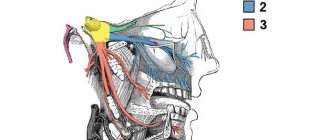
Symptoms and causes
The scientific name of this pathology is paresthesia. The main symptoms by which one can suspect the onset of the disease are: a burning sensation, the appearance of goosebumps and slight tingling in the soft tissues, numbness of part of the dentition or the entire jaw at once. This condition can be caused by many reasons. It is important to understand that numbness is not always a sign of a developing disease, but it is still worth seeing a doctor.
The main factors that provoke the loss of usual sensitivity: inflammatory processes in the root system, for example, periodontitis, severe injuries to the jaw, problems with the temporomandibular joint and malocclusion, disruption of the work algorithm during installation of implants, poor-quality dental treatment, stress and tension, violation integrity of nerves, etc.
Less common causes today are allergic reactions (to medications used by the dentist or to a sudden change in air temperature) and a significant outflow of blood from the head.
Trigeminal nerve injury
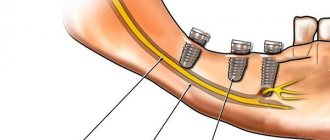
Prolonged numbness of tissues after implantation can also be caused by incorrect selection of the length of implants or their installation without taking into account the anatomical characteristics of the patient. In this case, damage to one of the processes of the trigeminal nerve is possible. Most often, when screwing in dental implants, the inferior alveolar nerve is affected. If it is damaged in the area of the lower lip, cheek and gums (up to the second molars), the following may occur:
- complete numbness of tissues;
- not disappearance, but a violation of sensitivity, without other unpleasant phenomena;
- a change in sensitivity, which is accompanied by an abnormal reaction to certain stimuli and other pathological symptoms.
If the lingual nerve is damaged during implantation, the following may also appear along with numbness:
- uncontrolled tongue biting;
- increased salivation;
- loss of taste;
- swallowing dysfunction;
- difficulties with pronouncing sounds.
If such symptoms appear and prolonged loss of sensitivity after implantation, you should contact the dentist who performed the operation.
Diagnosis and treatment
As a rule, it is possible to determine the presence of numbness and find the cause of this ailment already at the stage of conversation with the patient. The dentist must conduct an in-person examination, on the basis of which he may prescribe the following studies: radiographic, tomographic, and Dopplerography of the vessels of the jaw. Unfortunately, without a thorough preliminary diagnosis, making a correct diagnosis and prescribing a treatment regimen is impossible. That is why, if necessary, it is not recommended to refuse to do some tests.
Most often, therapy is limited to the use of certain medications without the need for surgery. Sometimes it is necessary to perform an operation using one of the methods of jaw microsurgery. In both situations, the doctor’s main goal is to relieve the patient of discomfort and return the tissues to their former sensitivity.
It is important to understand that timely seeking help guarantees the fastest possible cure. A disease whose duration exceeds 3 months will be much more difficult to overcome. If numbness persists for a year, then it will be almost impossible to regain sensitivity. After treatment, the following therapeutic procedures may be prescribed: UHF, electrophoresis, laser therapy, exposure to diadynamic currents, etc.
Why does my upper lip go numb?
Physiological and cosmetic reasons
The appearance of the symptom is provoked by eating too cold or too hot food.
Numbness can also be a consequence of previous irritation of the upper lip from pepper or hot spices. At the same time, similar sensations are observed on the tongue and oral mucosa. The symptoms quickly disappear after stopping contact with the product. At sub-zero temperatures, strong winds, and high humidity, lips easily become chapped and crusty. Crusts impair the perception of tactile stimuli by nerve receptors, so their formation is accompanied by a feeling of numbness, which is complemented by a feeling of tightness due to a decrease in the elasticity of the skin, and the appearance of cracks.
In women, a decrease in lip sensitivity can be explained by individual intolerance to cosmetics (lipstick, lip gloss). Local itching, burning, and signs of skin irritation are possible. In some cases, the symptom is caused by an incorrect tattooing procedure or errors in lip care in the first days after manipulation.
Dental pathologies
One of the most common causes of numbness in the upper lip is diseases of the teeth and gums. The symptom is especially noticeable in severe inflammatory processes, accompanied by severe swelling of the oral mucosa and soft tissues of the face. It is provoked by gumboil, periodontitis, and gingivitis. In addition, numbness of the lip is observed after dental procedures performed under local anesthesia.
