Causes of bleeding Classification How to stop?
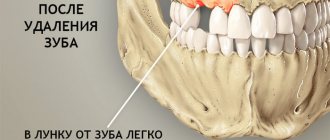
Dentist's help Prevention Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure that cannot be performed without damaging tissues and blood vessels. This causes bleeding from the tooth socket. The blood forms a clot that protects the wound from bacteria. Usually, it stops coming out of the wound after a few minutes, but there are cases when bleeding continues for several hours or even days.
Local reasons
- Vascular rupture during traumatic surgery;
- breaking off the root septum or alveoli (socket);
- inflammation in the area of the tooth that was removed;
- the effect of adrenaline (after the narrowing of blood vessels, the second phase begins - their expansion);
- melting of blood clots clogging blood vessels under the influence of purulent secretions;
- local hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels). Occurs from hot food, drinks, rinses or compresses.
Under no circumstances should you apply heat to the wound after extraction!
Thus, the occurrence of bleeding can be provoked not only by a doctor’s error, but also by the patient’s actions.
Signs if perforation was left without the attention of a doctor
Symptoms of inflammation after unsuccessful treatment occur in different ways - after a few days, weeks or even years. Depends on the sterility of the foreign body in the sinus, its ability to cause inflammatory processes, and the characteristics of the patient’s immune system. The following manifestations are possible:
- feeling of heaviness;
- pain when chewing;
- purulent and serous discharge from one nostril;
- elevated temperature;
- impaired sense of smell;
- pain when lightly tapped under the eye and in the nose area.
These are typical signs of odontogenic sinusitis caused by poor quality dental treatment. The key difference from rhinogenic sinusitis (when sinus infection occurs from the side of the nasal passages as a result of ARVI or influenza) is that signs of the inflammatory process are detected only on one side, where treatment was carried out.
Common reasons
The most common of them is a sharp rise in blood pressure as a result of a hypertensive crisis, excessive physical activity, and thermal procedures (bath, sauna, hot bath).
In second place are diseases that affect blood clotting: hemophilia, leukemia, hemorrhagic diseases.
Profuse bleeding occurs with unrecognized vascular tumors (hemangiomas). Therefore, it is important to conduct an X-ray examination, which shows such changes.
Taking anticoagulants can also provoke socket bleeding after removal.
What are the dangers of sinus injury?
Since the complication does not always manifest itself immediately, symptoms of sinusitis that arise after a few years force the patient to consult a regular ENT doctor. Treatment, as a rule, does not bring results - in most cases the cause is not found. You start going from one doctor to another, and precious time is lost. The longer a foreign body is in the sinus, the higher the risk of tumor formation. If sinus perforation is left unattended, it can lead to:
- chronic sinusitis and sinusitis
- inflammation of the roots of adjacent teeth
- osteomyelitis of the jaw
- encephalitis and meningitis
Classification of bleeding
Bleeding is divided into primary, which begins immediately after surgery, and secondary, when bleeding begins after some time.
The intensity of bleeding is determined depending on how much the hole bleeds after removal:
1st degree
– blood flows
for 20-30 minutes
, saturates the tampons and colors the saliva.
2nd degree
– bleeding continues for more than 40 minutes, blood and saliva mix intensively.
3rd degree
– the bleeding does not stop for more than an hour, the patient spits blood.
With prolonged bleeding, the patient's general condition worsens. Weakness, dizziness appear, and the skin turns pale. Blood pressure drops, the heart begins to beat less frequently. In case of bleeding, dentists advise not to delay a visit to the doctor so that he can take measures to stop the bleeding and prevent the condition from worsening.
How to prevent perforation
If patients with anatomical features of the location of the roots in the sinus are treated according to the standard protocol, the threat of rupture of the membrane is very high
The doctor must have the necessary information about the anatomical and topographical features of the patient and be prepared for an emergency situation.
- To prevent perforation of the sinus membrane, computed tomography is required. After studying the CT image, the doctor selects the optimal treatment tactics. But not every equipment allows you to identify all the nuances. In our Center, diagnostics are carried out using a modern 3D tomograph Sirona Galileos with ENT mode settings. Provides high quality images, allows you to evaluate the structural features of the upper jaw and sinus, calculate the height of the septum, find out the location of the roots, their anatomy.
