Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Dental treatment under general anesthesia
Panic fear, a strong gag reflex, allergic reactions to anesthetics and many other conditions are indications for the use of general anesthesia during dental procedures. The patient’s condition after such an intervention is somewhat different from his normal state of health, and this article is devoted to how to behave for the first time after treatment under anesthesia or drug sedation in dentistry .
Why general anesthesia is dangerous - myths about anesthesia
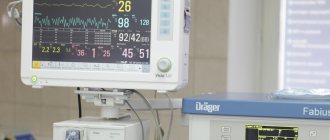
Over the past decades, general anesthesia has become much “softer”: the introduction of drugs with fewer side effects, a significant reduction in the use of narcotic drugs, the development and active use of a new generation of gas mixtures that enter the lungs through a ventilator and support a person in medicated sleep as much as necessary, all this has led to the fact that modern anesthesia has become practically safe. Proof of this is the fact that these days there is practically no question about the duration of anesthesia. If in the 70s, hours were counted, and the longer a person was in medicated sleep, the worse he “moved away from it,” but now serious operations last for 10–12 hours, and the next day the patient is transferred to a ward, which called “with a clear head.”
Another brick in the safety wall is the active introduction of imaging techniques in anesthesiology. If previously a doctor punctured large vessels and installed catheters in them blindly, based only on anatomical landmarks and his own experience, today everything happens under ultrasound control, the risk of error and the development of complications tends to zero.
The equipment controls the depth of anesthesia, automatically changes breathing parameters, selecting optimal criteria for each specific moment of the operation. The workplace of an anesthesiologist is difficult to distinguish from the cockpit of an airliner.
As you know, in the past, the liver and brain suffered the most from serious anesthetic drugs. Therefore, special attention is paid to neuro- and hepatoprotection. Modern drugs have minimal hepatotoxicity and virtually no damage to the liver, neurotoxicity is also significantly reduced, and special drug regimens are used to protect the brain. And it works, because stories about memory loss or deterioration of brain activity after anesthesia are becoming less and less common.
Proper patient care after surgery is the key to a speedy recovery
Home Articles Proper patient care after surgery is the key to a speedy recovery
As you know, it is not enough to perform a successful surgical operation. Proper care after the operation also plays a great role in the recovery of the operated patient. This stage continues directly from the time of the operation until the moment when the patient returns to his usual lifestyle and work.
The duration of the recovery period depends on the patient’s condition, the occurrence of complications, and is determined by the nature of the surgical intervention.
After major operations, the patient remains in the recovery room or in the intensive care unit and is located on a special bed. Special equipment is connected to it to support the patient’s vital functions.
Purpose of care in the postoperative period:
- ensure healing of scars and sutures;
- avoid complications after the intervention;
- restore body functions.
One of the tasks of patient care staff at this stage is to combat the pain that the patient initially experiences not only in the sutures, but also in organs damaged by injury.
The second is the prevention of thromboembolic complications. During surgery, the body itself tries to protect itself from blood loss - it releases a special substance thromboplastin into the blood. In this case, another danger arises - blood clots may appear in the venous system.
That is why, to prevent blood clots, a number of measures are taken to improve blood circulation and ventilation of the lungs:
- do not allow dehydration;
- force the patient to turn over in bed and begin to get up as early as possible;
- the patient is shown breathing exercises and therapeutic exercises already on the first day after surgery;
- he is taught to press down on the wound with his hand when coughing;
- if the patient has varicose veins, the legs are bandaged and coagulants are administered.
Third is control of the surgical wound. The nurse or medical staff monitors the condition of the stitches after surgery and checks the bandages. They must be applied correctly and remain clean and dry. The nurse also replaces tampons and drains if they are in the wound.
After the operation, any complications may occur. The most common are the development of bleeding, high fever, decreased urine output, problems with breathing or cardiovascular activity. Complications depend on the nature of the injury or illness suffered.
Most complications can be avoided by carefully following your doctor's recommendations and proper care after surgery.
Epidural anesthesia
Many operations take place while the patient is conscious. For example, operations on the lower extremities, genitals, hernias, and many others. Mainly due to the use of various types of spinal anesthesia, mainly epidural block. In this case, for pain relief you will need several milliliters of the drug, which are injected into the epidural space running along the spinal column. But for several hours, the absence of sensitivity below the level of the catheter is guaranteed.
Childbirth is increasingly taking place under epidural anesthesia. But we must remember that it is not recommended in cases of weak labor, when contractions, on the contrary, have to be stimulated. As for the situation when childbirth proceeds normally, data from many years of research indicate that epidural anesthesia during childbirth is safe and effective.
Today, many people prefer to undergo unpleasant examinations under general anesthesia - gastro- and colonoscopy, various biopsies and punctures. This is really a solution for those who are very afraid of even a little pain and do not want to experience painful minutes. The main thing is that the procedure is carried out under the supervision of an anesthesiologist, who accurately calculates the dosage of the drug and turns off consciousness to the minute. He monitors the patient's breathing and, if necessary, adds a little medicine. If these rules are strictly followed, studies under intravenous general anesthesia are absolutely safe.
