Ultracaine D-S forte. Carpules 1.7 ml
Active substance:
– articaine hydrochloride 40 mg/ml. Note, 40 milligrams in one milliliter! This means that in one carpool there are 68 mg. This is actually very important. Why - see below.
– epinephrine hydrochloride 12 mcg/ml. Again, note that we are talking about micrograms (millionths of a gram) per milliliter. It turns out that the carpul contains 20.4 mcg of epinephrine hydrochloride. Well. or 17 mcg, in terms of pure adrenaline.
Inactive substance:
– sodium disulfite (sodium metabisulfite) – 0.5 mg/ml (0.85 mg/carpule)
– sodium chloride (saline solution) – 1 mg/ml (1.7 mg/carpule)
– water – everything else.
Other information:
According to a number of studies (A. I. Marakhova, M. A. Zhuravleva et al., 2015), the drug Ultracaine D-S forte, according to high-precision chromatography, contains about 0.047% of impurities, which the authors attribute to articaine derivatives.
The pH of the Ultracain D-S forte solution is 3.960. Moreover, pH fluctuations are allowed within the range of 3.0-5.0
Origin:
Sanofi-Aventis Deutchland GmbH, Germany.
Ultracaine for toothache. Features of the use of Ultracain in dentistry - detailed instructions
The good old Lidocaine has been replaced by the modern and fast-acting drug Ultracaine.
Its appearance can be safely called a small revolution in dentistry, as the range of manipulations with anesthesia and the age of patients from 4 years have expanded.
The article will tell you about the principle of action of the anesthetic, contraindications, pharmacokinetics, effectiveness and types of Ultracaine.
Brief information
Ultracaine is a transparent liquid, without specific aromas or by-products.
The medical product belongs to the amide subgroup of anesthetics with high purification parameters and does not contain antiseptic substances and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), which often cause an allergic reaction in patients.
In dentistry it is used as an anesthetic drug for local or conduction anesthesia. The active reagent is articaine hydrochloride.
The mechanism of action of the drug Ultracain is a local analgesic effect. It blocks depolarization of the nerve ending membrane. Because of this, the nerve impulse does not pass through.
Ubistezin forte
Active substance:
– articaine hydrochloride 40 mg/ml , which corresponds to 68 mg in one carpule.
– epinephrine hydrochloride 12 mcg/ml , which corresponds to 17 mcg of adrenaline in the capsule.
Inactive substance:
– sodium sulfite – 0.6 mg/ml (1.02 mg in carpool)
– sodium chloride – 1.125 mg/ml (1.913 mg in carpool)
– water – everything else.
Other information:
Stabilization of Ubistezin by pH is carried out with a buffer solution of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide, which are obviously present in the form of impurities, but for some reason are not indicated in the analytical passport.
The pH of the Ubistezin forte solution is 3.90. The pH of the solution may vary from 3.6 to 4.4.
Origin:
3M Deutchland GmbH, Germany
===========================
In general, what can I say about these two drugs... the difference between them, as you can see, is very small. So insignificant that you have to be a completely anesthetic sommelier or a drug addicted chemist to notice it. Someone here argued that the whole difference is in the pH value, but it is also very, very insignificant.
So why do doctors, and very well-known and authoritative ones, claim that Ubistezin works worse than Ultracaine? And why is there a legend among dentists that Ultracain is more effective and safe than Ubistezin?
We decided to look into this.
Without local anesthesia, intervention at a dental appointment is unthinkable. The choice of anesthetics is large. Let’s focus on the main thing, to help especially novice clinicians, so that when using them, they are guided not only by their price.
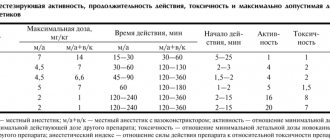
First of all, the degree of their toxicity. The likelihood of intoxication occurring depends on the drug used, its dose, and exposure to a blood vessel. When toxicity increases 10-40 times (it is necessary to do an aspiration test before administration), age, children and the elderly require increased gender attention (more often in women).
Working conditions are complicated by concomitant diseases and medications taken in connection with this. They enhance the toxicity of the anesthetic or the vasoconstrictors added to it. Remember that the administration of small doses can cause complications if the patient is hypersensitive to what is being administered.
In addition, additives to anesthetics, and they are needed, can also cause local and system-wide complications. And this:
1. Sulfites - protect the vasoconstrictor from inactivation by oxygen. All MAs containing epinephrine or norepinephrine are stabilized by sodium sulfite.
2. EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) - protects the vasoconstrictor from decomposition by aluminum or lead ions contained in carpool glass. The acid can cause local irritation; it is used in the treatment of atherosclerosis and related cerebrovascular accidents, diabetes, depression, and acute respiratory viral infections. The resulting headache is explained by instability of blood pressure under the influence of vasoconstrictors of the anesthetic and the psycho-emotional state of the patient.
3. Parabens - protect the anesthetic from bacteria, fungi, and prevent oxidation. May cause an allergic reaction.
To prevent allergies in the anamnesis, specify as much as possible the presence of allergies in the past, it was itching, redness. rashes, suffocation, drop in blood pressure.