- When working with the canals of teeth located in the sinus, all manipulations must be extremely careful. The dental canals are very thin, sometimes tortuous, the doctor must control every action. Endodontic dental treatment in our Center is carried out using a Seiler dental microscope. Multiple magnification expands the view, allows you to examine the entire length of the dental canal in great detail, and prevent the filling material from leaving the root.
- The experience of a specialist is of great importance so that he can give an adequate assessment from a CT image, choose tactics, and calculate efforts. Our Center employs highly qualified endodontists, with excellent clinical thinking and honed manual skills. Qualifications and skills allow us to prevent complications and act promptly in the event of an emergency situation.
We have minimized the likelihood of complications after dental treatment
. Advanced CT diagnostics in ENT mode and work using a dental microscope allow us to select competent tactics to prevent perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich Chief physician and founder of the Doctor Levin center
After endodontic treatment, control CT diagnostics is mandatory! This preventive measure allows you to timely identify perforation (even if the doctor did not notice it during treatment) and take measures to eliminate the consequences.
If a piece of instrument or filling material gets into the sinus, removal of the foreign body must be prompt and urgent ! Otherwise, there is a high risk of infection, development of inflammatory processes and neoplasms.
How to stop bleeding from a socket after tooth extraction
After the tooth is removed, the dental surgeon cleans the wound and applies a sterile swab. The patient is asked to tightly clamp the tampon with his teeth and hold it for about half an hour. If the tampon quickly becomes saturated with blood, it should be changed.
If the bleeding does not stop after 20-30 minutes
, the dry swab is replaced with one moistened with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
A cold compress can be used to constrict blood vessels. Ice is applied to the cheek, after wrapping it in a towel so as not to freeze the skin. Keep the compress for 10-15 minutes
, then take a break and repeat the procedure.
After surgery, the dentist recommends painkillers. You should follow these recommendations to avoid accidentally taking a product containing aspirin, which thins the blood and can cause bleeding.
If after all the manipulations there is still bleeding from the tooth socket, you need to contact a dental clinic.
Treatment methods
If you find that there is bleeding from your gums, you should immediately contact your dentist. The doctor will determine the cause and prescribe adequate treatment. The most effective ways to combat bleeding gums are:
- Professional teeth cleaning and ultrasonic calculus removal.
Waves completely eliminate plaque. During pregnancy, methods that are safe for the fetus are used.
- Rinse with antiseptics.
Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Rotokan, Chlorphyllipt, Furacilin, Tantum Verde, etc. are prescribed as a solution for sanitation. It is acceptable to use decoctions of sage, chamomile, calendula, and oak bark. The procedure is carried out in the morning, before bed and after each meal. The course lasts no more than 10 days.
- Dental gels and ointments.
The most effective drugs are Metrogyl Denta, Asepta, Dental, Cholisal, Parodium, Stomatofit, Solcoseryl, Salvin. The composition quickly penetrates the mucous membrane, has an antimicrobial effect, relieves inflammation, pain and bleeding. The products are applied twice a day, after rinsing and drying with a cotton swab.
- Additional medications.
For concomitant diseases of the oral cavity, antibiotics, painkillers, “Parodontocid” spray, lozenges Septolete, Faringosept, Grammidin, etc. are prescribed.
- Physiotherapy.
Gum restoration is accelerated by procedures such as ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, current treatment, oxygen treatment, balneo-, light- and vacuum therapy. Various types of massage are effective: water, hardware, manual. As a rule, a course of physiotherapy includes 5 procedures.
- Proper oral care.
It is necessary to brush your teeth twice a day. Dentists recommend using only soft brushes marked Soft and pastes for bleeding gums: Parodontax, Lacalut, ROCS, BlanX, Mexidol Dent. After eating, you need to carefully remove food debris with dental floss and use an alcohol-free mouth rinse: Silca, Lacalut, PresiDent, Forest Balm. You can also use a solution of water with salt or hydrogen peroxide.
- Taking vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
Popular drugs are “Dentovitus”, “Alphabet”, “Vitrum”, “Immunal”, “Calcinova”, “Calcium D3 Nycomed”, and lemongrass tincture. To reduce the fragility of capillaries, Ascorutin is additionally prescribed.
- Nutrition correction.
