Possible reasons
| The exact cause of this disease has not been identified. Experts believe that the cause is a violation of the formation of tooth buds in the embryonic period. For example, this can happen if a woman took certain medications during pregnancy, had bad habits, or suffered from certain infectious diseases. |
There is also a version that the pleasant appearance of abnormally located teeth is atavism. The essence of this theory is that in past centuries people had a larger number of teeth than today, so some patients show signs of returning to the original structure of the dentition. According to statistics, this anomaly occurs in 7% of cases.
What should a parent be wary of in this case?
The strange shape of the erupted tooth, as well as its position in the dentition.
In adults, as a rule, there are no symptoms. Supernumerary teeth simply erupt and create discomfort, injuring the mucous membrane and making the bite incorrect, or they remain in the bone tissue without showing themselves.
In some cases, if there are impacted extra teeth, an adult may have:
- loosening of permanent units,
- periodic discomfort at the location of the extra tooth,
- bone deformation if the tooth is located at the edge of the jaw.
In what cases is it necessary to remove supernumerary teeth?
Removal of supernumerary teeth is recommended in 90% of cases. You can refuse surgical intervention in the following cases:
Simply put, if a supernumerary tooth causes inconvenience, pain or discomfort, it is removed. |
Supernumerary Teeth on Both Sides of the Upper Jaw
Supernumerary teeth (SD) or hyperdontia are any number of teeth that exceed the normal number of primary or permanent teeth. Alternatively, teeth that fall outside the normal dental formula, regardless of their location and shape, can be classified as SZ. Unlike accessory teeth, SZs typically do not resemble the teeth they are associated with.
Although SZ can erupt in both the primary and permanent dentition, they are more common in the permanent dentition with a predominance of 1.5% to 3.5%. In the temporary dentition they occur with a frequency of 0.3% to 0.8%. Their prevalence in the molar area ranges from 0.18% to 0.33%.
In the permanent dentition, the SZ can be located in any area of the maxilla or mandible and is often located along the midline of the maxilla. In the temporary dentition, the SZ are usually located in the upper jaw. The SZ can erupt singly (single), multiple (several, more than one) on one side or on both sides, as well as on one or both jaws. The prevalence of one SD ranges from 76 to 86% of cases, two SDs from 12 to 23%, and 1% of people have multiple (that is, more than 3) SDs.
Paramolars are relatively rare supernumerary molars. A limited number of cases of paramolars localized bilaterally in the maxilla and mandible have been reported. This case report describes bilateral maxillary premolars and their treatment in a 15-year-old girl whose chief complaint was food accumulation in this area. After diagnosis of bilateral premolars in the maxilla and confirmation by orthopantomogram, both paramolars were removed.
Theories and etiology of development of supernumerary teeth
Several theories for the development of supernumerary teeth, primarily related to genetic and evolutionary influences, have been proposed to explain the development of SZ. These include atavism (evolutionary return), bifurcation of the tooth germ, genetic and environmental factors, and hyperactivity of the dental lamina. SZ may be transmitted as an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive trait with incomplete penetrance, or may be associated with X-linked disorders. However, the specific etiology of SZ is still unclear. The most common belief is that SD develops as a result of horizontal proliferation or hyperactivity of the dental lamina.
Paramolars most likely develop due to localized and overactive dental lamina. According to this theory, lingual elongation of an additional tooth germ leads to the formation of a eumorphological tooth. However, the rudimentary form arises from the proliferation of epithelial remnants of the dental lamina, which in turn are caused by the pressure of the full dentition. The development of SD can also be considered multifactorial.
Classification of forms of supernumerary teeth
SZ can be classified by number, morphology or topography. Based on the number, they can be single or multiple. Morphologically, the SZ can be accessory (eumorphological or normal in appearance) or vestigial (dysmorphological or a variant appearance of normal teeth). Further morphological classification of the dysmorphological type SZ includes conical, tuberculate and molar subtypes. Topographically, the SZ occurring in the anterior region, between the incisors on the upper jaw, is called mesiodentus (middle incisor). SZs occurring in the molar region may be classified as parapremolars, paramolars, or distomolars. The paramolar is often small and dysmorphological, located buccally or palatally/lingually to one of the molars. It has been reported that paramolars are more common in the mandible than in the maxilla. Distomolars (sometimes called fourth molars) are located distal or distal-lingual to the third molars. The orientation of the SZ can be vertical, inverted or transversal.
Paramolars are a relatively uncommon supernumerary anomaly, occurring in the molar region with a predominance of 0.09% to 0.29%. Paramolars generally erupt singly; bilateral eruption is rare. Very few cases of bilateral paramolar eruption have been reported in the literature. This article describes a clinical case of bilateral paramolars in a 15-year-old girl and its treatment.
Clinical case
A 15-year-old girl and her parents presented to the Department of Pediatric Dentistry and Preventive Dentistry, Subharti Dental College and Hospital, Meerut, India with the chief complaint of food accumulation in the bilateral maxillary molar area. Both her medical and family histories were clear. Written informed consent was obtained from her parents prior to examination and treatment.
