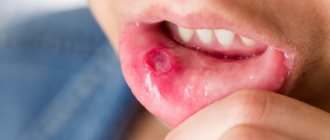
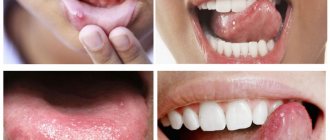
This article describes all the possible causes of the appearance of bubbles in the mouth on the mucous membrane and effective methods of treating the resulting pathology.
The first sign that allows you to suspect the occurrence of a formation in the mouth is the sensation of a foreign object.
Depending on its location, the bubble will cause various symptoms:
- Pain when chewing food if the bubble is located on the gums or tongue.
- Pain when talking or smiling occurs when a bubble appears on the inner surface of the lips.
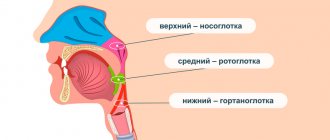
- Pain and the sensation of a fish bone stuck in the throat occurs if the bubble is located at the root of the tongue, in the oropharynx or in the upper part of the larynx.
If you look at the neoplasm, you can see and evaluate the nature of the changes in the tissue:
- An elevation above the level of the mucosa in the form of a tubercle.
- Redness around the raised area.
- Swelling of the tissue around the elevation.
The 3 above signs are often signs of an inflammatory process and require careful monitoring of the course of the disease in order to promptly and correctly prescribe treatment.
It is worth noting that the bubble can be not only inflammatory in nature. If the formation of a vesicle and its presence are not accompanied by pain, redness, or swelling of the mucosal tissue, then the cause of the vesicle is not an inflammatory process, which narrows the range of possible causes and radically changes the direction of treatment.
In this case, you need to contact a dermatologist who will assess your health. In this case, treating yourself is dangerous to your health.
Various ways to treat this disease
Traditional medicine
There is no universal treatment for mouth blisters. First, a diagnosis is made, and then a specialist prescribes treatment specific to the identified disease. But the focus of treatment of any disease is associated with the complete destruction of the provoking factor.
- For aphthous ulcers, the use of gels and rinsing the mouth with Cholisal and Chlorphyllipt is indicated.
Healing, antiviral and antiseptics are prescribed as local drugs. The acute course of the disease is accompanied by treatment with antibiotics. - Candidiasis is a fungal disease, therefore the treatment regimen is based on antifungal drugs.
The most popular drugs are Flucanazole, Polizhenax, Nystatin, Pimafucin. Blisters in the mouth are treated with anti-inflammatory ointments and solutions. - Herpes is a common disease.
Treatment should begin immediately after the onset of initial symptoms. Antiviral drugs, painkillers and anesthetics are shown here. - Treatment for pemphigus is fundamentally different from other primary causes of blisters in the mouth. The doctor prescribes corticosteroid hormonal drugs, treatment takes place in a hospital.
After the end of the period, when new outbreaks of rashes appear, maintenance doses of drugs are prescribed.For a speedy recovery, rinsing the mouth with Miramistin and using pain-relieving ointments and gels are allowed. Multivitamin complexes are prescribed to normalize the functioning of the patient's immune system.
Treatment of any disease should only take place under the supervision of a physician. It is not recommended to self-medicate or treat exclusively with folk remedies.
Diagnosis of the disease is the primary task of the patient and the doctor. Treatment depends on the identified disease and lasts two to three weeks.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods are good for relieving inflammation and swelling, having antimicrobial properties.
- Aloe or Kalanchoe is an anti-inflammatory agent. Used as lotions. A leaf is cut from the plant, cleaned, and the pulp is applied to the wound.
- Herbal rinse. Chamomile and rose hips disinfect the oral cavity and reduce inflammation.
- Propolis lotions. Soak cotton wool or a cotton pad with liquid propolis and apply it to the site of inflammation.
Before using traditional medicine, you should consult your doctor.
Diagnosis of diseases accompanied by the formation of lumps in the mouth
Tumors have appeared in the mouth, and the question is, which doctor should I contact? This symptom is a prerequisite for visiting the dentist. To diagnose the disease, the doctor will first conduct a visual examination and palpation, and collect an anamnesis. A puncture is taken from the resulting lump and a bacteriological examination is carried out, which makes it possible to determine the cause of its occurrence.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor determines the need to use other diagnostic methods:
- general tests;
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound;
- biopsy.
If the cause of the formation of a lump on the upper palate is beyond the scope of the dentist’s competence, the patient is prescribed consultations with other specialists (pediatrician, therapist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, hepatologist). Only after making a diagnosis will the doctor determine how to treat the disease.
