Symptoms Causes Consequences Alveolitis Diagnosis and treatment Features of wisdom teeth Treatment at home Prevention
Tooth extraction is one of the most popular and simplest operations in medicine. Usually it passes without complications, but due to a number of general or subjective reasons, deviations may occur. One such postoperative complication is dry socket.
The fact is that after extraction of a tooth, a cavity forms in its place, which, in a positive scenario, is filled with a blood clot. It prevents the penetration of microbes into an open wound and promotes its speedy healing. A dry socket after tooth extraction is the absence of that same blood clot in the socket. This can happen for two reasons:
- Loss or resorption.
- Severe bleeding that prevented a clot from forming.
Whatever the reason, the healing process can take weeks and be accompanied by serious discomfort, which is not always possible to eliminate on your own.
Symptoms
Dry socket syndrome is very painful. It is quite easy to identify if the following symptoms appear within 2-3 days after tooth extraction:
- inflammation of the gums, accompanied by severe pain;
- pain in the cervical region and ears;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- taste of pus in the mouth;
- partial hearing loss;
- general malaise
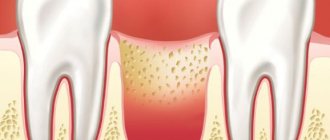
Visually, a dry socket is an empty depression at the site of tooth growth, first exposing the jawbone, and then turning into a reddened, purulent wound.
Normally, the socket is a cavity that, after tooth extraction, is filled with ichor. Over the next three days, the clot thickens, and light fibrin stripes appear on it - the beginning of the formation of new gum tissue. There may be slight soreness at the wound site. From 4 to 7 days, swelling gradually subsides, and the gums acquire their usual pink color. There is no pain.
What to do after the extraction is complete
It is possible to realize that the hole is healing correctly on the 3rd day. The gums hurt moderately, and a white coating appears on it. It is extremely important not to remove it, since it is new epithelium. After 2 weeks, the onion should be completely covered with granulation tissue. After a month, bone tissue begins to regenerate in the entire socket. After 50 days, bone tissue fills the entire hole. And only after five to six months the hole is completely healed and does not differ from other bone tissue.
The gums will recover faster after tooth extraction is completed if you follow easy recommendations.
In the first days after surgery, minor bleeding may occur. Under such conditions, you need to take a small piece of cotton wool or gauze, soak it in hydrogen peroxide, and apply it to the hole. It is much better to go to the pharmacy immediately after removal and buy a hemostatic sponge. A small piece must be applied to the hole; it will dissolve on its own.
Causes of dry socket
There are several causes of dry socket. Some of them can be prevented by following simple recommendations regarding personal hygiene and caution. Causes:
- smoking. In this case, there is a decrease in pressure in the oral cavity, which can lead to the loss of the formed clot;
- neglect of oral hygiene;
- low blood clotting;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- mechanical damage to the hole itself or the tissues around it.
In addition to the above reasons, a dry socket can appear as a result of an incorrectly performed tooth extraction procedure. During a complex extraction, when the tooth had to be removed from the gums in parts. All rules recommended before and after extraction must be followed.
Features of formation and structure
The jaw begins its development in the prenatal period, the rudiments are separated from the dental plates, bone crossbars appear around them - the walls of the dental alveoli are laid (as shown in the photo below). It is noteworthy that the rudiments of both permanent and baby teeth are located within the same alveolus.
Important! A formation such as the alveolar process appears much later, when babies begin to erupt their first teeth.
The inside of the alveoli is lined with spongy plates corresponding in size to teeth. The upper and lower jaw recesses are no different from each other. Each of them contains a nerve and many small blood vessels.
The sockets of the central and lateral incisors, as well as the canines, have lingual and labial sides. The recesses of large and small molars (molars, premolars) have buccal and lingual plates. The largest alveolar cavity is at the fangs - its size can reach 18 mm. The walls of the alveoli are attached on one side to the teeth, on the other to the jaw.
The holes of different depths in which the dental roots are located are called alveoli
Consequences
If during the first two days after tooth extraction pain appears, swelling does not subside and the temperature rises, then most likely these are signs of inflammation. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, as dry socket syndrome can lead to serious complications. Such as:
- flux.
