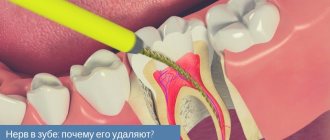
What is mandibular nerve injury?
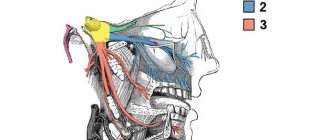
By this concept, dentists mean injury to one of the nerves:
- chin;
- lingual;
- alveolar.
Types of injuries include sprain, compression, crushing and rupture - partial or complete. The cause of the stretching is the long-term retraction of the mucoperiosteal flap, which is created by an implant of greater length than necessary. Crush injuries and compression are caused by needle injuries during the administration of anesthesia. Rupture occurs in two cases: when cutting the mucosa or during preparation of the hole for the implant.
Causes
The main causes of damage to the NAS are:
- implantation (doctor’s errors, lack of a full preliminary examination);
- removal of dystopic “eights” on the lower jaw;
- errors when performing conduction anesthesia;
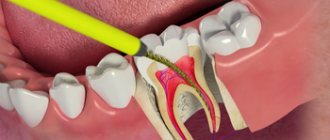
- exit of the filling material beyond the root apex into the nerve canal;
- infectious lesion of the periapical region of the lower row.
But the most common reason is the first reason - damage as a result of implant installation, usually in the chewing area.
Causes and prevention of mandibular nerve injuries
The only cause of such damage is considered to be medical errors. Since in preparation for implantation, X-rays of the jaw are taken, which the doctor must carefully study so that when choosing an implant and a place for it, he does not injure the nerve, the injuries are caused by his unprofessionalism or negligence.
Damage to the mandibular nerve most often occurs when:
- improper administration of anesthesia - needle injury;
- choosing an implant that is too long;
- damage by an instrument - when preparing the site for the implant.
The only way to avoid such an injury is for a doctor to responsibly approach the stage of preparation for surgery, carefully studying the condition and structure of his patient’s jaw. The only way of prevention for the patient is to choose a trusted clinic and a highly qualified doctor. Specialists at the Implantmaster clinic have been able to reduce the number of injuries of this kind to 2%, since they carefully study three-dimensional photographs of a person’s jaw before implantation, and can correctly assess the condition of the bone tissue, the location of nerves and blood vessels, and select the optimal size of the implant.
Description of the pathological condition
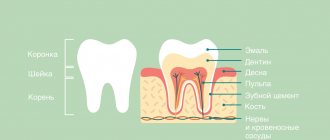
The disease of the nerve branches located in the tongue and lower jaw is accompanied by pain and salivation disorders. Nerve clusters (nodes) located in this area belong to the peripheral parts of the NS. Despite the fact that neurologists anatomically separate the sublingual and submandibular nodes, degenerative processes occur in them simultaneously. This is due to the fact that numerous neural connections are distributed between the channels. This allows the pathology to be classified as one disease.
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
Classification
In accordance with Seddon's classification, the following types of NAS injuries are distinguished:
- Neuropraxia. This injury is reversible; the sheath of the nerve fibers does not suffer, that is, there is no development of degeneration. After treatment, the problem goes away, which usually takes a couple of weeks.
- Axonotmesis. A reversible type of lesion, for which long-term, intensive treatment is prescribed - from three to six months. The development of degeneration and fiber damage are observed.
- Neurotmesis. A serious disorder affecting all structures, including fibers and connective membranes. Scar tissue develops, and surgery is indicated to correct the problem.
In accordance with the generally accepted WHO classification, there are five categories of NAS injuries:
- compression, nerves are not damaged;
- swelling of tissues;
- partial rupture of fibers;
- complete ruptures of the NAS are observed;
- post-traumatic fibrosis develops.
Assessment methods
To determine the cause and extent of the disorder, diagnostics are required. For this purpose they prescribe:
- mechanoceptive methods, in which the response to mechanical irritation and stimulation is recorded;
- nociceptive, allowing to determine sensitivity to painful stimulation.