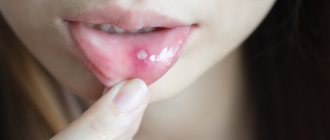
Blood blisters
The cheeks, due to their vital importance, are well protected, this is how it happened evolutionarily. Therefore, the muscle and mucous tissue of the cheeks are well innervated and richly vascularized, that is, they are supplied with blood
However, it also happens that this seemingly useful process becomes a problem. Many people are faced with the fact that a blood ball appears in the mouth on the mucous membrane of the cheek. Often such formation does not foreshadow anything dangerous. A blood bubble that forms in the mouth on the cheek is just the result of a mechanical injury. Most likely, the cheek area was bitten by the teeth while eating or talking. Since the oral cavity is a complex biological system in which a huge number of microorganisms live, it is natural that when such a microtrauma occurs, it becomes contaminated with various kinds of pathogens. As a result, a whole cascade of body responses is activated:
- since the pathogen is a foreign substance in the inner layer of the cheek, the immune system is immediately activated. Leukocytes, monocytes and macrophages quickly arrive at the site of infection, capture the pathogen and destroy it, and often die themselves;
- due to the death of immune cells that have absorbed pathogenic microflora, their internal contents are released into the environment. These biologically active substances are chemotaxis factors, that is, they signal to other cells, as a result of which substances such as histamine, serotonin, bradykinin - inflammatory mediators - are released in the area of inflammation;
- inflammatory mediators cause spasm of the circulatory system, which makes blood flow difficult; and after some time the vessels relax, and all the blood that has accumulated at the site of narrowing immediately flows into the source of inflammation. Since such blood flows at high speed and under high pressure, it forms a detachment of the mucous membrane - a bubble - and a blood ball appears in the mouth.
Thus, the blood blisters that form in the mouth are just part of the body's defense mechanism, which has been formed over centuries. When such a pathology appears, you should not panic too much. Regular blood blisters reorganize on their own within 3-4 days. But if the blood bubble does not self-destruct within a week, consult a dentist to rule out the diagnosis of unwanted neoplasms. The doctor will not only prescribe a pain reliever (since the appearance of a neoplasm on the mucous membrane is sometimes accompanied by pain), but will also take a sample of the epithelium for histology analysis.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of developing pathologies in the oral cavity, you should follow a number of recommendations:
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- normalize nutrition - do not eat hot, salty and spicy foods, introduce fermented milk and plant products into the diet;
- carefully and regularly observe oral hygiene;
- start treatment of any pathologies in a timely manner;
- Take vitamin complexes periodically (after consultation with your doctor).
If you experience the slightest discomfort in the palate, you should see a dentist. Paying attention to your health prevents the development of complications.
Features of the pathology
A hematoma is a hemorrhage in the submucosal layer, so it will look like a bloody bubble, a burgundy or bright red ball. The blood inside it may be liquid or clotted. Hematomas that appear in the submucosal layer of the oral cavity are called superficial submucosal.
In addition, the hematoma cavity may be filled with colorless serum fluid secreted by the serous membranes. Such a neoplasm forms without damage to blood vessels, as evidenced by the absence of blood in the hematoma cavity. The healing period of the hematoma in this case will be shorter.
A hematoma in the mouth, due to the sensitivity of the soft tissues, can cause significant discomfort. But as a rule, the pain goes away 1-3 days after the bloody blister appears.
Hematomas can be localized on the palate, tongue, cheeks and gums.
Angioma
It is a benign formation, which in most cases is a congenital pathology in children. It consists of blood vessels and is dark red in color. Sometimes it looks like a small ball on a leg. Lymphangioma, formed from lymphatic vessels, most often appears on the soft palate. It looks like a small bump with a bubbly surface. First, the tumor grows inside, then a swelling appears that hurts.
The choice of treatment method depends on the type of vessels. The angioma is removed or reduced by sclerotherapy, alcohol injection, or radiation therapy. If there is a risk of severe swelling, the formation is excised with a scalpel. The ball-shaped angioma is removed using a galvanoacoustic loop.
Factors that can provoke the development of problems in an adult
Blisters on the gums of an adult can appear for many reasons. Such a problem can manifest itself not only due to dental diseases, but also as a complication of certain infectious pathologies.
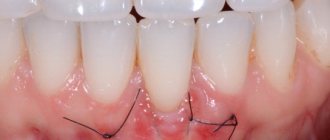
- Blisters on the gum tissue can develop due to inflammation near the tooth. The damage causes caries, which destroys tooth tissue. If treatment is not started on time, periodontitis may form, and over time, complications in the form of an inflammatory process will appear.
