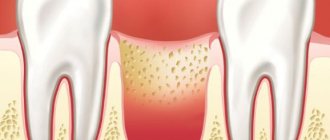
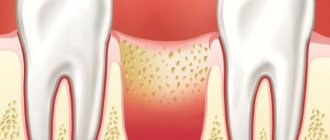
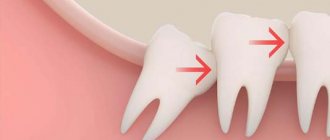
If the dental crown breaks almost at the very root, there is a risk of it becoming overgrown with gum tissue. A tooth can break for various reasons - mechanical damage, trauma, for example, a strong blow, carious process, etc. Small fragments gradually come out on their own, but the root remains inside the gum. Gum tissue grows, gradually covering the rest of the tooth.
An overgrown root may not bother the patient for a long time. As the pathological process develops, painful sensations appear, the gums become inflamed and swollen. Patients often complain of pain when chewing.
An overgrown root must be removed, as overgrowth is quite dangerous and can cause serious problems:
- Dental disorder.
- Damage to adjacent teeth.
- Inflammation of the gums.
If a crown breaks off, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The specialist will assess the complexity of the problem and select a treatment program.
If the tooth is overgrown and the pathological process has spread to the surrounding tissues, the patient will face a rather complicated operation with a long recovery period. The wound may take a long time to heal. A timely visit to the clinic will help avoid this.
What it is
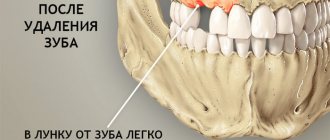
Alveolitis of the socket is an inflammatory disease that appears after a tooth has been removed and the socket becomes infected. In case of a severe operation, injury to the tooth socket or gum, the risk of possible complications increases. If we talk about the norm, then the hole should heal after 2 weeks maximum. If alveolitis appears, the healing process will take much longer.
The disease occurs if an infection gets into the wound. And to avoid complications, it is worth maintaining oral hygiene after tooth extraction.
Prevention
To prevent the mucous membrane from growing into the tooth hole, you need to take some preventive measures to avoid the formation of carious lesions:
- visit the dentist promptly when the first signs of caries appear;
- monitor oral hygiene;
- use a toothbrush of medium or low hardness;
- pay special attention to the selection of toothpaste;
- lead a healthy lifestyle: do not abuse smoking and alcohol;
- eat a balanced diet.
The growth of mucous membrane in a tooth hole is often provoked by carious processes, which lead to the development of various pathologies in the oral cavity. Surgery, as well as the use of drug therapy, will help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of mucous membrane ingrowth into a tooth hole.
Bibliography
- Barer G.M. – Periodontal diseases. Textbook, M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008.
- Maksimovsky Yu.M., Mitronin A.V. - Therapeutic dentistry - M.: Geotar-Media, 2012.
- Grigoryan A.S., Grudyanov A.I., Rabukhina N.A., Frolova O.A. — Periodontal diseases, M., 2004.
- O. O. Yanushevich, V. M. Grinin [and others] - Periodontal diseases. Modern view on clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects, M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2010.
- Ijndhe J. - Textbook of Clinical Periodontology. 1995. Copenhagen.
- Ivanov V.S., Urbanovich L.I., Berezhnoy V.P. — Inflammation of the dental pulp, M., Medicine, 1990.
- Stephen Cohen - Pathways of the Pulp - Mosby - 1980
- Ivanov V.S., Urbanovich L.I., Berezhnoy V.P. — Inflammation of the dental pulp, M., Medicine, 1990.
Find a clinic
Causes
After a tooth has been removed, alveolitis of the socket often occurs. Certain factors may contribute to this:
- the blood clot, which prevents infection from entering the wound, has been destroyed;
- bone fragments, stone, plaque got into the hole during the removal procedure;
- the specialist did not clean the hole very well from granulations and granules;
- sterility was compromised;
- the removal was very traumatic;
- the patient did not follow all the doctor’s instructions;
- The patient's body is exhausted, immunity is quite low.
When a regular tooth or wisdom tooth has been removed, you should not rinse your mouth too vigorously, as there is a risk that the blood clot located in the socket will be washed out. The result is that microbes get inside and provoke an inflammatory process.
How to prevent a relapse?
Any treatment, including surgery, unfortunately, does not exclude recurrences of the disease.