The first type of research includes tests of the following types:
- tests with a brush, during which the Patient’s lip is passed with a brush and asked to determine the direction of movement;
- two-point irritation using a probe.
The second diagnostic method includes:
- pin tests;
- Temperature tests for sensations of cold or heat.
Tests are also carried out for the presence of deficits in the sense of taste, and data from the right and left sides of the maxillofacial apparatus are compared. The accuracy of the research should be no more than 1 mm.
Treatment
The following regimens are used for therapy:
- observation of the Patient at intervals of 2, 3, 4, 6 months;
- drug therapy;
- unscrewing, removing the implant;
- microsurgical intervention.
There is no strict protocol; tactics are determined individually in each case. But there are limitations to surgical intervention - it will be effective only in the first year, after which this method is considered ineffective.
Drug therapy includes:
- taking painkillers;
- use of hydrogen pump blockers;
- prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticosteroids are prescribed);
- therapy for sensory impairment.
If symptoms appear in the first 1.-1.5 days after installation of the implant, its removal may be indicated. During this period, the prognosis is favorable, but over a longer period of time, removing the artificial root will no longer bring a noticeable improvement. The reason is irreversible changes in nerve fibers.
Surgery is indicated in cases where all previous measures have not brought the expected effect. To do this, the doctor must determine the location of the NAS and evaluate sensitivity disorders. The effectiveness of the operation is influenced by the following factors:
- time between injury and surgery;
- severity, type of lesion;
- blood supply;
- Preparation;
- tension zone;
- Patient's age, health status.
Predictions and prevention
Treatment has an uncertain prognosis; with microsurgical intervention, the positive result is in the range of 55-82%. If the damage is severe, complete recovery does not occur with any treatment method. According to some experts, complications such as pain persist even after the intervention. It is also worth noting that the success of treatment depends entirely on the extent of the lesion. It is impossible to guarantee a high result in any situation, that is, the forecasts are uncertain.
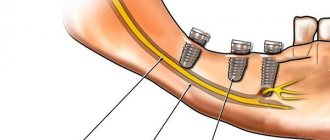
To avoid complications, prophylaxis is recommended. This is a mandatory full examination before the implantation procedure. The specialist will determine the exact location of the nerve, the topography of the nerve trunks and the maxillofacial system. This allows you to exclude the development of pathology and conduct conduction anesthesia correctly, without the risk of complications.
The main preventive measures include:
- competent selection of implantation system;
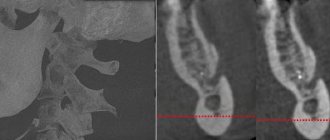
- diagnostics, including CT, production of a surgical template, computer modeling;
- planning the procedure for introducing an artificial root;
- determining the paths of nerve trunks, ensuring the distance between them and implants is not less than 2 mm;
- when drilling, it is necessary to avoid excessive force;
- When immersing a drill or implant, stoppers are used to limit the depth and ensure safety.
Treatment of damage to the mandibular nerve during implantation requires the doctor to have high qualifications and experience. But even under such conditions, the success rate does not exceed 82%. Some complications may remain, such as numbness or soreness.
Symptoms and stages of damage
The symptoms by which this complication can be recognized are as follows:
- numbness of parts of the head - tongue, lips, chin, cheeks, etc.;
- biting lips and tongue;
- choking while eating or drinking;
- profuse salivation.
All this creates a number of inconveniences for the patient: it makes it difficult to eat and talk, disrupts facial expressions, and also prevents men from shaving and women from applying makeup. The severity of this injury is determined by its degree: a minor one goes away on its own or with the help of drug treatment, a severe one leads to irreversible processes of nerve degeneration and is not curable. Damage to the mandibular nerve, the symptoms of which the patient observes, requires immediate consultation with a doctor - only a specialist will be able to determine its extent and provide timely assistance.
Dentists distinguish the following stages of this implantation complication:
- minor - neuropraxia;
- more severe, but partial damage - axonotmesis;
- a serious injury that leads to complete loss of sensitivity - neurotmesis.