- If the dentist does not install the denture correctly, mechanical damage may occur on the mucous membranes in the mouth, where microbes enter. This becomes the source of small blisters on the gums.
- If a person develops herpes sore throat, the infection can travel through the bloodstream to the mouth. As a result, the formation of multiple purulent blisters in the oral cavity is noted, due to which the patient feels pain and discomfort while eating.
- A white blister on the gum can develop with shingles. In this case, the soft tissues near the teeth become swollen and hyperemic (the blood vessels overflow).
- A deep wen containing adipose tissue may appear in the form of a bubble in the oral cavity. As a rule, such a neoplasm does not cause pain, but it can increase in size and bother you while eating.
If a blister appears on the gum, you should immediately seek help from a dental clinic for examination and diagnosis. If the cause of the problem lies in diseases of an infectious nature, you may need to consult not only a dentist, but also other specialists.
Causes
The most common reason why blood blisters appear in the mouth is an accidental injury to the mucous membrane. There are three possible damage options:
Mechanical
A blood blister is formed when accidentally biting while talking or eating. The mucous membrane can also be injured:
- hard foods: candies, crackers, bones;
- broken, chipped teeth or incorrectly made dental structures: braces, bridges, crowns, dentures;
- during hygiene procedures - tissues are damaged due to careless movements while brushing teeth with a brush or toothpick.
In addition, you can bite your cheek during an epileptic seizure, during sleep, or during severe excitement. In these cases, the patient may not remember the moment the injury occurred.
A blister may appear after biting with your teeth.
Important! Less commonly, a bloody blister can form due to dental surgery. It is associated with careless actions of the doctor during sanitation of the oral cavity.
Thermal
A blister on the cheek can form when the mucous membrane is burned by hot drinks, dishes, when inhaling steam or accidentally touching heated cutlery. In this case, the appearance of a bubble is accompanied by a burning sensation, swelling, redness and slight pain.
Chemical
The cause is tissue damage by aggressive chemical elements: accidental ingestion or inhalation of vapors at home or at work may cause bubbles to appear. As with thermal injury, mucosal hyperemia and painful sensations are observed.
Important! Provoking factors for the appearance of blisters in the oral cavity include smoking, abuse of strong alcohol, and hypovitaminosis. It is believed that under the influence of harmful elements and a lack of vitamins, the walls of blood vessels become thinner. This provokes hemorrhage and the formation of hematomas.
Traumatic causes are typical for single bloody or serous formations. If bubbles appear regularly, there are many of them, they are localized not only on the cheek, but also on the tongue, gums, lips, and are accompanied by other symptoms (plaque, itching, unpleasant odor) - this indicates diseases of the oral cavity or systemic pathologies. Among these factors are:
- stomatitis;
- syphilis in the mouth;
- tuberculosis;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- hemangioma;
- vascular tumor;
- pemphigus.
Provoking factors for the appearance of blisters in the oral cavity include smoking, abuse of strong alcohol, and hypovitaminosis.
Characteristics of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
The mucous membrane protects the entire body from the negative influence of the environment, from harmful microorganisms, various types of pollution, and also has a fairly high level of regeneration.
If blood blisters regularly appear on the oral mucosa, then you should take this signal seriously and take action. A bloody ball in the mouth is a hematoma (bruise), which is characterized by the accumulation of blood in a certain place in the oral cavity. The appearance of bloody blisters is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs due to trauma to the capillaries and thin vessels of the mucous membrane.
A blister on the mucous membrane may contain clear serous fluid without the presence of blood. This means that the vessels were not damaged and the resulting wound is superficial. Such blisters on the mucous membrane heal much faster. The presence of blood in the bladder indicates a deep injury and a longer period of healing and blood resorption.
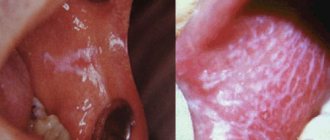
What do blisters look like on the roof of your mouth?
Outwardly, it looks like several transparent or white bubbles or spots that appear on the palate and other areas of the oral mucosa. Depending on the reason for their appearance, each bubble may be surrounded by a small roll of hyperemia.
Most often, such rashes are grouped in certain areas close to each other.
Symptoms and causes
The reasons for the appearance of a blister on the roof of the mouth vary greatly: the same symptoms in children and adults may indicate completely different infections and viruses. Remember that in children they can appear due to very sharp teeth or malocclusion. Let's look at the main reasons for their appearance.
Thermal burns
When drinking hot water or food (especially in children), burns to the oral mucosa may occur. There are 3 stages of damage:
- tissue inflammation;
- the appearance of transparent blisters on the palate;
- tissue death and rejection.
