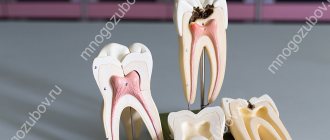
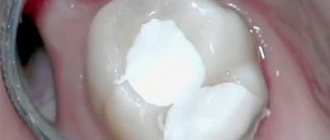
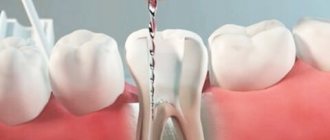
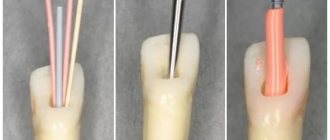
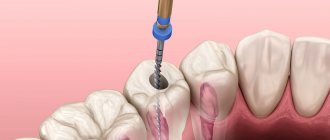
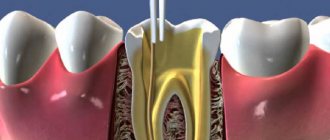
So, when caries develops to a deep degree, and the inflammatory process spreads to the pulp (in other words, the nerve), there is a high probability that the doctor will have to fill the canals.
First of all, we note that filling can be temporary - for treatment or permanent. Permanent filling is the final and most important stage of endodontic treatment. This will be discussed later.
The purpose of obturation (sealing, completely closing the lumen in an empty canal) of the root canal is to eliminate the paths of leakage of various substances from the oral cavity into the root canal system and to seal internal irritants that cannot be completely removed during the cleaning and shaping process.
There are many filling methods; we will briefly describe the main ones.
Injection (liquid) gutta-percha technique
In this technique, gutta-percha is used in the form of blocks, which are placed in a heating device, in which gutta-percha is heated to a temperature of 185-200°C and fed into the canal in liquid form. alloescort
The liquid gutta-percha technique, when performing the protocol, ensures the penetration of gutta-percha and sealer into both the main root canal and the dentinal tubules . The increase in temperature on the outer surface of the root is insignificant and has minimal damaging effects on the tissue.
The effective use of this technique, however, is determined by the doctor's skills, developed and honed on extracted teeth.
Main stages of filling
Filling the canals is carried out under local anesthesia. Before starting work, sterilization using special means is required. Additionally, preliminary cleaning is carried out. This process prevents bacterial damage and, as a consequence, inflammation.
The root canal filling procedure includes the following steps:
- treatment of caries;
- removal of damaged areas (tissues);
- removal of connective tissue;
- analysis of the anatomical features of the canal;
- treatment of the canal for the subsequent installation of a filling;
- sterilization of the canal using disinfection;
- introduction of material to fill the channels;
- removal of residual filling material;
- hermetically sealed.
Important! Pulp removal is carried out if there is severe tooth decay. This action is aimed at preventing re-infection.
Possible complications
After canal filling, complications may develop. In practice, the following cases are often recorded:
- perforation of the root wall. This complication is characterized by severe pain and bleeding;
- infectious damage caused by insufficient treatment;
- development of infection in the tooth, which is the result of incomplete filling of the canal;
- exit of the filling material beyond the root apex. Manifested by intense pain and severe sensitivity;
- response to channel temperature changes;
- pain due to instrument breakage during treatment;
- development of a cyst or granuloma;
- periodic inflammatory processes;
- change in tooth shade due to improper treatment;
- inflammation of the supporting tooth;
- loss of filling;
- development of an allergic reaction.
The likelihood of developing complications depends on the actions of the doctor and the patient. Therefore, when choosing a dental clinic, it is recommended to study reviews and select highly qualified specialists. But there are a number of rules for the patient that will help reduce complications after treatment to a minimum:
- See a doctor if pain and discomfort develops;
- consult a doctor if an allergic reaction develops;
- urgently consult a doctor in case of acute pain, severe swelling, fever;
- follow the doctor's recommendations;
- do not self-medicate.
Remember, self-medication is fraught with the development of serious complications! If you experience severe discomfort, contact your doctor! Modern filling materials in the hands of a qualified specialist minimize the likelihood of developing any complications.
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Choosing temporary filling material: proceed without mistakes
Every practicing dentist knows how important the correct selection of filling material is for effective treatment. Modern dentistry offers a huge selection of materials, which are divided into classifications depending on composition, properties, time of use, purpose, etc. A fairly large place among them is occupied by a group of filling materials for temporary fillings, as well as insulating and therapeutic pads.
Materials for temporary fillings
Based on the time of action, they are divided into bandages and temporary fillings. Inexpensive materials are used for dressings. The most common option: water-based dentin or dentin-paste. The period of use of these materials should not exceed 14 days. At the same time, the bandages do not differ in aesthetics and durability. All temporary fillings are cements : zinc phosphate, zinc eugenol, polycarboxylate, glass ionomer, etc. The period of their use in the patient’s oral cavity ranges from several weeks to six months.