Clinical examination
Clinical examination revealed supernumerary teeth on both sides (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2) buccal to the maxillary first and second molars.
Rice. 1
Rice. 2
The location of the supernumerary teeth suggested a diagnosis of bilateral paramolars in the upper jaw, which was confirmed by an orthopantomogram (OPTG) X-ray (Fig. 3). Clinical examination of the left and right maxillary first and second molars showed normal morphology with the expected buccolingual and mesiodistal width of each crown compared to their contralateral counterparts. This study showed a lack of fusion with adjacent paramolars.
Rice. 3
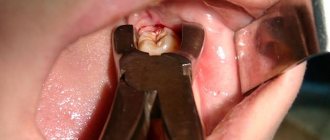
Both bilateral paramolars were then removed under local anesthesia with a vasoconstrictor (lignocaine hydrochloride 21.3 mg with epinephrine 0.005 mg). Extraction was performed carefully using left and right forceps on the maxilla to avoid damaging the adjacent permanent teeth, which could subsequently cause ankylosis and destruction of these teeth. Possible clinical complications of such extraction include injury to blood vessels and nerves during manipulation of the paramolars, perforation of the maxillary sinus, pterygomaxillary space or orbit, and fracture of the maxillary tuberosity.
The paramolars removed from both sides (Fig. 4) were dysmorphic and conical in morphology, single-rooted with three poorly developed projections. Together with periodontologists, the sockets were closed using bone tissue regeneration using a cancellous bone graft. Ensuring complete attachment of soft tissues and preventing the appearance of postoperative defects in periodontal pockets. Soft tissue closure was achieved with interrupted sutures using 3.0 silk sutures. Oral hygiene instructions were carefully explained to the patient and her family. Healing of postoperative sockets occurred without complications.
Rice. 4
Additional x-rays revealed a cystic lesion in the area of the missing first permanent molar in the mandible. This large radioluminescence was assumed to represent a dental cyst or odontogenic keratocyst. This lesion was subsequently enucleated by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and was histopathologically diagnosed as an odontogenic keratocyst.
Discussion
Paramolars are usually small, vestigial or dysmorphological. Located buccally or lingually in relation to the maxillary molar. In this patient, the paramolars on both sides were dysmorphological and conical.
Multiple SDs may be associated with different syndromes. These may include cleft lip and palate, Gardner's syndrome, cranioclavicular dysostosis, Fabry's disease, Ellis-van Creveld syndrome (chondroectodermal dysplasia), Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, Nance-Horan syndrome, pigment incontinence, and trichorinophalangeal syndrome. . The more common ones are cleft lip and palate, cranioclavicular dysostosis, and Gardner's syndrome. However, the patient in this case had paramolars on both sides without the presence of any syndromes. The presence of several SDs without a developmental disorder or the presence of a syndrome (as in this patient) is very rare.
SZs can be found in almost any area of the dental arch, although they have a striking “love” for the upper jaw compared to the lower jaw. However, multiple SDs without associated syndromes are more common in the mandible and premolar region, followed by the molar region and anterior region. In this patient, the SZ on both sides were located on the upper jaw. Although the patient was a girl, men are twice as likely to experience cervical teething as women.
SZs such as paramolars can be diagnosed during a routine, clinical, or radiographic evaluation and typically do not have any noticeable adverse effects on adjacent teeth. They can sometimes cause various complications such as delayed eruption, failure to erupt, crowding or displacement (including rotation of permanent teeth), and, less commonly, the development of odontogenic cysts or resorption of adjacent teeth. Delayed eruption is the most common complication of SZ. In this case, the patient's main complaint was the accumulation of food in the paramolar area on both sides.
Traditionally, two-dimensional radiographs have been used to locate (visualize) paramolars. The OPTG is a very useful radiograph to locate (visualize) the SZ, along with additional anterior views of the mandible and maxilla in the format of occlusal or periapical radiographs. In this case, OPTG was used to view the paramolars bilaterally in the maxilla. Recent advances in radiology such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) have also been useful for imaging SZ. CBCT provides 3D images and can accurately predict the location of the SZ as well as surrounding structures.
Differential diagnosis of paramolars is carried out with additional structures in the area of the maxillary molars, such as the supernumerary tooth and the paramolar cusp formed on the buccal surfaces of the maxillary and mandibular molars. The paramolar tubercle was first described by Bolk in 1916. This structure is usually present on the buccal surface of the mesiobuccal ridge (edge of the tooth) or paracone, and sometimes in the area of the distobuccal ridge or metacone. It is derived from the cervical tubercle and must be differentiated from the paramoral teeth.