Mechanical injuries
There are people who like to chew nuts, hard sugar, etc., since the mechanism of blistering is similar to the formation of calluses (when the skin is rubbed).
Follicular tonsillitis
The most dangerous type of sore throat, accompanied by inflammation of the tonsils. During the pathology process, follicles (small lymph nodes) develop in the form of transparent blisters.
They are easily identified during a routine examination of the oral cavity using a mirror. As a rule, follicular tonsillitis is acute and is characterized by the following symptoms: severe headache, intoxication of the body, fever and cutting pain in the throat.
Dühring's disease
An autoimmune pathology that develops as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
This video explains what symptoms you should see a doctor for:
Herpetic stomatitis
An acute pathology affecting the oral cavity, during which blisters appear in large numbers on its surface. The cause of this condition is the herpes virus.
Herpangina
Inflammation of the palate and back of the throat. It is characterized by the appearance of a large number of transparent blisters, more reminiscent of follicles and can be caused by the Coxsackie virus, staphylococcus or streptococcus.
This pathology is contagious and has the following symptoms: high fever, sore throat and abdominal pain, fever, intoxication and inflammation of the maxillary sinus.
Abscess and pharyngitis
These pathologies can provoke the formation of blisters, which can persist for a month even after complete recovery (depending on the state of the immune system).
Vesical vascular syndrome
Most often found in people with heart disease and looks like a large red blister. The reason for its appearance is an increase in blood pressure.
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome
A childhood disease caused by the Coxsackie virus. Its symptoms are very easy to identify: the presence of blisters on the roof of the mouth and on the limbs, fever, pain and dehydration.
Pemphigus or pemphigus
A dangerous pathology, most often observed in older people and has several varieties: vulgar, leaf-shaped, vegetative and erythematous.
The main symptoms of pemphigus are: the formation of complete blisters, a cheesy coating, deterioration in health and bad breath.
Exudative erythema (multiform)
It is characterized by a long course with repeated relapses. Main symptoms: increased body temperature, general malaise, burning in the mouth, body aches, the formation of blisters that cause pain while eating and talking.
Congenital epidermolysis
This pathology is detected from the very birth of a person and does not leave him until the end of his life. It has a simple and dystrophic form, and can also be benign or malignant.
In addition, the formation of blisters on the palate may be signs of the following pathologies:
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- heart and kidney diseases;
- hypovitaminosis;
- cancer;
- immunodeficiency;
- respiratory diseases;
- chicken pox;
- reaction to chemotherapy;
- syphilis;
- Saturnisms.
Thus, the presence of blisters on the palate is a sign of dangerous pathologies or poisoning, therefore, in order to completely cure them, it is necessary to establish a correct diagnosis and eliminate the root cause of their appearance.
Drug treatment
The existence of a huge number of treatment methods does not mean that it is possible to quickly and easily eliminate both the blister itself and the pathology that caused it.
The main treatment should be comprehensive and should be prescribed by a doctor. Medicines (sprays and ointments) purchased at the pharmacy help relieve pain, burning and itching. This especially applies to drugs that contain an antibiotic:
rinse your mouth with an antibiotic solution; Apply the required amount of ointment (Vishnevsky, Tetracycline or Levomikol) to a cotton swab; Carefully treat the blister and the skin around it with ointment; wait until the product is absorbed and dry (leave your mouth open and tilt your head back slightly); The blister should be treated every 5 hours, after consulting with your doctor; can be treated with iodine, hydrogen peroxide or potassium permanganate (a very weak solution); Irrigating the mouth with Chlorhexidine and rinsing with Iodinol will help get rid of the infection; pharmaceutical tablets (for resorption): Gramidin, Septolette, etc. help get rid of infection in the oral cavity. However, they should be used very carefully so as not to damage the palate
If blisters appear (without headache, cough or fever), you must urgently contact a specialist to diagnose and determine the exact cause of the disease
However, they should be used very carefully so as not to damage the palate. If blisters appear (without headache, cough or fever), you must urgently contact a specialist to diagnose and determine the exact cause of the disease.
Professional treatment includes:
- rinsing with antiseptics;
- use of anti-inflammatory drugs;
- anesthesia;
- antibacterial therapy;
- use of antiviral and antifungal drugs;
- treatment with antihistamines (for allergies).
In addition to prescribed medications, the patient must follow certain medical recommendations.
Treatment with folk remedies
The use of folk remedies to treat blisters on the roof of the mouth perfectly complements medication treatment. Let's look at the most effective of them:
- Soda solution: 1 tsp. dissolve soda in 1 tbsp. water (warm). This remedy relieves inflammation and has an antimicrobial effect.