1) Zinc sulfate cements (“artificial dentin”)
The main components of the composition are zinc sulfate and zinc oxide. Adding water helps the mass harden. The most famous materials of this group: “Dentin for dressings”, Dentine paste, Vinoxol, etc.
2) Zinc-eugenol cements
The basis of the composition is zinc oxide and eugenol. According to Smith's classification (1996), this subgroup includes three main types of cements: simple zinc oxide eugenol; reinforced zinc oxide eugenol with filler and cements based on orthoethoxybenzoic acid (EBA). The materials consist of zinc oxide powder, into which 1-2% zinc acetate, acetic anhydride or rosin are added, which accelerate hardening. Purified eugenol or clove oil is used as a solvent. Additionally, to speed up the hardening process of cement, acetic acid or 1% ethyl alcohol, as well as a small amount of water, can sometimes be added. The most popular representative of this group is Cariosan. Zinc-eugenol cements are used not only for temporary fillings , but also for therapeutic linings. It is important to take into account that eugenol disrupts the polymerization process of composites, so experts do not recommend using this type of cement in combination with them. That is why today zinc-eugenol cements are practically not used for therapeutic linings in commercial clinics, but they are still in demand in pediatric dentistry and in municipal clinics for the treatment of deep caries in two visits.
3) Zinc phosphate cements
75-90% of the cement base is zinc oxide with the addition of other modifying oxides. The liquid part is an aqueous solution of 38-44% orthophosphoric acid containing phosphates of zinc, aluminum, magnesium, etc. Among the most famous zinc-phosphate cements presented on the Russian market are: Phosphate cement from Raduga-R, Uniface ( “Medpolymer”), Adgesor (“Dental Spofa”), DeTreyZinc from “DeTrey/Dentsply”, etc. As a rule, metals containing silver are added to these compositions to impart a bactericidal effect. As an example, we can o), Phosphate with silver and bactericidal Foscin (“Rainbow-R”), as well as cements containing bismuth oxides: Visphate cement and Dioxyphosphate (Medpolymer).
The undoubted positive properties of these cements are: ease of use, low thermal conductivity, good X-ray contrast, and impermeability to acids and monomers. However, they have quite a lot of negative characteristics. Among them: weak adhesion, low resistance to the aggressive effects of saliva, shrinkage, low mechanical strength, the presence of free acid and lack of aesthetics.
Most often, zinc-phosphate cements are used as an insulating spacer for filling baby teeth and permanent crowns, fixing cast stump inlays, pins, crowns and bridges.
4) Polycarboxylate cements
The basis of cement is thermochemically treated zinc oxide with the addition of magnesium oxide, which reduces the reactivity of the first component. Aluminum is also often added to powders. The solvent is represented by a 32-42% aqueous solution of polyacrylic acid. During the hardening process, cement turns into an amorphous zinc-polyacrylate gel, which contains zinc oxide particles.
The positive properties of these cements include: satisfactory chemical adhesion to enamel and dentin, strong bond with metals, weak toxicity to the pulp compared to phosphate cement and high biocompatibility with tooth tissues. Negative properties: high solubility under the influence of saliva, short formation time in the oral cavity and insufficient fluoride adhesion.
Polycarboxylate cements are used as insulating spacers when filling teeth under artificial crowns, for fixing orthopedic and orthodontic structures, and in the treatment of baby teeth (1-2 years before their replacement).
All materials for temporary fillings must be:
- harmless to the pulp;
- have high plasticity;
- inactive for other drugs;
- insoluble under the influence of saliva;
- sealed for at least two weeks;
- have a certain strength;
- easily removed from the dental cavity using an excavator, probe or drilling.
Insulating and healing pads
The purpose of these materials follows from their name. Despite the fact that they can be conditionally classified as filling materials, the application of gaskets is an integral step in the treatment of medium and deep caries. spacers when treating medium and deep caries . They contain calcium hydroxide, which has an anti-inflammatory effect on the pulp and stimulates the deposition of replacement dentin. Among the most popular materials are: “Calmecin”, “Dycal”, “Calcimol” and “Alcaliner”, as well as modern insulating gaskets made from glass ionomer cements, such as: “Fuji 2”, “Chelon Fil”, “Base Line” and etc.
Today the following requirements apply to insulating gaskets:
- reliably protect dentin from chemical and temperature irritants;
- easy to install;
- withstand the effects of saliva when the filling is damaged;
- withstand chewing load;
- have good adhesion to tooth tissues;
- do not have an aggressive effect on the dental pulp;
- do not affect the color of tooth enamel.