Local anesthetics of the amide group are practically devoid of allergic properties. These are articaine, lidocaine, trimecaine. Ultracaine, ubistezin, and septanest are made from articaine
The drug of choice is mepivacaine . Local allergy manifests itself in the form of local erythema, urticaria, edema, and dermatitis. Systemic reactions are rare, but rashes, bronchospasm, drop in blood pressure and even anaphylactic shock (history) may occur. A 2% solution of mepivacaine is similar to a 2% solution of lidocaine, but is less toxic. It has a slight vasoconstrictor effect, does not stimulate the cardiovascular system, and can be used without a vasoconstrictor.
Mepivacaine is recommended for patients with cardiovascular failure, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, and bronchial asthma. In pregnant women, in case of urgent need, it is better to use mepivacaine 2% without a vasoconstrictor, articaine 4% without a vasoconstrictor. In the absence of these drugs, you can use articaine with adrenaline 1:200000, ultracaine DS, ubistezin.
Ultracaine contains in 1 ml of a 4% solution 40 mg of articaine, 0.005 mg of adrenaline (ultracaine DS), 1 mg of sodium chloride, 0.5 mg of sodium metabisulfite, and 1.7 mg of water for injection.
Ultracaine-DS forte contains 0.01 mg of adrenaline, does not contain parabens and EDTA - this reduces the risk of allergies. 20ml bottles contain parabens.
Septanest differs from ultracaine in the presence of EDTA.
Ubistezin differs from ultracaine in having 10% less sulfites and is recommended for the elderly and children.
In order to prevent toxic reactions, administer the anesthetic solution slowly, 1 carpule over 60-90 seconds. For a single administration, use no more than 50% of the maximum permissible dose.
Anesthesia experts.
A quick survey of doctors (113 people in total) showed that the number of fans of one or another anesthetic is approximately equal. Almost 98.9% of doctors explain their fanaticism by habit, but there are no clear answers to the question “why did you choose this particular anesthetic?” We have not received. In addition, to the question “what is the difference between Ubistezin and Ultracaine D-S forte?” we received the following responses:
In my opinion, any fanaticism is bad and can affect the results of the study, so we invited independent experts who have never performed anesthesia in their lives. This means that their opinion is absolutely unbiased and can be trusted.
These are members and employees of Tseleevo Golf and Polo Club. With HCP penis length not exceeding 28.0 cm.
Research method.
In general, we asked our experts to make a drive (long shot) with two carpules - Ubistezin and Ultracain. Tests were carried out with a Titleist Practice ball and different drivers at a side wind speed of 0.5-1 m/s. A total of 10 injections of drive anesthetic were made from each type of carpule.
Research results and discussion.
Based on the results of the study, experts made the following conclusions:
- Doctor Vasiliev, are you completely stoned there, or what? – in general, a correct judgment. Non-negotiable.
– what kind of granny is this anyway? – rather a question rather than a result.
– getting drive from an anesthetic carpule is strange, to say the least. Respected experts told me the same thing.
– the length of the drive does not depend in any way on the brand of anesthetic. The effectiveness of anesthesia, obviously, too.
Articaine or ultracaine, which is better? It doesn't hurt! Modern methods of anesthesia
We are publishing an article by Natalya Lvovna Mayorova, a dentist and therapist, head of the therapeutic department of the Dentalika clinic.
Pain relievers used in modern dental practice can work wonders. After receiving an anesthetic injection, the patient does not feel any pain or even particularly unpleasant sensations. To ensure that the injection itself is painless, before the procedure the doctor “freezes” the injection site with a special preparation with a delicious smell of cherry, lemon, or apple.
Local anesthesia is the main method of pain relief used in dental practice. With local anesthesia, the patient remains fully conscious, and this allows the doctor to fully control the entire course of treatment, communicate with the patient, and monitor your reaction.
The quality of dental interventions depends on the results the doctor obtained during local anesthesia. Therefore, achieving 100% pain relief is necessary not only for the patient, but also for the doctor, in order to carry out treatment calmly, slowly, and efficiently. Hence the following requirements for local anesthetics:
- they must have a strong analgesic effect, easily penetrate into tissues and remain there for as long as possible;
- have low toxicity, causing a minimum number of both general and local complications
Based on these wishes, we chose several widely used drugs:
- Ultracaine DS forte (4% articaine, adrenaline 1:100,000);
- Ultracaine DS (4% articaine, adrenaline 1:200,000);
- Scandonest SVC (3% mepivacaine; without vasoconstrictors - adrenaline).
Now in more detail about their action.
Ultracain DS
The analgesic basis of the first two drugs is ARTICAINE (amide anesthetic from the thiophene series), an antispasmodic - lowers blood pressure. It is characterized by rapid action - anesthesia occurs in 0.5-3 minutes. Articaine is 2 times stronger than lidocaine and 6 times stronger than novocaine (anesthetics of previous generations), less toxic, relatively quickly eliminated from the body. Its half-life is, on average, 22 minutes, that is, all traces of the drug disintegrate in 44 minutes and are then completely eliminated from the body. Has high penetrating ability. It is distinguished by high purity of the solution. Allergic reactions to articaine are very rare - one in one hundred thousand injections; the use of articaine, according to studies, is safe in 99.4% of cases. They also contain a vasoconstrictor (a substance that causes constriction of blood vessels and a decrease in blood flow in them) - adrenaline. The use of a vasoconstrictor continues and enhances anesthesia. The drug also contains antioxidants (sulfites) - substances that prevent the oxidation of adrenaline.