The treatment strategy for paramolars is governed by the presence of associated syndromes, tooth position, potential impact on adjacent structures and associated malocclusion, caries and periodontal pathology. Clinical cases similar to this have previously been described in the literature. Treatment options for paramoral repairs include observation, both clinical and radiological, if asymptomatic or removed. If a paramolar is symptomatic, as is the case when food accumulation has been associated with paramolars on both sides, extraction is the recommended treatment option. This patient required regular follow-up to ensure there were no future complications.
Paramolars
Paramolars are a relatively rare type of supernumerary teeth, especially those that erupt bilaterally. Knowing about paramolars and their treatment can help dentists understand the potential problems they can cause and treatment options.
The translation was carried out by S. Filanovich specifically for the OHI-S.COM website. Please, when copying material, do not forget to provide a link to the current page.
https://www.aegisdentalnetwork.com/
How is removal carried out?
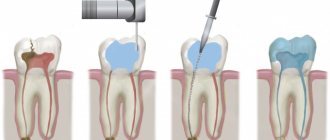
If the abnormal tooth is single and it is not difficult to get to it using surgical instruments, then there will be no problems, and the tooth will be removed using a standard method. If there are several teeth, they are located in hard-to-reach places, have several roots, or have not fully erupted - in this case, removal is carried out as follows:
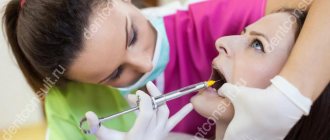
- The doctor administers an anesthetic so that the patient does not experience pain during the procedure.
- A small incision is made on the mucous membrane.
- If the roots of the tooth are deep, the doctor may make a small hole using a special bur to provide access to the root system of the tooth.
- The tooth and root are removed using forceps.
- Next, the area is disinfected using antiseptic agents.
- Stitches are applied.
- To avoid complications, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. may be prescribed.
Please note that before surgery, an X-ray diagnosis is required. In this way, the doctor assesses the condition of the root system and other features. Only after the diagnosis is carried out is the issue of tooth extraction decided.
Symptoms
Pericoronitis is accompanied by a number of symptoms.
- Objective symptoms that can be seen by the patient himself or the dentist during an examination of the oral cavity.
The presence of a mucosal hood on the surface of the erupting tooth and a pathological gingival pocket are determined [6,9,10]. Externally, at the site of the erupting tooth, the gum tissue is hyperemic (red), voluminous due to swelling. The causative tooth may be mobile.
During the examination, the dentist evaluates the regional lymph nodes (cervical, submandibular, preauricular), their size and the presence of pain. An increase in the latter indicates a prolonged course of pericoronitis. With mild severity, the body temperature rises to 37°C, and in the presence of purulent complications - to 38-39°C [2,5,13]. The face with pericoronitis is asymmetrical, due to swelling and enlargement of soft tissues on the affected side.
- Subjective symptoms caused by the patient’s sensations.
Pain in the gums occurs at rest and intensifies when brushing teeth, chewing food, talking and opening the mouth. Pain sensations can spread along the branches of the trigeminal nerve to the ear and eye[7]. There is an unpleasant, putrid odor from the mouth. General health worsens, weakness occurs, sleep is disturbed, appetite and performance decrease. In response to pain, the masticatory muscle spasms, making it difficult to open the mouth, chew and swallow food[11].
Other treatments
| Another way to solve the problem is orthodontic treatment. This is true if the abnormal unit is located close to the dentition. Braces are usually used to straighten it, since this method is the most effective. The duration of treatment is determined individually, depending on individual characteristics. Orthodontic treatment may also be prescribed after the removal of a supernumerary tooth in order to normalize the bite. |
What is polyodontia?
Supernumerary teeth are extra units in the dentition. There can be 33,34,36 or even more than 100. Normally, the number of teeth in a child’s primary occlusion should not exceed 20, and in an adult – 32 units.
Most often, additional incisors or canines appear. It is much less common for a person to grow extra wisdom teeth, and they usually remain impacted.
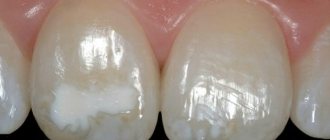
Supernumerary teeth in an adult differ from the rest in size, development of the crown and root. They can also have a different shape, resembling, for example, a thorn or a drop.
If the extra units have not erupted, then polyodontia usually does not cause any unpleasant sensations. Therefore, we often learn about the existence of supernumerary teeth only during radiography.
Causes of dental damage in children
The increase in injury cases is primarily due to the growing popularity of team, contact and other sports. For example, hockey, wrestling, boxing, football and others. Also, the cause of dental damage in children of different ages can be accidental falls during active games on the street or school. No less common are injuries sustained in everyday life, fights, road accidents and other cases where there is a high probability of being hit by a hard object.
The risk of tooth damage increases if a child has orthodontic pathologies. For example, in patients with a distal bite (with protrusion of the upper jaw), injuries occur 5 times more often than in those with an orthognathic (normal) bite.
Also, dental damage often occurs in children with visual impairments, problems with the musculoskeletal system and various neuropsychiatric diseases.