Teeth are important organs that provide several human needs at once: an aesthetic effect and calmness of the nervous system, chewing food and the proper functioning of the digestive system, the formation of a bite, and therefore correct speech. At the same time, they are very delicate, and this is fraught with serious health problems for a person. If many often encounter painful caries, cysts in the gums, and destruction of the crown, then the situation when such a terrible disease as tooth cancer develops turns out to be very unexpected. If only because many people cannot even think about this type of oncology. AiF.ru told about how tooth cancer can be hidden behind a harmless wound on the gum or a lump on the lip director of the dental studio Fedor Zakharov.
Question and answer Which brush is better: with natural bristles or synthetic?
What is the essence of the problem
The term “dental cancer” is used in everyday life, but it is not entirely correct. Yes, tumors can develop from tooth tissue: odontoma, cementoma, etc. But these are benign formations. Malignant is adamantinoma, which develops from tooth enamel, but is extremely rare and not fully understood. Most often the problem occurs in the lower jaw. Adamantinoma, in cases where it has been discovered, affects people at a fairly young age: 18-26 years. It is located in the area of the outer chewing teeth and in the corner of the mandibular bone. It can be of two types: dense and cystic. The first is a formation with a large number of cavities. The second is a formation filled with a brown mass.
The process resembles a cystic lesion of the cavity. As the tumor grows, the bone structures begin to thicken, which later combine into one bulge.
What can provoke such a terrible disease? These can be the most trivial reasons: chronic injuries to the mucous membrane, exposure to ionizing radiation, bad habits (smoking, chewing nasvay), occupational hazards (working in hot shops or dusty rooms), unhealthy diet (excessive consumption of spicy, pungent foods). In addition, there is a risk of developing jaw cancer in cancer patients with tumors of the kidneys, stomach, and lungs. In this case, they will talk about secondary oncology.
Drink milk and chew apples. How to eat for healthy teeth Read more
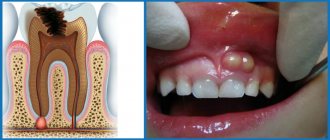
Gum cancer: stages and symptoms
One of the rarest but most dangerous dental diseases is gum cancer.
The occurrence of a disease is said to occur when the gum tissue is affected by malignant cells. It is not always possible to detect the presence of cancer due to its scanty symptoms, which usually resemble other diseases, such as gum disease. To make an accurate diagnosis and early diagnosis, you should adhere to the main rule - visit the dental office at least 2 times a year. Since the development of gum cancer is a slow process, any changes that occur in the oral cavity may signal danger. If the disease is neglected, there is a risk of damage not only to the entire oral cavity, but also to other parts of the body. The disease can spread to vital organs, transmitted through blood vessels, and even cause death.
No one is immune from this disease. But (according to statistics) gum cancer is more susceptible to:
- representatives of the strong half of humanity over 40 years of age (face the disease 5 times more often than women);
- smokers;
- drinkers;
- people who do not take good care of their oral cavity;
- workers in hazardous industries;
- people with bad heredity;
- people with dental diseases (bad bite, caries).
Dangerous symptoms
It is clear that diagnosing dental cancer is not so easy. It is worth being wary in cases where there is the appearance of long-term non-healing ulcers on the oral mucosa, deformations that are sometimes already noticeable to the eye, pain in untreated and intact teeth, when sensitivity changes. These are alarm bells that need to be responded to urgently and immediately run to the dentist. The earlier a tumor is detected, the greater the chance of minimizing losses.
It is also worth considering such an important sign as bleeding gums. If in a normal state, in order for blood to flow, you need to damage the gum, then in the case of cancer, light pressure will be enough. Also, swelling of the gums and increased body temperature may appear in parallel.
What symptoms to look out for
To recognize a tumor at an early stage, dentists advise being guided by your own feelings. The first symptoms that raise suspicion may be:
- slight bleeding of the gums that occurs as a result of gentle pressure on the gums;
- change in the color of the gum tissue and the appearance of swelling, which is often perceived as gingivitis;
- the appearance of neoplasms on the gums that have a pronounced red color, as well as light-colored ulcers and inclusions.
There is no need to panic if your gums are bleeding. This can be the cause of a number of diseases that are not related to cancer (periodontal disease, gingivitis, periodontitis). But plaques and ulcers should alert you and be the reason for an immediate trip to the dental clinic. At this stage, the disease can still be defeated and the likelihood of causing harm to the body can be reduced.
- Admin
- Oncology,
- Dentistry
Treatment
Tooth cancer requires surgery. And often, after tumor removal, reconstructive bone surgery may be required. Naturally, auxiliary types of therapy will also be determined if necessary: chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.
What happens to your teeth if you don't brush them? Infographics Read more
Diagnosis of oral cancer
Methods for diagnosing oral cancer are described below.
Biopsy
A biopsy takes a small piece of tissue from an area that may be affected by cancer. The tissue is sent to a pathologist (a doctor who examines body tissue to diagnose diseases). A pathologist will examine it under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Typically, biopsy results are ready no earlier than after 5 days.