Simple measures taken by the patient himself will help minimize their risk. Necessary:
- Give up some habits. Namely, stop smoking, minimize alcohol, give up soda. Dishes and drinks should be consumed warm. Too hot or cold promotes chemical/thermal damage and usually relapse.
- Brush your teeth with soft bristles (low or medium hardness) and Sensitive toothpastes for painfully sensitive teeth. Initially, after treatment, it is better to use baby hygiene products that are mild and without aggressive components.
- Visit the dental office regularly to monitor the process of regeneration of operated tissues and prevent any unhealthy changes. It is necessary to come to the doctor for examination every 1-1.5 months.
Symptoms
Already 3 days after removal, symptoms of socket alveolitis can be observed:
- severe pain appears in the area where the tooth was pulled;
- pain spreads to areas that are located nearby;
- the body temperature rises, the patient feels unwell and shudders;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- the gums become red, swollen, inflamed;
- no blood clot;
- there is a specific gray coating;
- the lymph nodes under the jaws increase in size;
- there is purulent exudate.
Incorrect growth of wisdom teeth
70% of people who turn to the clinic for help with the eruption of a wisdom tooth are diagnosed with its incorrect location. Often the concept implies a horizontal tilt, excessive grinding into the seven, or the growth of the eighth tooth into the root part of the neighboring one.
- The growth of a tooth under the gum harms the rest. The sooner a person shows interest and finds out exactly how even an unerupted wisdom tooth is located in the jaw, the easier it will be to eliminate the problem when it is discovered. It happens that the figure eight harms the healthy seventh tooth, while still hidden under the gum. While growing, the third molar seems to be trying to push out the neighboring one or rests against its walls, causing damage. It is better to remove such a wisdom tooth in advance, otherwise the risk of damage to a healthy molar increases. Later, you will have to get rid of both the third and second molars, which have lost functionality.
- A similar situation develops when a wisdom tooth erupts at an angle. As it continues to grow, it will begin to prop up the seven. A particularly alarming picture emerges if there is a lack of space on the jaw. Then the dentition loses its alignment. More often this problem occurs in women.
- The recumbent position of a wisdom tooth is also considered unfavorable , especially when the tooth is turned towards the adjacent seventh tooth. A person sometimes argues that preserving his own, albeit pathologically growing, tooth may be useful in the future, when the time comes to install a crown on the tooth. And the recumbent tooth takes up a lot of space in the row, shifting the others and causing their uneven arrangement.
- The fit of the figure eight to the second molar , even with an anatomically correct location, is also not considered a good sign. Excessive crowding of teeth in the depths of the oral cavity almost always causes the development of caries.
- At first glance, the direction of the wisdom tooth towards the cheek However, this is an imaginary impression. A tooth growing sideways regularly causes microdamage to the vulnerable mucous membrane of the cheek. Often leads to gum inflammation and pericoronitis. The seriousness of the situation is enhanced by the fact that the mucous membrane of the cheeks is not rich in pain receptors, so a person sometimes does not even feel the harm being caused.
- As a result, the cheek is damaged from the inside, and the wounded area becomes a gateway for infection and becomes severely inflamed. Gradually, the cells of the mucosa, under the pressure of what is happening, are transformed and replaced by foreign, denser tissue. This indicates the emergence of neoplasms at the site of permanent injury - benign or carcinogenic.
Dentists recommend removing wisdom teeth that are positioned incorrectly in advance. This information is available to the patient after undergoing an X-ray examination. The picture immediately shows how the figure eight is located inside the gum; it becomes possible to predict the result when it erupts.
Ultrasonic removal of wisdom teeth using a piezotome
You don’t even need to wait for the mentioned process to begin; the modern level of development of dentistry allows the doctor to intervene while the tooth is “sleeping” and perform an operation to extract it in adolescence. In youth, such manipulation is tolerated much easier, and tissue regeneration occurs faster and more completely. And by the time you turn twenty-five, the undesirable scenario of the eruption of a crooked wisdom tooth will be a thing of the past.
Make an appointment with surgeons at Dr. Lopaeva’s clinic
Make an appointment
Or call +7(985)532-21-01
Diagnostics
Such a diagnosis is made only by a doctor when he examines the oral cavity. You can't diagnose yourself. After all, alveolitis of the socket is a serious disease.