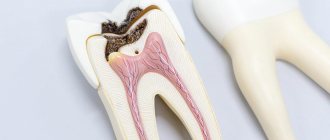
It begins to form when an infection gets into the hole. Characterized by severe swelling and pain. Requires immediate specialist intervention. - alveolitis
This is a deeper penetration of the infection - deep into the gums. Bacteria spread quickly and, if this process is not stopped in time, there is a risk of tissue necrosis. In this case, the losses can be very serious.
Attention!
The consequences of untimely or incorrect treatment can be irreversible. Do not neglect your doctor's advice. A wound on the mucous membrane is always a vulnerable area, subject to attack by bacteria and their rapid spread.
What can you do at home -
After the acute symptoms of inflammation have subsided, there is no need for antiseptic turundas inside the socket, because they do not help the wound to heal (epithelialize) faster. At this stage, the best treatment method will be to fill the hole with a special Dental adhesive paste (Solcoseryl). This drug has an excellent analgesic effect (after 2-3 hours the pain will practically stop, and after 1-2 days it will go away completely), and also speeds up healing many times over.
Scheme of use - this paste is added to a hole that has been washed with an antiseptic and slightly dried with a dry gauze swab (completely filling the hole). The paste is perfectly fixed in the hole and does not fall out of it. There is no need to remove the paste from the hole, because... it slowly dissolves on its own, giving way to growing gum tissue. The only thing that may be required is to periodically add it to the hole.
How to rinse the hole from food debris -
In some situations (when the turunda has fallen out of the hole, and there is no way to see a doctor right away), it may be necessary to wash the hole. After all, after each meal, the hole will become clogged with food debris, which will cause new inflammation. Rinsing will not help here, but you can easily rinse the hole with a syringe.
Important : from the very beginning you must bite off the sharp edge of the needle from the syringe! Next, bend the needle a little and fill a 5.0 ml syringe with a solution of Chlorhexidine 0.12-0.2% (it is sold ready-made in every pharmacy for 20-30 rubles). Screw the needle tightly so that it does not fly off when pressing the syringe plunger! Place the blunt end of a bent needle into the upper part of the socket (do not insert too deeply to avoid injuring the tissue), and rinse the socket under pressure. If necessary, do this after every meal.
In principle, after this the hole can be dried with a gauze swab and treated with Solcoseryl. We hope that our article on the topic: Alveolitis after tooth extraction, symptoms, treatment - turned out to be useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author’s education in surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.), 5. “Propaedeutics of surgical dentistry” (Soloviev M. .).
Forms of alveolitis
Depending on the course of the complication, three stages are distinguished:
- Serous.
It makes itself felt
2-3 days
after tooth extraction. At this stage, pain occurs when eating, headache. Lymph nodes increase in size. - Purulent.
This is the next form that occurs after the serous one, if timely treatment is not carried out. Diagnosed a week after the tooth was removed. The pain becomes unbearable and is also felt in the head or ear. The hole becomes covered with a purulent, dirty yellow coating. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. Swelling and lymph nodes enlarge and become painful. Opening your mouth and eating food is extremely difficult due to pain. - Hypertrophic.
At this stage, it seems that the symptoms are subside: the condition is normalized, the temperature decreases. However, atrophied tissue grows, and when pressure is applied, pus is released from the inflamed wound.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should not self-medicate, but rather consult a dentist.
Additional physiotherapy treatment (click to expand)
Physiotherapeutic treatment is an important addition to drug therapy; with the help of physiotherapy, the intensity of inflammation can be significantly reduced and healing time can be accelerated. For alveolitis, the following techniques are used:
- UV therapy - the hole is irradiated with short-wave ultraviolet light, which kills pathogenic microorganisms and reduces the level of inflammation.
- SMV therapy is a method of treatment with an electromagnetic field, based on the effect of centimeter waves on the area of inflammation. The procedure helps improve blood circulation and metabolism, due to which toxic substances are removed from tissues faster and regeneration processes are accelerated. SMV therapy also has an analgesic effect.
- UHF therapy – the body is exposed to a high-frequency electromagnetic field. For alveolitis, UHF therapy is used if the patient's regional lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Electrophoresis – medications are injected into inflamed tissue using electrical impulses. For post-extraction alveolitis, electrophoresis is used to reduce pain. For this purpose, solutions of novocaine, lidocaine, trimecaine are used.