Therapeutic pads have an anti-inflammatory, regenerating and analgesic effect, therefore they are used in the treatment of deep caries. They are characterized by good ductility, the material hardens quickly. Basically, the therapeutic component of modern medical pads is calcium hydroxide, which has a bactericidal effect and shifts the pH environment in the tooth cavity to the alkaline side, which ensures neutralization of acids. The base material can be polymer, water-based, oil-based or monomeric. Dentists use either ready-made medicinal pads or prepare them themselves. The use of a therapeutic pad significantly reduces the risk of the formation of microcracks and the development of secondary caries. However, with all their advantages and positive effects on the pulp, these compositions have noticeable disadvantages:
- low adhesion to dentin, which determines the weak adhesion of the filling to the tooth tissues;
- lack of resistance to the aggressive effects of saliva, which creates conditions for further infection;
- accidental contact of gasket particles with the walls of the formed cavity can lead to secondary caries.
It is recommended to apply therapeutic pads in cases where the bottom of the formed cavity is located too close to the pulp. It is believed that in order to prevent infection of the pulp by toxins, the minimum thickness of the dentin layer should be 2 mm. When placed correctly, the therapeutic material completely covers the bottom of the carious cavity or lies pointwise in the areas where the pulp horns adjoin. In this case, it is necessary to carefully remove it from the walls of the cavity in order to avoid disruption of the adhesion of the filling material and the development of secondary caries.
Regardless of their purpose, all temporary filling materials must meet the same clinical requirements:
- do not have a toxic effect on the enamel, dentin and pulp of the tooth, as well as mucous membranes;
- be harmless to the body as a whole;
- have antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and anti-caries effects;
- be chemically inert and resistant to aggressive environments such as alkalis and acids;
- have sufficient adhesion to dental tissues, mechanical strength and wear resistance;
- do not change the color of the tooth and do not lose its original color over time;
- do not cause the appearance of galvanic currents in the oral cavity;
- do not change shape and volume during hardening;
- have good radiopacity.
For an experienced specialist, purchasing filling material, like any other dental consumable, usually does not cause any particular difficulties. However, the dental market, being one of the most dynamic and rapidly developing areas of global business, is constantly changing, which makes it difficult to keep track of new products and truly profitable offers in a timely manner. Today, the marketplace of the Internet portal “Dentists Club” is rightfully considered one of the most reliable and positively proven resources. This aggregator has been successfully operating in the dental market since 2017 and has already proven itself as a proven and honest partner. At the same time, the Dentist Club market is the only aggregator of offers in the field of dentistry today, which allows you not only to purchase the necessary goods at the guaranteed best prices, but also in addition to receive a cashback of 1.5% back to your account!
What other benefits does the Dentist Club market provide?
1. Time saving
- You don’t need to go to all the search results sites to find what you need
- There is no need to call companies and try to explain to them over the phone what you need
- No need to send a request and wait for managers of trading companies to answer or call you back
2. The Dentist Club Market service helps when communicating with doctors
- You can easily find the desired product by description and photo
- Determine the desired model and its modification
- Check all these parameters directly with your doctor and get his approval
- Place an order in one click.
3. Lowest prices on the market guaranteed
- You can simultaneously see the prices of all companies offering the required product
- Compare the prices presented and choose the most profitable one
- The manager of the selected company will call you back. He doesn’t need to explain ten times what you need, because... He sees all the necessary information in the generated order.
- And don't forget about cashback!
4. 100% order security
- Absolutely all companies - suppliers of dental equipment and consumables, collaborating with the marketplace, have already been checked for legal purity by lawyers of the Dentists Club. That is why all purchases made on the Dentists Club market are absolutely reliable!
5. Ease of use
- You can install the Dentist Club Market service on your phone so that it is always at hand. Open the app, find the products you need, and order. Everything is quick, accessible and simple. Application in the App Store on iPhone (iOS) or on Google Play for Android.
Aida Levasheva – senior nurse at the dental clinic (Samara):
“To be honest, purchasing dental supplies was my least favorite job until recently. I do not have a dental education, and until recently this created certain difficulties. Of course, before purchasing, I asked doctors what material was more convenient for them to work with. The problem was that everyone had their own preferences. I had to search for what I needed all over the Internet, compare prices, and call managers of trading companies for half a day to find out the terms of payment and delivery. This often took almost the entire working day. And in the end, the head physician, looking at the list and prices, crossed out half of the points. The Dentist Club Market was recommended to me by one of my classmates at medical school. I really liked the resource. For me, the most important thing is a very convenient and simple interface, which you can easily understand even without a dental education. I especially liked the function where you can compare prices for the desired product! If you need professional advice, you can get it directly on the website and immediately pay for your order there. All this is very convenient and saves a lot of time!”
Go to Market >>>