- A decoction of oak bark will help remove the infection and also relieve redness: 1 tbsp. l. bark pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, put on fire and simmer over low heat for about half an hour, then cool. Rinse your mouth with the resulting decoction 5-6 times a day.
- Aloe compresses: remove the skin from 1 leaf of the plant and knead thoroughly, wrap the pulp in gauze and apply to the blister for 20 minutes.
- A decoction of calendula helps relieve itching from a blister on the roof of your mouth and is also an excellent antiseptic. Use for rinsing.
- Goldenseal infusion: 2 tsp. plants pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 2 hours and use for rinsing.
- Decoctions of rose hips, propolis and chamomile provide an excellent anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, they are all absolutely safe.
To treat blisters, you should stop the underlying pathology, and not hope that the disease will go away on its own. If treatment is not started in time, the situation will only get worse.
Blood ball in the mouth: what is it and what to do with it
The oral mucosa is an important component of the human body, which consists of different tissues that perform protective, absorption and excretory functions. It is involved in thermoregulation and is responsible for the perception of the taste of food. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the oral mucosa and, if there are changes in the integrity of the epithelium, consult a doctor.
Characteristics of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
The mucous membrane protects the entire body from the negative influence of the environment, from harmful microorganisms, various types of pollution, and also has a fairly high level of regeneration. If blood blisters regularly appear on the oral mucosa, then you should take this signal seriously and take action.
A bloody ball in the mouth is a hematoma (bruise), which is characterized by the accumulation of blood in a certain place in the oral cavity. The appearance of bloody blisters is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs as a result of trauma to the capillaries and thin vessels of the mucous membrane.
A blister on the mucous membrane may contain clear serous fluid without the presence of blood. This means that the vessels were not damaged and the resulting wound is superficial. Such blisters on the mucous membrane heal much faster. The presence of blood in the bladder indicates a deep injury and a longer period of healing and blood resorption.
The main causes of a blood blister
The general condition and integrity of the oral mucosa usually indicates the level of health of the body. Often, by examining the appearance of the oral mucosa and blisters, the doctor makes a final diagnosis.
After all, the symptoms of most infectious, bacterial, chronic, and acute processes that occur in the body are associated with changes in the integrity and color of the oral mucosa.
Therefore, it is important to understand the main reasons that cause blood blisters to appear in the mouth. Multiple blood blisters on the oral mucosa occur with stomatitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, disorders of the endocrine system
Multiple blood blisters on the oral mucosa occur with stomatitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system.
The cause of the sudden appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth is damage to the mucous membrane.
There are the following types of injuries to the oral cavity:
- mechanical injury.
The cause may be various objects, solid food, biting the cheek; - chemical injury.
It occurs due to the consumption of spicy, salty foods, and exposure to chemicals on the mucous membrane. This irritates the delicate oral mucosa and causes injury; - thermal injuries.
Their appearance is provoked by too cold or hot food or drinks.
The mechanism of formation of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
Bloody blisters in the mouth in most cases are not life-threatening. They are formed as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. When microtrauma occurs, harmful microorganisms attack the damaged area.
After this, a number of responses are activated in the human body:
- The immune system is activated. Monocytes and leukocytes, as well as macrophages, instantly arrive at the damaged area, attacking the harmful pathogen and quickly destroying it.
- Immune cells die.
This is a signal for other cells and substances are released in the affected area that are mediators of inflammation of the mucous membrane - serotonin, histamine and bradykinin. - These substances cause a strong spasm of the circulatory system and the outflow of blood is hampered.
After the spasm is relieved, all accumulated blood immediately flows to the site of inflammation. It moves at high speed and under pressure. A detachment of the mucous membrane occurs in the mouth, and a bloody blister appears.
Treatment of bloody blisters in the mouth
A blood blister in the mouth is only part of the body’s defense reaction and goes away on its own within a week.
If this does not happen, then you should consult a doctor to rule out serious diseases of the body and neoplasms.
He will be able to make an accurate diagnosis after a thorough examination, studying the data of clinical tests and histology. After this, the doctor will prescribe the correct treatment.
If there are red spots on the sky - this is stomatitis
With stomatitis, the spots that appear on the palate are located separately from each other or merge to form islands. Their color can range from pale pink to bright red.
Experts distinguish several types of the disease:
- viral;
- herpetic;
- candida;
- aphthous;
- bacterial;
- traumatic.
In addition to redness, the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- swelling of soft tissues;
- nervousness due to pain in the mouth;
- refusal to eat;
- in some cases, an increase in temperature.
