality must be replaced. “Black triangles” and deep pockets are corrected by dental surgeons. There is no way around it without surgery. Teeth crowding, spasms and diastema can be corrected with orthodontic therapy. To eliminate these defects, it is better to use the method of aesthetic restoration of teeth with crowns, veneers and fillings. Tartar is removed using a special procedure using a professional method, followed by root polishing.
Veneers are microprostheses that restore the aesthetic appearance of teeth, allow you to choose the color and shape of one or a group of teeth, and eliminate interdental spaces.
Why does the taste of blood appear in the mouth?
Inflammation of the gums under the denture is manifested not only by a specific smell from the mouth, but also by the appearance of a blood taste.
Inflammation of the gums around the crown is called gingivitis. Often the cause of gingivitis is rubbing of the mucous membrane due to the irregular shape of the prosthesis. For example, when the lower edge of the crown extends too deeply behind the gum, which leads to injury and bleeding. Blood is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microbes that readily multiply, causing inflammation of the soft tissue around a tooth with a poorly fitting denture.
Broken prosthesis that goes unnoticed. The bridge structures scratch the mucous membrane, leaving cuts and abrasions on it.
Bleeding is also the result of poor-quality tooth treatment before prosthetics. Against the background of inadequate filling of the dental canals or incomplete removal of the pulp, pathogenic microbes inside the tooth provoke a purulent process, which is accompanied by tissue destruction with the release of blood.
Diagnosis and treatment
Has a pocket formed under the crown? To determine the cause of the pathology:
- carry out an examination of the oral cavity,
- take a photo.
Treatment may include:
- removal of soft bacterial plaque and hard dental plaque;
- curettage – thorough cleaning of pockets;
- vestibuloplasty;
- splinting – can be temporary or permanent, aimed at stabilizing the position of teeth in the sockets.
If a pocket has formed under an artificial crown, it may need to be removed and re-treated. In case of extensive inflammation, the affected tooth is removed.