If it is not treated promptly, serious complications are possible, including blood poisoning. If there is no blood clot at the place where the tooth was pulled out, then this indicates alveolitis.
Features of treatment of fistula with concomitant diseases
Are there any particularities in the treatment of fistula if the process is accompanied by other diseases in the oral cavity, such as periodontitis? No, in fact there is no particular connection. Periodontitis is an inflammation of the periodontium of a tooth, while periodontitis is an inflammation of the apical tissues surrounding the tooth. Of course, in some very severe forms, periodontitis can lead to the formation of fistulas, but often these are all unrelated, and one should be treated separately. First, cure periodontitis, if the tooth is healthy, if it does not wobble and can be preserved, and then treat periodontitis.
How long does it take for a patient to recover after fistula treatment?
The treatment of chronic periodontitis itself is not quick, since the patient must first open the tooth canal, clean it, disinfect it with special antimicrobial drugs, and only after that the tooth canal is sealed. If we talk about rehabilitation, when the results are visible, the fistula “goes away” almost immediately, and the bone takes a long time to recover.
If we talk about the surgical method
treatment of periodontitis, when the apical part of the tooth is opened according to the type of resection, but the apical part of the root is polished, the mucous membrane is restored quite quickly - this is
3-5 days
.
Solution
Such a diagnosis must be treated in time, then after a few days the person feels better. The process includes:
- removal of remnants of a blood clot, this is done under local anesthesia;
- processing the hole and its walls with a special tool;
- treating the hole with an antiseptic solution so that the infection does not go further;
- prescription of antibiotics;
- the use of drugs that relieve pain;
- rinsing the mouth, for this you should take antiseptic solutions;
- physiotherapeutic procedures that promote rapid wound healing.
In the absence of timely treatment, osteomyelitis of the jaw bone may occur.
Medicines prescribed by specialists
When the patient has visited the dental center and had a professional treatment of the hole, he must start taking medications to cure the alveolitis. Drugs that have proven their effectiveness include:
- Hexicon. This is an antiseptic drug that is taken topically. You can use it to rinse, make mouth baths, and applications;
- Corsodil. An antiseptic medicine that has a bactericidal effect. It is also used to disinfect the mouth. Corsodil can be used to create applications, irrigation, rinsing;
- Stomatidin. An antiseptic that prevents infection from spreading. You can make applications with it, as well as rinse your mouth;
- Chlorhexidine. Antiseptic, which is known for its wide spectrum of action. It is used to treat the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and treat purulent wounds;
- Eludril. It has an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect.
IMPORTANT! Professional dentists prescribe their own medication to each patient in accordance with the clinical picture and characteristics of the body, therefore it is not recommended to self-medicate so as not to aggravate the condition.
Recommendations after fistula treatment
After treatment of the fistula, no special recommendations need to be followed. If the treatment was related to surgery and was carried out jointly with a therapist, then yes:
- baths with antimicrobial agents must be done carefully,
- eat soft food
- Do not put your tongue into the area of the healing wound.
If we are simply talking about therapeutic treatment, then there are no special restrictions at all.
How to avoid the appearance of a fistula on the gum
Are there any prevention methods to avoid the development of periodontitis? Of course, you can avoid the appearance of a fistula on the gums, and the prevention of these fistulas is a regular visit to the dentist in order to avoid these fistulas, not to lead to chronic periodontitis, and to keep your teeth healthy, beautiful and functional.
Therefore, once every six months
You need to come to the dentist for an examination and early diagnosis of any diseases, diagnosis of caries. It is better to cure caries at an early stage than to treat canals later, or to re-treat canals that can lead to the formation of a sinus tract and a fistula on the gum.
Can a fistula on the gum go away on its own?
Yes, it can only go away on its own if the causative tooth is removed, then it will go away on its own. It's a joke! In fact, the fistula cannot go away on its own as long as there is a chronic process that occurs in the gums, in the hard tissues of the upper or lower jaw. This chronic process is ongoing, and through this fistula there is an outflow, all purulent masses are drained along with exudate. And all this goes into the body, the body is certainly poisoned. There is a constant infection - these are staphylococci, which can then provoke all sorts of sore throats and various other diseases in the oral cavity. This is unhealthy flora that is constantly in your mouth, which constantly oozes, flows out and poisons you from the inside.
The fistula itself cannot go away
. It must be treated either therapeutically or surgically.