Trigeminal nerve injury
Isolated numbness of the upper lip rarely develops and is caused by trauma to the small branches of the n. maxillaris for bruises and open wounds of this anatomical area. A more common sensory disorder, simultaneously covering the upper part of the cheek, the side surface of the face, the outer corner of the eye, and the lower eyelid, is caused by damage to the trunk n. maxillaris, which is the second branch of the trigeminal nerve. It is found in fractures of the upper jaw, zygomatic bone, and compression by tumors.
Numbness of the upper lip
Migraine with aura
In patients with migraine with aura, an attack of cephalgia may be preceded by a transient loss of sensitivity in the hand, spreading to half the face and upper lip. Subsequently, the attack proceeds as usual. There is a throbbing or pressing pain in half of the head, nausea, slight dizziness, high sensitivity to bright light, loud sounds.
Cerebrovascular disorders
Numbness of the upper lip and other parts of the face and body is part of the clinical picture of a transient stroke or stroke. The symptom occurs against the background of headache, weakness, nausea, vomiting, vegetative-vascular manifestations (trembling, sweating, hot flashes), short-term disturbance of consciousness. Hemiparesis, decreased strength of certain muscle groups or one limb, facial asymmetry, and speech impairment are possible.
Hypoglycemia
Numbness of the lip is sometimes detected in patients suffering from severe diabetes mellitus; it develops as a result of severe hypoglycemia when using too high doses of insulin or poor diet. Combined with pallor, sweating, tachycardia, hand tremors. There are feelings of fear, excitement, followed by drowsiness, confusion, and fainting. Without help, coma is possible.
Quincke's edema
Numbness is caused by rapidly increasing swelling of the eyelids, cheeks, upper and lower lips. Quincke's edema forms against the background of an acute allergic reaction upon contact with pollen, animal hair, food, and other allergens. May be a consequence of pseudo-allergy. The condition develops suddenly within a few minutes, less often – hours. Hypoesthesia is often combined with skin itching, lacrimation, the appearance of copious nasal discharge, and difficulty breathing.
Herpes zoster
The cause of the pathology is the virus that persists in the body and causes chickenpox. Shingles symptoms may appear many years or even decades after the viral infection. The upper lip, as well as other parts of the face, become numb due to trigeminal neuritis. Typically, simultaneous involvement of the intercostal nerves, a rash along the affected nerve trunks.
Multiple sclerosis
The disease often manifests itself as weakness in the legs, combined with sensitivity disorders. Numbness and paresthesia are detected in the face, upper lip, torso, and limbs. There is a high probability of developing optic neuritis with reversible vision loss. Subsequently, with multiple sclerosis, paresis, symptoms of cerebellar damage, pyramidal disorders, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs are observed.
Pernicious anemia
The disease is caused by a disorder of hematopoiesis due to a deficiency of vitamin B-12. Manifested by weakness, tachycardia, dizziness, pale skin, puffiness of the face. Possible hypoesthesia of the upper lip, other areas of the face or limbs, and gait changes associated with neurological disorders. A characteristic sign of pernicious anemia is a “lacquered tongue.”
Neuroses
Loss of sensation in various parts of the body most often occurs in patients with hysterical neurosis. The patients’ complaints do not fit into the picture of a specific somatic pathology and are distinguished by pretentiousness and unusualness. Numbness of the upper lip is also sometimes seen in people with anxiety disorders. It may be part of the clinical picture of a panic attack or occur when the level of anxiety increases.
Numbness after implantation
One of the most common reasons for decreased sensitivity of the dentition is a violation of the implantation technique, that is, the implantation of an artificial tooth root. The situation can also be aggravated by the introduction of poor-quality anesthesia or nerve damage during an injection with a syringe with an anesthetic composition.
Numbness can also occur when a pin is made of the wrong size and length. As a result, during installation, the doctor accidentally injures the nerve or compresses it too much. Today it is customary to distinguish three stages of tooth numbness due to a doctor’s mistake during an operation to implant an artificial root.
The first stage is neuropraxia. At this stage, there is only slight numbness and decreased sensitivity. Usually all symptoms disappear within a couple of hours after the intervention or after 1-2 days, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. The second stage is axonotmesis. It is characterized by loss of sensitivity for a month or more. The most difficult case is neurotmesis; numbness can haunt a person for several months.
Causes of paresthesia
Jaw numbness after wisdom teeth removal is a fairly common complication. It is due to the location of the “eights”. Their roots are located next to the jaw nerves, so during surgery the latter are often damaged, which leads to loss of sensitivity. Most often, paresthesia occurs:
- with long curved roots of the removed dental unit,
- severe bleeding during surgery,
- damage to the alveolar process.