Causes of neuralgic anomaly
Factors in the development of neurological disorders in the jaw area are both internal and external primary sources. Internal reasons include:
- frequent hypothermia;
- systematic damage to oral tissues by inflammatory processes;
- complications after medical and dental procedures;
- infections of the mouth and throat, sore throats, inflammation of lymphatic deposits;
- chronic diseases of the peritoneum, gastrointestinal tract, pelvis, sternum.
External provocateurs of the disease are:
- severe intoxication or chronic poisoning with industrial poisons;
- constant interaction with household chemical compounds;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- accumulation of slag, intoxicating substances that are not excreted by the liver;
- metabolic disorders as a result of diabetic syndrome;
- damage to the endocrine system.
A variety of allergic conditions, vegetative-vascular dystonia, chronic blood pressure disorders, hypotension, and hypovitaminosis can aggravate the situation.
Recovery and treatment
In the first case, self-recovery takes approximately 1 month; the help of doctors is not needed, since there is no anatomical damage. Symptoms of the second appear after a while - usually 6-8 weeks, so recovery can be painful and incomplete: it will take more than 2 months. In the third stage of damage to the mandibular nerve, treatment gives results only at the beginning and is performed surgically, since we are talking about degeneration with a violation of integrity. Loss of sensitivity, which is observed in a patient for more than 3 months, indicates a high probability of losing it forever. Damage to the mandibular nerve, the consequences of which is the lack of sensitivity of the nerve for a year, leads to irreversible changes. Only the professionalism and responsibility of the doctor, which is guaranteed by the specialists of our Implantmaster clinic, can protect the patient from such unpleasant injuries.
Author:
Facial neuritis - symptoms and treatment
Neuritis (neuropathy) is a disease of the nervous system, manifested in dysfunction of a nerve or a certain group of nerves.
In recent years, the Greek word “pathos”, which means “suffering”, has been used to denote syndromes of damage to the peripheral nervous system, and previously used terms, for example, “neuritis”, have been replaced by “neuropathy”, “sciatica” by “radiculopathy”, etc. d. If several nerves are inflamed, then it is polyneuropathy, if one nerve is inflamed, then it is mononeuritis. When the cause of inflammation of the nerves is, for example, diabetes, we talk about diabetic polyneuropathy, [1] and if there is an infection, then about infectious polyneuropathy (for example, herpes, diphtheria, etc.); [2] if the factor is hereditary, then it is hereditary polyneuropathy; if associated with a nutritional disorder, for example, alcohol abuse, then alcoholic polyneuropathy; if polyneuropathy appears against the background of reduced immunity, then it is idiopathic polyneuropathy, etc. [3]
Many types of peripheral neuropathy are often caused by exposure to toxic chemicals, malnutrition, injury and nerve compression, and also occur as a result of certain medications, such as those used to treat cancer and HIV/AIDS. [4]
As an example, consider such a common type of neuritis as neuritis of the facial nerve, also called Bell's palsy, the incidence of which is 23 people per 100 thousand, in all age groups, regardless of gender. The average age of patients is 40 years.
Most often, facial paralysis occurs as a result of local hypothermia. The source of infection is often chronic processes in the mouth, throat, and ear. In acute otitis media, nerve damage is caused by perineural edema of vascular origin. But more often, facial paralysis is caused by the herpes zoster virus in the area of the external auditory canal and eardrum. [5]
Facial neuritis develops as a result of:
- tumor processes in the cerebellopontine angle and posterior cranial fossa, temporal bone, parotid gland;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- acute, chronic otitis, mastoiditis;
- infections - syphilis, tuberculosis, Lyme disease, HIV infections, malaria, diphtheria, typhus, etc.;
- sarcoidosis, collagenosis, amyloidosis;
- Guillain–Barré syndrome;
- multiple sclerosis and many other diseases.
- Sometimes the development of neuropathy of the facial nerve is observed during pregnancy against the background of nephropathy.[6]