Drug treatment involves the use of topical and oral drugs:
- Famciclovir – taken orally, daily dose – 1500 mg;
- Valacyclovir - take the drug 2 times a day, 2000 mg;
- Miramistin - used for rinsing the mouth 4 times a day, the duration of one treatment is at least 1 minute;
- Amiksin is a means to strengthen the immune system, prevents relapses, and is taken according to the schedule.
To enhance the effect of drug treatment, it is allowed to use rinsing compositions prepared according to traditional recipes:
- decoctions based on chamomile, calendula and other plants that have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- carrot juice diluted half with warm water;
- horseradish root juice mixed with an equal amount of water;
- white cabbage juice, diluted with a small amount of water;
- linden infusion (200 ml), mixed with soda (1/2 tsp).
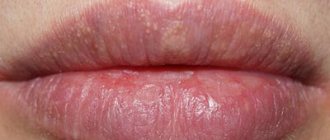
Why did a transparent blister appear on the sky?
A bubble that appears on the mucous membrane of the palate may, in essence, be a manifestation of:
- Received injury, in particular chemical or thermal burns. If very hot liquid or chemicals come into contact with the palate, a watery blister may appear. It is extremely rare that a bubble on the roof of the mouth appears due to careless consumption of food - hard nuts, etc., as well as due to injury from dental materials. Such a tumor causes significant pain and can easily burst, leaving behind painful erosion.
- Cyst formation. In this case, the neoplasm does not cause painful sensations, but they can occur when injured.
- A simple callus. This problem is often observed in young children during teething. If your baby constantly puts his fingers or teether in his mouth, he can rub the delicate mucous membrane with it, which can lead to the formation of a callus.
- Herpetic sore throat. This is a viral disease in which the tonsils (tonsils) become inflamed, and the roof of the mouth and back of the throat become covered with blisters (as with chickenpox or herpes). The blisters subsequently burst, leaving behind erosions, which in turn heal without a trace. The development of herpetic sore throat is usually accompanied by severe sore throat and an increase in temperature.
Vesical vascular syndrome. This is a fairly rare condition, which is manifested by the appearance of blisters with a dense covering and hemorrhagic (bloody) contents on the soft palate and cheeks. They are present on the mucous membranes for several days, then open up and form erosions or disappear without a trace. The appearance of this syndrome is associated with disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, namely with increased permeability and increased fragility of capillaries in the mucous membranes. Past injuries can contribute to the formation of blisters. Wen or lipoma. This is the name for a benign tumor that does not cause pain, but can cause significant discomfort - the patient constantly feels a foreign body, a “sticking piece”.
If the appearance of bubbles in the mouth on the mucous membrane is accompanied by an increase in temperature, it is better to call a doctor at home, as there is a risk of the patient being potentially infectious to others.
Treatment
Usually a bloody blister does not require specific treatment. Since it is a natural response of the immune system to external stimuli, the formation goes away on its own within a few days.
Important! If the resulting blister did not appear due to injury, often recurs, or multiple growths are noted, a doctor’s consultation is required to rule out possible pathologies.
In some cases, therapy for hematoma is indicated. It is required for large bladder size, pain and discomfort. When treating, the dentist takes into account the following factors:
- size of education;
- time and factor of appearance;
- location of the bubble: on the cheek, tongue, lip, gums;
- whether there are other blisters or sores.
If the bubble does not go away, contact your dentist.
Treatment of a bloody ball consists of a puncture, ensuring the outflow of accumulated fluid and antiseptic treatment. Rarely, surgical excision of tissue is required to remove the lesion.
When blisters appear due to chipped teeth or incorrect dental work, the defects must be corrected. Otherwise, the cheek will be constantly injured.
Important! If the doctor suspects that the bubbles have formed not due to injuries, but as a consequence of systemic pathologies, the patient will be prescribed a comprehensive examination. Further therapy will be based on test results.
According to indications, multivitamin complexes with a high content of vitamins C, K, E, A, and group B can be prescribed. This will strengthen the walls of blood vessels and prevent hemorrhages.
After surgery, the patient is recommended to:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol for a while;
- do not eat food that irritates the mucous membranes: salty, smoked, spicy, pickled, rough;
- treat the oral cavity with medicinal solutions and herbal infusions with an antiseptic and wound-healing effect: chlorhexidine, miraministin, soda-saline solution, decoctions of chamomile, oak bark, sage.
To be safe from complications, rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution for several days.
What can and cannot be done if a blister appears on the cheek?
The formation of a blood globule is always a cause for concern. However, there is no need to panic. First of all, it is necessary to establish the reason why it could appear: whether there were injuries, whether hot or irritating food was consumed. Further actions are aimed at relieving inflammation and disinfection:
- The mouth is treated with antiseptic drugs.
- Rinsing with a solution of baking soda and salt will help relieve inflammation.