- Fluctuarization is a treatment technique with pulsed currents of a sinusoidal shape with a low frequency. As a result of the procedure, blood circulation and lymph flow improves, swelling resolves, and the level of inflammation decreases.
- Laser therapy - the hole is exposed to infrared laser radiation, which has an anti-inflammatory effect, reduces swelling and redness of soft tissues, and accelerates healing.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
Diagnostics at a dentist's appointment will help confirm the symptoms of a dry socket. After an examination, the doctor will prescribe treatment. As a rule, it depends on the stage of inflammation. In the case of a mild form, drug treatment with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs is possible. At the middle stage, you will need antibacterial therapy, as well as cleaning the hole from pus and filling it with an anti-inflammatory drug. All actions are performed under anesthesia. If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed.
At the third stage, the most advanced stage, the patient may need hospitalization and even surgical intervention. With proper care and no complications, the hole heals within seven days. And a month later there is no trace left of her.
How many days does it take for the socket and gums to heal?
During a complex operation, the dentist may damage the jaw or push the tooth root into the maxillary sinus. If you do not seek help from a dentist for a long time with such complications, even more terrible conditions appear - gumboil, cyst, osteomyelitis.
Complete healing of the gums after tooth extraction occurs within several weeks. All this time, the mucous membrane hurts a little, but is simply anesthetized with local drugs.
The healing time of the hole is personal for each patient. Recovery takes a long time if care recommendations are not followed. The gums after tooth extraction do not heal even after a couple of weeks, if an infection was introduced during the operation or after the end.
The gum heals in 14 days, and complete restoration of the socket occurs in six months.
Features of wisdom tooth removal
Dry socket after wisdom tooth removal is not uncommon. This syndrome occurs especially often in the lower jaw due to the fact that as a result of swallowing and opening the mouth, the muscles tense, aggravating the appearance of a dry socket and, as a result, alveolitis. Dry socket occurs in approximately 50% of cases
. Due to the anatomical features of the jaw, the blood clot often falls out.
When extracting a wisdom tooth, you must carefully observe precautions and resort to this procedure only in cases of extreme necessity. After all, the inaccessibility of the place complicates treatment.
Correction of common complications
General violations occur less and less often in dentists’ offices. This is due to the latest technologies in this area, which allow treatment to be carried out painlessly and quickly, as well as the development of asepsis and antiseptics. But some complications still arise, although this does not happen as often as before.
If the patient’s eyes are cloudy due to fear of intervention, use a cotton swab soaked in ammonia. It is brought 7-10 cm from the nose, which brings the person to his senses. If anxiety does not go away, medical sleep is offered as pain relief.
If there is a large loss of blood during the operation, you need to carefully and promptly make up for the deficiency. Otherwise, vascular disorders develop, including hypovolemic shock and cardiac failure. Therefore, treatment should be carried out only in well-equipped clinics.
Low-grade fever is considered a normal reaction of the body to the intervention. But if it goes beyond 38.5 ºС for several days, you need to inform your doctor about this - the symptom may indicate the onset of a complication.
Treatment of dry tooth socket at home
If the pain from dry socket inflammation is too severe, you can take painkillers. In the first two days, apply cold compresses to the inflamed side at intervals of 20 minutes, then change to warm ones.
Drink more fluids, especially water. It removes harmful substances from the body. Avoid alcohol.
Rinse your mouth with a salt water solution. This clears the wound of dead cells and relieves inflammation. But you should not apply pressure in the area of the hole - you can provoke the displacement of the blood clot. You should rinse your mouth after every meal and before going to bed.
You can also apply a drop of clove oil to the wound to relieve pain. Rinsing with sage and chamomile flowers, a decoction of burdock leaves and aspen bark, and anise infusion will also have a positive effect.
If after all the treatments the pain has not subsided, the swelling has not subsided, and your health has only worsened, then you should urgently consult a doctor. There is a high probability that the process of rotting has begun.
In the dental office, the doctor, under anesthesia, will clean the hole or prepare the gums - depending on the degree of neglect of the case. Fill it with antiseptic gel.
Healing process
The stages of wound healing are as follows:
- The first day: the hole fills with blood, which turns into a clot due to coagulation. It becomes the basis for bone formation in place of the void, and also protects against infection.