Indications for general anesthesia
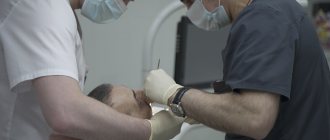
Under general anesthesia in dental practice, it is possible to eliminate almost all problems that arise in the oral cavity - from simple dental caries to complex maxillofacial operations. The patient seeks this type of help, most often, not because of pain, but because of severe fear or medical conditions that interfere with the doctor’s work (allergies, gag reflex, mental illness, etc.). More information about the types of anesthesiological support and how treatment is carried out with switched off consciousness can be found on our website. Here we will talk about the process of postoperative restoration of the patient’s activity , depending on the method of pain relief and the medications administered.
Anesthesia in dentistry
And one more question that interests many: is it worth agreeing to general anesthesia when installing dental implants? In fact, in this case there is no choice. After all, if we are talking about installing 1-2 implants, you can really get by with local anesthesia, but when a dentist does half of the jaw at a time, then working without anesthesia will turn into real torture for both the doctor and the patient. Considering these facts and the safety of modern anesthesiology, most patients agree with the doctor’s proposal and prefer to wake up with a finished result.
Rule one. You shouldn't endure pain just to avoid anesthesia.
Almost any manipulation associated with causing severe pain is more harmful to the body than anesthesia. Therefore, in the civilized world they adhere to this point of view: where it is possible to relieve a patient of pain, this is certainly done. Modern medicine has very wide possibilities for this.
In addition, anesthesia with the use of artificial respiration devices significantly expands the capabilities of surgeons and allows them to provide assistance to those patients who cannot be helped with other types of surgical intervention. Of course, all contraindications of the patient, his age, and body capabilities are taken into account.
Rule three. Recovery from anesthesia depends on the type of anesthesia and the characteristics of the body.
Typically, the patient recovers from anesthesia within one to four hours, depending on the amount of anesthesia used and his individual characteristics. The fact that recovery from anesthesia was normal can only be assessed by a doctor based on various indicators of the body’s functioning.
The patient himself usually remains half asleep for quite a long time during the day. His relatives who are present should not be afraid. The patient's body is simply under the influence of analgesics. They are necessarily administered in order to alleviate pain after surgery - after all, the anesthesia has ended, but the cause of the pain remains.
Article on the topic
In facts and figures: epidural anesthesia does not work for 1 in 20 patients
There may be another condition after anesthesia - excessive excitement. This usually happens if a person has previously abused alcohol or had mental problems. This complication is also amenable to medical control - the patient will simply be given sedatives and sleeping pills for a while.
Before general anesthesia: preparation
Preparation for surgery under anesthesia has a great influence on the effectiveness and safety of general anesthesia and the course of the postoperative period. You will have to undergo a comprehensive diagnostic examination, including detailed blood tests, coagulogram, and ECG. According to indications, consultations with narrow specialists are prescribed.
The presence of chronic diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems is of great importance. Be sure to tell your doctor about the following diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- chronic obstructive bronchitis;
- arterial hypertension;
- IHD;
- history of stroke.
Do not under any circumstances hide the fact that you have a history of chronic diseases and acute vascular events (heart attack, stroke). Not only the outcome of the operation, but also your life depends on this! Also provide your doctor with a complete list of medications you take, including “harmless” analgesics for headaches or menstrual pain.
As practice shows, excess weight negatively affects the rate of recovery after operations under general anesthesia. If you are planning plastic surgery in advance, pay attention to weight loss issues. It is advisable to quit smoking in about six months. If you have not done this, stop smoking a week before the operation, but you should not “quit” the day before anesthesia - this may complicate the rehabilitation period.
On the eve of the operation, pay special attention to nutrition and hydration. You should not drink alcohol 24 hours before plastic surgery. On the day before surgery, you should limit yourself to breakfast and lunch. On the day of surgery, eating and drinking is strictly prohibited!
Rule two. Follow the anesthesiologist's recommendations
The anesthesiologist must talk to you the day before if you are undergoing elective surgery. Tell us in detail about all the problems that bother you and how you endured anesthesia before.
Take seriously the regimen that you will be advised to follow before the operation - do not smoke, do not drink liquids. It is prescribed to prevent complications and extreme situations.
Article on the topic
Advice from an anesthesiologist: Which anesthesia is safer?
If you are prescribed any medications the night before or the morning before surgery, do not ignore this order. As a rule, strong sleeping pills are prescribed before surgery, which already represent the first stage of anesthesia. They will ensure that you get a deep, relaxing sleep before surgery and that other painkillers work properly.
After general anesthesia
Even after a good general anesthesia, in the first hours there is short-term confusion, disorientation in space and time, drowsiness, nausea, and dizziness. As the anesthetic drugs wear off, pain appears in the postoperative wound, but it is successfully relieved by the administration of strong anesthetics.
After general anesthesia with an endotracheal tube, patients complain of pain and sore throat caused by irritation of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, but this symptom, like nausea, passes very quickly. As a rule, patients feel well 3-4 hours after surgery, and on the second day they leave the clinic and return home.