- Provoking factors are excluded: smoking, alcohol, consumption of salty, sour, spicy, pickled foods.
If after a few days the ball does not shrink and signs of healing are not visible, you should consult a doctor: dentist or therapist.
It is strictly forbidden to pierce the formation yourself. This can lead to infection or even greater injury.
Bloody blisters in the mouth most often appear as a result of injuries: biting, burns, chemical injuries. Less common factors are diseases of the oral cavity and systemic pathologies. As a rule, no special treatment is required. If the formation interferes, the dentist pierces it and prescribes antiseptic treatment.
How to treat a blood bladder?
General therapy
Depending on the type of pathological condition that caused the appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth, treatment can be carried out with the following medications:
- For candidal stomatitis, antifungal drugs such as Levorin and Nystanin are effective.
- For diseases of viral etiology, the treatment regimen includes Viferon, Amoxicillin, Tsiprolet, Azithromycin.
- To combat gingivostomatitis, where it is expected to remove areas affected by necrosis, antiallergic medications, antibacterial agents, and vitamin complexes are used.
- In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents. If there is pain, the doctor may prescribe Cholisal, Ketoprofen, Voltaren, Lornoxicam, Kamistad.
- To eliminate tuberculosis, appropriate chemotherapy is prescribed, which includes Rifampicin, Ioniazid, Pyrazinamide.
Local therapy
To speed up the healing process, regularly rinse with antiseptic agents. Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Stomatidine, Betadine, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide solution, Iodoform, Chlorophyllipt show good results.
Treatment of the affected tongue with disinfectant solutions should be performed twice a day, at a minimum, but before that you must brush your teeth and remove any remaining food.
It is advisable to eat food after the procedures within 30-60 minutes, which will significantly increase their effectiveness.
Traditional methods
Aloe or Kalanchoe juice has a wound healing effect
To alleviate the condition, it is good to use healing decoctions based on chamomile, sage, yarrow, St. John's wort, and viburnum fruits.
They are prepared at the rate of 1 tbsp. herbal raw materials per 1 glass of water.
The mixture is brought to a boil and left for 2-3 hours to infuse. Before use you need to strain.
Aloe or Kalanchoe juice has a wound-healing effect.
Oil from sea buckthorn and rosehip also has the same property. They are applied directly to the affected area.
These agents accelerate the regeneration process, prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and anesthetize the lesion.
A solution prepared from salt (1 tsp), 3 drops of iodine and soda (1 tsp) is a universal remedy in the fight against inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
These components are mixed in one glass of warm boiled water and used for lotions and rinses. It is also good to treat the affected areas with hydrogen peroxide.
What to do if a bubble is detected?
- Determine the appearance of the formation.
- Guess the time of its occurrence.
- Suggest the reason for its occurrence.
- Treat the oral cavity with local antiseptic preparations 4-5 times a day.
- After 12-16 hours, evaluate the effect of antiseptics, and if the result is positive, continue treatment. If the result is negative, seek medical help.
You should not neglect treatment in such a delicate problem, since a person is a social creature and his appearance can greatly influence his fate.
What other diseases can cause the appearance of red spots on the palate in children and adults?
If red spots appear on the palate of yourself or your child, be sure to consult a doctor.
A person can encounter the problem of redness of the palate only once during his life or periodically, which is due to the nature of the disease that has these symptoms. Relapses include herpes, thrush, and enterovirus infections.
Once the body has been affected, it is impossible to get rid of them.
When conditions are favorable for viruses and bacteria, the disease worsens, so it is important to take preventive measures to suppress the pathogen
The characteristic red rash in the mouth is one of the symptoms of other diseases.
- One of the symptoms of tuberculosis is flat red spots on the oral mucosa. Over time, the reddish or red-yellow inclusions merge to form plaques. The surface of the formations is heterogeneous, the color becomes red-bloody.
- ARVI is recognized in particular by red spots on the soft palate and tongue. Associated symptoms are characteristic of acute respiratory diseases.
- Oncology, among a large number of signs, has one more, which is related to the oral mucosa. A small ulcer forms on the palate, increasing in size over time. However, at first it does not cause discomfort, there are no painful sensations. Reaching large volumes, the ulcer begins to interfere, and difficulty is experienced when swallowing.
- Vitamin deficiency is characterized by a deficiency of vitamins and minerals important for all body systems. Their deficiency weakens protective functions and increases vulnerability to bacteria, fungi, viruses and infections. Red spots with vitamin deficiency are located locally on the skin and mucous membranes, without spreading intensively to neighboring areas.