- 3-4 days: the clot is replaced by granulation tissue. By this time, the severity of pain decreases, and sometimes the area of surgery stops hurting completely.
- Week: a clot remains inside the socket, but most of it has already been replaced by granulation tissue.
- Two weeks: the wound is filled with granulation tissue, turning into bone along the edges and bottom.
- 2-3 months: the hole completely turns into bone.
In order for recovery to occur correctly, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Prevention
Preventing dry socket is always easier and cheaper than treating dry socket. To do this, you need to follow a number of preventive measures. Namely:
- If possible, limit physical activity for several days after tooth extraction;
- do not touch the removal site with your hands or tongue;
- do not chew on this side;
- eliminate the use of tobacco and alcohol;
- do not eat too hot, cold or spicy foods;
- It is advisable to grind food into puree.
Expert of the article Bolshakova Evgenia Vladimirovna Dentist-hygienist
More than 11 years of experience
Trigeminal neuritis
Today, traumatic neuritis of the trigeminal nerve is considered one of the most common causes of pain syndromes in the maxillofacial area.
As a complication, it occurs during the removal of permanent molars of the lower jaw, due to damage to the lower alveolar nerve in the mandibular canal. The apices of the roots of the lower molars are in close proximity to the mandibular canal and in some cases may be located in the canal itself. Sometimes, due to chronic apical periodontitis, the bone between the root apex and the wall of the mandibular canal is resorbed. When a tooth is loosened by an elevator, the lower alveolar nerve can be injured, which will lead to partial or complete disruption of the functions of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve. The result is pain in the jaw, numbness of the lower lip and chin, decreased or absent sensitivity of the gums, decreased electrical excitability of the dental pulp on the affected side. Usually all these phenomena gradually disappear after a few weeks.
Electroodontometry
Electroodontometry is the most effective method for assessing the functional state of the trigeminal nerve when it is damaged. EDI is based on a study of the reaction of the teeth of the lower jaw to electrical stimulation. The method is performed on all teeth of the lower jaw, with preserved pulp both in the affected area and on the opposite healthy side.
S.N. scale Fedotova (1997) to assess the severity of damage to the inferior alveolar nerve based on electrical odontometry data:
- mild degree - reaction of teeth with preserved pulp on the side of nerve damage within 20-40 μA;
- moderate severity – reaction of teeth to currents from 40 to 100 µA;
- severe degree - complete loss of pain sensitivity, reaction of teeth to currents above 100 μA
The use of EDI to diagnose traumatic injuries of the inferior alveolar nerve is impossible if:
- lower jaw teeth endodontically treated
- lower jaw teeth are covered with orthopedic structures
- metal elements of splinting structures are fixed on the teeth
- missing teeth
Locations for measuring electrical excitability of facial skin
Assessment of the area of paresthesia in traumatic neuritis of the inferior alveolar nerve
The zone of paresthesia is identified - impaired sensitivity of the skin based on a tactile test, photographed, followed by an assessment of the area of the paresthesia zone: points are drawn on the border of areas of normal sensitivity of the skin, the red border of the lips and the paresthesia zone, which are then connected by a continuous line. Zones of hyper-, hypo- and anesthesia were marked with different colors.
I - vertical lines:
- midline,
- a line passing through the outer edge of the philtrum,
- a line passing through the outer edge of the wing of the nose,
- pupil line;
II - horizontal lines:
- lip line,
- a line running along the lower edge of the red border of the lips,
- the border line between the chin and lower lip,
- a line drawn along the most protruding part of the chin,
- line of the border of the chin and submental areas.
Schematic representation of the areas for measuring facial skin paresthesia.
Each of the 12 resulting squares was assigned a score depending on the nature of the sensitivity disorder:
0-sensitivity is not impaired;
1-skin hyperesthesia
2-hypoesthesia of the skin;
3-anesthesia of the skin.
Next, the sum of points was calculated and divided by 12 (quadrants).
With the results:
3.0-2.1 – severe sensitivity impairment was diagnosed;
2.0–1.1 – moderate severity;
less than 1.0 – mild severity of the pathology being studied
Treatment in the clinic
The optimal solution for treating a diagnosis of dry socket or alveolitis is a visit to the dentist. It is better to go to the same doctor who performed the tooth extraction, since he already knows the course of the operation, did the diagnostics and remembers the characteristics of your body.