If you have not yet had a biopsy, it may be done at your first appointment with your doctor at MSK. If you have already had a biopsy, a pathologist at MSK will review tissue samples taken during the biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
Medical imaging
You may also have medical imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or panoramic X-rays of your upper and lower jaws. A panoramic x-ray shows the entire upper and lower jaw, including the sinuses. These images provide detailed information about the lesion (an area of diseased or damaged tissue). This can show how deep the tumor has gone and whether it has spread to other organs.
to come back to the beginning
Problem statistics
Tooth cancer, like any other type of oncology, is dangerous due to its active development. And here the rule also applies: the earlier it is detected, the greater the chances of recovery. According to statistics, tooth cancer cured at stages 1-2 gives an 80% chance of five-year survival, at stage 3 the prognosis is 40%, at stage 4 - less than 15%. It is important to understand that the jaw is located close to the brain, and oncology is a metastatic disease. Therefore, you should not play Russian roulette; it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
At the same time, no one has canceled prevention: even if nothing bothers you, you should visit the dentist once every six months. This will allow you to identify any pathologies at an early stage. After all, prevention is easier than cure.
Stages of gum cancer and main symptoms
It is customary to distinguish the following stages of cancer depending on the area of damage:
Null , called "cancer in situ" and denoting a non-invasive tumor. The chances of a successful cure in this case are significantly higher than when the tumor is detected at a later date. However, difficulties in diagnosis may arise due to the lack of symptoms. But a routine examination at the dentist will definitely allow you to find out.
The first , which is a formation whose diameter does not exceed 2 cm. Such a tumor does not pose a danger provided that it is treated promptly and competently, since it does not have time to metastasize to the lymph nodes and internal organs.
The second , which looks like a formation reaching 4 cm in diameter. Most often, only this stage of cancer can be diagnosed, but a complete cure is also possible.
The third , when the size of the affected area exceeds 4 cm, and the formation itself begins to metastasize to nearby lymph nodes.
The fourth , which does not give a prognosis for the patient’s full recovery. The danger comes from metastases that grow into lymph nodes and organs.
Despite the difficulty of diagnosis, strange changes in the oral cavity can be detected at an early stage during a routine visit to the doctor. The first signs of the disease, which can be noticed independently, appear only as the tumor grows and compresses the nerves. Painful sensations cannot be ignored, as they may indicate the development of carcinogenesis. But many people prefer to endure the pain and not attach any importance to it, thereby triggering the disease and reducing the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Over time, another symptom joins the pain - bleeding gums. But even in this case, people often try to eliminate the problem on their own, “prescribing” medications for themselves and counting on the miraculous effect of herbal decoctions. You can become completely confused about the symptoms even after a recent tooth extraction. Pain is considered the result of surgical intervention in the dentofacial apparatus.
Care after surgery for oral cancer
Changes in diet
You will be able to drink fluids immediately after surgery. Your doctor will tell you when you can start taking pureed foods. You can start eating soft foods when your doctor allows, as long as you can tolerate them.
Read the resource Recommendations for Pureeed and Mechanically Gentle Diets for nutritional recommendations. You can also take liquid supplements that are high in protein and calories. For example, Ensure®, Boost® and Carnation Instant Breakfast®. Do not eat regular solid foods until your doctor tells you to.
If you have had surgery on the lining of your mouth or lower gum, chew food on the other side of your mouth until you have your first doctor's appointment after surgery.
Oral care
- Your doctor will tell you whether you can brush your teeth after surgery.
- Keep your mouth clean with rinses or an oral irrigation device. Your nurse will give you an oral irrigation device and teach you how to use it.
- To make a rinse solution, mix 1 quart (250 ml) warm water with 1 teaspoon salt and 1 teaspoon baking soda. You can store it at room temperature. Do not use mouth rinses that contain alcohol. They can cause oral irritation and slow healing.
Caring for the incision
- Do not wet the stitches on your lip or neck for the first 48 hours (2 days). After 48 hours, you can shower as usual. Do not direct the water stream towards the cut itself. Instead, let the water run down the cut and pat it dry with a clean towel.
- Apply bacitracin ointment twice daily if your doctor tells you to do so. Before you leave the hospital, you will be given bacitracin if you need it.
- The absorbable sutures will loosen and fall out 6 to 8 weeks after surgery. When you feel them in your mouth, simply spit them out. As long as they stay in place, they don't require much care other than keeping your mouth clean.
- Non-absorbable sutures will be removed at your first appointment with your doctor after surgery.
- If you have had lip surgery, avoid stretching your lip, such as when smiling, until the area has healed.
Speech changes
- If you have had surgery on your tongue, floor of your mouth, or soft palate, your speech may change. Your tongue may become swollen and numb, and you may not be able to move it freely. This will subside as the area heals. If you have significant changes in your speech, you will be referred to a speech therapist for further help.
Anesthesia
- Most people experience pain or discomfort after surgery. You will be given a prescription for pain medication before you leave the hospital. Take it as prescribed.
- If pain medication doesn't help, call your doctor.
- Painkillers may cause constipation (having bowel movements less frequently than usual). To prevent constipation, take a stool softener such as docusate sodium (Colace®) 3 times daily. If this does not help, take a laxative (eg 2 Senokot® tablets) before bed. Both drugs are available without a prescription. If constipation persists after taking these medications, call your doctor. For more information, read the resource Constipation.
Follow-up appointment
The day after surgery, call your doctor to make a follow-up appointment.
to come back to the beginning