Patients at increased risk of paresthesia after surgery include:
- over 30 years old,
- with a history of nerve ending injuries,
- endocrine diseases,
- neuralgia.
Prevention
Unfortunately, modern dentistry has not come up with any special preventive measures aimed at reducing the risk of dental numbness. This is explained by the fact that the main causes of pathology are usually severe trauma and mechanical damage to the nerve during surgical procedures. However, it is still possible to minimize the risk of the disease; to do this, you should adhere to several rules.
If you need to undergo treatment or install an implant in place of a missing tooth, you need to choose a truly experienced specialist. After surgery, it is very important to give the body time to fully recover, so do not neglect rest. It is also not recommended to stay outside for a long time, especially in severe frost or gusty winds.
Teeth numbness is a rather unpleasant syndrome that can cause a lot of inconvenience to its owner. In most cases, the pathological process requires specialist supervision, as it does not go away on its own. If the problem is not properly addressed, numbness can develop into a more serious dental disease.
previous post
How to overcome your fear of dentists?
next entry
Diagnostics
Determining the cause of numbness is the responsibility of a neurologist. Due to the possible connection between upper lip sensitivity disorders and dental pathologies, a dentist is often involved in the examination. Sometimes a consultation with an allergist or endocrinologist is required. The diagnostic program includes the following methods:
- General inspection
. The doctor evaluates the patient’s appearance and the condition of the tissue at the site of the lesion. Identifies signs of inflammation, traumatic injury, skin rashes, and other symptoms indicating the cause of numbness. - Dental examination
. Provides for the study of teeth and soft tissues of the oral cavity to detect caries, pulpitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, and other dental diseases. - Neurological examination
. Includes sensory and movement testing. The specialist asks the patient to close his eyes, stretch out his lips, bare his teeth, and stick out his tongue. Tests reflexes and muscle strength of the limbs. - X-ray of the tooth.
Informative for dental diseases, allows you to detect inflammatory processes, osteomyelitis, tumor lesions. According to indications, it is supplemented with other hardware diagnostic methods. - Tomographic techniques.
Effective for multiple sclerosis, stroke and cerebral circulation disorders. They help determine the location, volume and nature of the lesion, and choose the optimal treatment tactics. - Lab tests
. Necessary to confirm pernicious anemia, hypoglycemia in diabetes mellitus. To clarify the type of allergen that caused the development of Quincke's edema, allergy tests are performed.
Electroneuromyography
Complications after local anesthesia
The human factor plays a big role in dental procedures. Often, the inexperience or carelessness of a specialist leads to serious consequences.
General complications that arise during local anesthesia in dentistry can be of different nature:
- Discomfort at the needle insertion site. This is due to the drug being administered too quickly or too slowly.
- Hematoma at the injection site. The occurrence and growth of a hematoma indicates problems with blood vessels or an incorrect choice of the needle insertion site.
- Allergic reactions. Despite the fact that reactions to drugs are determined before anesthesia, cases of severe allergies to the composition of the anesthesia are not uncommon, especially if it consists of two or more components.
- Inflammation of the gums, development of infection. This case suggests that several mistakes were made during the procedure, as a result of which bacteria entered unprotected tissue and caused inflammation.
- Numbness of the facial muscles. The symptom is often complicated to the point of paresis, lack of control over facial expressions, inability to close lips, and sagging areas of the face.
How to treat numb gums
If the patient's gums are numb, it is necessary to begin treatment early. The problem requires an integrated approach, since it is important to establish the cause of its occurrence.
The medications that are most often used if the gums are numb include:
- ► Antibacterial drugs. To eliminate pathogenic microflora in dentistry, Amoxiclav or Clindamycin are used. Preference is given to tablet or injection forms of release. The average duration of treatment is 7-14 days.
- ► Local antiseptics. They are used in the form of an ointment, gel or rinse solution.
- ► Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs reduce pain and tissue swelling. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often taken for two weeks. The doctor selects medications individually.
- ► Traditional methods. A decoction of chamomile or calendula has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, which restores tissue sensitivity if the gums are numb. However, traditional methods can only be used on the recommendation of a dentist.
If there is no effect from the drug therapy, surgical intervention is prescribed, which is aimed at removing purulent masses or the implant. This will improve the patient's condition and prevent the spread of infection to other organs and tissues.
At the recovery stage, when the gums become numb, physiotherapeutic procedures are used:
- ► laser therapy
- ► dynamic current treatment
- ► UHF therapy
- ► electrophoresis