Whatever clinic you choose to contact, study its website, the doctors who work there and reviews.
At the RUTT dental center we use the latest equipment and advanced materials. The experience of our doctors is confirmed by numerous diplomas, certificates and awards. You can be sure that you will be in the hands of a reliable specialist.
Why doesn't the hole heal?
The timing of wound healing is an individual question. It is determined by several factors - the traumatic nature of the removal, the presence of postoperative sutures, and the age of the patient. It is believed that partial epithelization takes about 2 weeks, complete - up to two months. These deadlines may increase for the following reasons:
- The bone was severely damaged. This happens, for example, during a complex extraction, when the tissue around the tooth has to be cut out with a drill.
- The clot has fallen out, so there is no basis for the formation of granulation tissue.
- Due to the doctor's fault, bone fragments remained in the wound.
- The patient ignores the recommendations received. The most common mistake is rinsing out the clot, after which an infection from the oral cavity gets into the wound.
- The mucous membrane around the wound is mobile, and no stitches were applied.
- Carious remains entered the cavity and inflammation began.
- The surgeon did not take into account individual characteristics. For example, with arterial hypertension, heavy bleeding begins, so drugs that lower blood pressure are additionally prescribed.
- Old age of the patient.
The wound is bleeding
In dental practice, there is only one known case in which a patient died after the removal of three adjacent teeth. The cause of death was not blood loss at all. The patient could not think of anything better after the operation than to drink a fair amount of alcohol and go to bed. Alcoholic drinks affect the liver, which increases bleeding. Due to alcohol intoxication, the sleep was sound, blood entered the respiratory tract, and the poor man choked.
In any case of bleeding due to an extracted tooth, the patient should calm down.
You only need to seek medical help in one case, if blood flows out of the wound in a stream.
If the patient is worried about bleeding, it is enough to make a tampon from sterile material and press it with your teeth to the wound for half an hour. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe special medications to stop bleeding. Doctors do not recommend using hydrogen peroxide in such cases.
If bleeding continues for more than a day, this is a symptom of a complication. Only a dentist, upon examination, will determine the cause of these complications and prescribe further treatment.
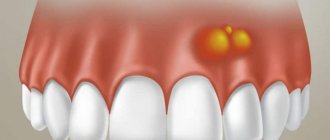
A growth has formed on the gum
After tooth extraction, there is often a complication such as the appearance of a lump on the gum. A growth in such a place indicates the onset of dangerous inflammatory complications. An infection can be caused if the clot is removed carelessly. Another source of infection is leftover food, so dentists prohibit patients from eating for several hours after surgery. During this time, a clot should form in the wound, protecting the gums from infection.
If a growth has formed on the gum, it may be an allergy to the anesthetics used or mechanical damage. Often a growth forms where the injection was given; such a new growth contains liquid inside, which in its structure is no different from a hematoma.
Such a lump will resolve in three days, unlike an infectious one, which often does not go away on its own and requires treatment.
Inside the growth, which is infectious in nature, there are purulent masses.
To determine the nature of the lump, the dentist performs palpation. By palpation, the doctor determines how hard the lump is and whether it contains liquid and pus inside. To make an accurate diagnosis, an x-ray or computed tomography may be prescribed. X-rays are not prescribed to pregnant patients. Based on the diagnostic results, the most appropriate treatment for the growth is prescribed.
- If there is no clot in the hole, it is cleared of inflamed tissues and treated with antiseptic materials. At the end of the manipulation, a hemostatic sponge is placed in the hole.
- The surgeon may decide to open the lump with a surgical instrument. After the procedure, the patient is invited to return for a follow-up visit in a few days.
- The general method of treating and preventing the growth is to take certain antibiotics.
Before coming to the dentist, the patient can rinse his mouth with furatsilin solution on his own. This drug cannot affect the size of the growth, but it will have an antimicrobial effect and reduce the intensity of inflammation. You can use dental ointments with an antibacterial effect. Folk remedies will not help get rid of the growth, but they can provide short-term relief. For this, soda and salt solutions are used. Rinsing should not be too vigorous, so as not to remove a blood clot that is beneficial for the body from the socket.