- Herpes is a viral infection that once it enters the body, does not disappear. The disease worsens against the background of weakened immunity. A characteristic sign: small red spots on the mucous membrane, increasing in size, transforming into small bubbles with liquid inside.
- Chickenpox is diagnosed mainly in children under 14 years of age, but this does not exclude the risk of infection in adults. Not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes are covered with spots. In the mouth you can first find small red dots, which turn into bubbles and very soon burst. This results in gray or yellow ulcers with redness around the circumference.
- Measles is characterized by a rash on the skin and mucous membranes, high fever, general physical weakness, and lack of appetite. The affected area even extends to the mucous membrane of the eyes. Initially, white spots form in the mouth behind the cheeks, and as it moves to other areas, the rash acquires a bright red tint.
- Infectious mononucleosis is recognized by its extensive affected area; spots cover not only the palate, but the entire oral mucosa. There is a soreness in the larynx, and the tonsils increase in size. Breathing becomes difficult due to nasal congestion. Characteristics of the spots: the color is bright, the parameters are impressive, they appear more often along the palate, and quickly spread to other areas.
- Scarlet fever is recognized by red spots that are localized on the soft palate. Other signs of the disease: headache, fever, nausea, pain when swallowing. The tongue becomes crimson in color, the mucous membrane is inflamed, and the rash on the skin is very itchy.
A similar mechanism for the appearance of spots in each individual case still has characteristic features and accompanying signs by which the diagnosis is made. But sometimes even the experience and colossal knowledge of a specialist do not make it possible to diagnose the problem without laboratory tests. Therefore, you should not postpone going to the clinic so that the situation does not get out of control.
Medicines
Drug treatment is prescribed based on the diagnosis. For aphthous stomatitis or pemphigus of the oral mucosa, the basis of treatment procedures is symptomatic therapy aimed at relieving pain - in particular, gels and ointments containing lidocaine (they can also be used for other pathologies).
Drug Indications Note Acyclovir (gel, ointment)
herpes simplex, shingles, chicken pox
Cholisal (ointment) is indicated for children under 3 months of age as injections.
cheilitis, stomatitis, candidiasis, mucosal injuries, teething in children
Not recommended for children under 3 years of age Prednisolone Dermatological diseases Children of any age under medical supervision Cyclosporine
atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pemphigus
Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components of Stomatidin
pathologies of the pharynx and mouth, candidiasis, hygienic use
Contraindicated in children under 5 years of age Chlorhexidine Bigluconate 0.5% Treatment of damage to the mucous membranes Contraindicated in dermatitis; use Solcoseryl with caution in children Helps accelerate tissue regeneration In case of surgical removal of the blood bladder
Dental diseases
At an advanced stage of periodontitis, a fistula forms near the tooth involved in the painful process. If periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum) develops, flux may appear. At first the lump is hard, but over time it becomes softer and filled with pus.
In case of periodontitis, the tooth is unfilled and the root canals are cleaned. After removing the exudate, oral baths are prescribed using special solutions. In case of periostitis, the dentist opens the tooth, places medications in the cavity, and closes it with a temporary filling. If this treatment does not help, the tooth is removed.
Causes of lumps in the mouth
The effectiveness of treating a lump on the lip depends on the correct and timely diagnosis of the disease. After the examination, the specialist determines the nature of the origin of the growth, the degree of damage, and only after this a treatment regimen for the disease and a prognosis for the speed of recovery are drawn up. The main reasons for the appearance of the ball are viral infection and mechanical trauma to the surface of the oral mucosa.
Often, experts note complaints that the patient has bitten his lip, and a growth forms at the site of the incision; this formation has another name - a mucocele cyst (or mucous cyst). This formation is characterized by a cavity in which salivary fluid accumulates. Due to damage to the salivary ducts, the secretion is not removed, which leads to the appearance of mobile, painless edema. The surface of the mucous cyst is blue, and the diameter varies from 2 to 10 mm (see photo).
How to tell by appearance and feel?
The causes of changes in the oral mucosa can be a lot of factors, which can be divided into 2 groups:
- A group of general causes: diabetes mellitus, scarlet fever, syphilis, HIV infection.
- A group of local causes: injury to the mucous membrane by a foreign object (caramel, toothpick), tooth growth in the wrong position, stomatitis, biting one of the areas of the mucous membrane between the jaws, local manifestation of herpes infection.
Depending on what causes the bubble and which group the neoplasm belongs to, treatment is prescribed.
The first group is characterized by the use of general medications and treatment in inpatient or outpatient departments.
To treat group 2 blisters, topical drugs are used that act directly on the formation on the mucous surface. These medications eliminate the cause of the disease, which prevents the appearance of new blisters and eliminates existing elevations.