Gums hurt
Often, after tooth extraction, the patient's gums hurt. Experts are confident that this is a natural reaction of the body to surgical trauma. In this case, the pain is moderate, but sometimes it indicates not only gum injury, but also inflammation. Medical statistics note that inflammation after tooth extraction occurs in 4% of operations. Gum pain as a result of inflammation becomes even more likely if not just one, but several hours of removal. How to determine whether a wound is healing? How to act in case of inflammation?
Normally, after a tooth is removed, a clot of dark blood forms in the socket, which over time acquires a white-yellow hue.
The duration of the pain depends on the level of injury and the appearance of inflammation; it usually hurts for no more than two days. The pain is much more serious if the inert tissue is severely damaged, which inevitably happens when cutting out bone using a bore. This surgical technique is used when it is necessary to remove a crown or extract a tooth in parts. In all other cases, prolonged pain indicates a medical error or problems in the body.
To relieve pain, the use of analgesics is allowed. Normally, they help a lot, but if the pill doesn’t work, this is evidence that the operation was performed incorrectly. Medical errors during tooth extraction occur frequently, especially in the following cases.
- When sawing out bone using a drill. Modern dental standards require the use of drill tips with a cooling component. But in domestic dentistry, most dentists use tips without cooling. As a result, the patient receives a burn, as a result of which superficial necrosis develops, accompanied by acute pain. If the pain does not go away after using NSAIDs, and a blood clot does not form in the socket, you will have to go to the doctor again. The doctor will clean the hole from dead tissue, after this manipulation the patient’s condition will return to normal.
- If there are sharp bones protruding from the socket. Such edges of protruding bones often injure the mucous membrane, especially if the bone is not completely covered by a clot in the socket. Most often, this problem occurs due to the fault of the surgeon who did not apply stitches to close the wound. The patient can independently determine the presence of cutting fragments by touching the tongue, as well as in case of severe pain when drinking drinks. In rare cases, bone fragments can be seen when examining the wound in the mirror.
- With mobility of parts of the bone in the wound. Sometimes the dentist does not notice significant pieces of bone that were formed when the tooth was rocked. Such pieces often cause pain and inflammation in the socket. The problem can only be corrected with a second visit to the dentist.
- Incorrect removal method. This is a common cause of complications after tooth extraction. Dentists have different experiences, so two doctors remove the same tooth in different ways. So, when removing, you can use forceps, but another doctor, to speed up the process, will divide the tooth into two halves and only then remove them.
- Excessive use of anesthetic, leading to spasm of the blood vessels of the gums. As a result of such an error, the hole after the operation does not fill with blood and a clot does not form. In an empty socket, the bone is exposed and reacts painfully to touch.
- The dentist did not apply stitches, which should be done even when removing some teeth with a single root. In the case of teeth with several roots, a suture is required in the vast majority of cases. A properly sutured wound reduces the intensity of pain and the likelihood of complications by half. With stitches, the wound heals much faster.
- The dentist did not prescribe antibiotics. These drugs are not always prescribed, but in difficult cases, inflammation and acute pain cannot be avoided without them.
Do not start taking medications without discussing with your doctor, relying on the recommendations of friends or the Internet. The pain normally lasts no longer than a couple of days and should be moderate. If the pain does not subside, bone particles are felt in the hole, the wound reacts to liquid, or an unpleasant taste appears in the mouth, you should immediately contact the dentist who performed the operation or any other similar specialist.
Carrying out the procedure
The tooth extraction procedure is carried out using effective, modern painkillers, so, as a rule, there is no pain during the operation itself.
The operation begins immediately after the anesthesia takes effect. A scalpel is used to loosen the ligament supporting the tooth.
If the procedure was traumatic, or the edges of the wound are too wide, the dental surgeon may use self-absorbing sutures. But most often, the wound is simply closed with a gauze pad with a special hemostatic agent. To stop bleeding, you need to lightly but firmly press the tampon onto the wound with closed jaws. After 20 minutes, the gauze can be spat out.
After 2–3 months and beyond
The gum gradually hardens, and the space remaining from the tooth is filled with maturing bone tissue. By the beginning of the 4th month, the gum bone tissue completes its formation. The gum can be called completely healed.
If the wound heals with suppuration, then healing of the wound can last up to six months.