It is recommended to avoid sugar, bread, spicy, sour and salty foods, carbonated drinks and alcohol. The diet should include fresh juices, vegetables and fruits, foods rich in protein, vitamins C, B, K, E. As a result, periodontal tissue will be strengthened, and the mucous membranes will recover faster. Spices are also useful: ginger, wasabi, sesame, cinnamon. Spices stop the proliferation of bacteria and relieve inflammation.
There are also emergency measures. If there is bleeding from the gums, it is necessary to apply a swab soaked in ice water to the tissue. This will quickly soothe the gums and stop bleeding.
The best treatment is prevention. Visit your dentist twice a year. A specialist will detect and eliminate all problems with teeth and gums in a timely manner. If you follow your doctor's recommendations, you will forever forget about bleeding gums.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.
What does a dentist do?
First of all, the doctor will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis. In accordance with it, the dentist will carry out treatment.
First aid is to stop blood loss. To do this, local anesthesia is performed, blood clots are removed, the wound is dried and the place where the blood is coming from is determined.
Methods to stop alveolar bleeding depend on its cause and location:
- if there is a rupture of the gums or mucous membrane, they are sutured;
- a ligature (a special thread for ligating blood vessels) is applied to the bleeding vessel;
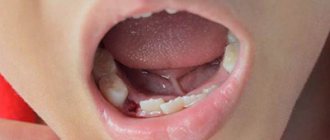
- If there is bleeding from the alveoli (socket), a tampon of iodoform gauze is placed on it. It is left in the wound for several days.
Tamponation is used as a prophylactic measure if there is a risk of bleeding. The tampon is left in the hole for several days. Then they take it out and see how well the wound has healed.
Removing wisdom teeth is potentially dangerous. Such operations are often difficult. Sometimes you have to cut the gum, saw the roots or the tooth itself and remove it piece by piece. Bleeding after such complex operations occurs more often than after ordinary ones.
Measures taken when a hole bleeds after wisdom tooth removal are the same as after regular removal. If there is a history of blood diseases, preparations are made for such an operation in advance. A blood test is carried out, in some cases calcium chloride injections and vitamin C
and
K.
_
If the cause of alveolar bleeding is systemic diseases, general hemostatic agents are used (calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, aminocaproic acid, dicinone, vikasol).
For hypertension, antihypertensive therapy is prescribed. After the pressure normalizes, the bleeding usually stops.
Causes of sinus perforation during dental treatment
The maxillary sinuses or maxillary sinuses are located inside the upper jaw. They are separated from the oral cavity by a septum and the alveolar process, which contains the roots of the teeth. Treatment of the canals of such teeth is complicated by the risk of sinus perforation for a number of reasons:
- Anatomically thin septum Sometimes the height is only 1 mm. It happens that the teeth penetrate the cavity with their roots and only the sinus mucosa separates.
- Treatment of teeth with inflammation on the roots If there is inflammation on the roots of the teeth (periodontitis, cyst), the surrounding bone melts and becomes thinner.
- Excessive efforts by the doctor If the dentist does not calculate the efforts when passing the canals, the canal may rupture, damage the root, or perforate the bottom of the sinus.
Without a preliminary diagnosis, the endodontist, having no idea about the size of the sinus septum and the location of the roots, may not calculate the effort and damage the tooth and the thin bone layer that lies between the maxillary sinus and the root. As a result, infection penetrates into the sinus cavity, and fragments of instruments and filling material may fail. In our practice, there are cases when a foreign body in the sinus attracts secondary infections with the development of neoplasms - fungal colonies, cysts, polyps.
A fragment of an endodontic instrument in a tooth canal
What to do if the tooth under the crown has completely rotted
One type of reconstruction of a severely damaged tooth is a stump inlay. It is a product that replicates the root system of the tooth. A crown is placed on the upper part of the structure protruding above the gum. The method is used only if there are healthy, undamaged roots.
Stump inlays are made of chrome-plated cobalt or alloys with precious metals (gold, silver). Preference is given to gold, as its shade resembles the color of natural enamel. The silver tab, despite its antibacterial effect, is used less frequently, since it shows through the crown as a dark spot.
If the roots are completely rotten and cannot be restored, the tooth is removed.
The choice of one or another method of dentition restoration in case of tooth loss remains with the patient, and his wishes regarding the material, type of structure, as well as financial capabilities are taken into account.
Treatment or removal - what determines the outcome
The doctor makes a decision on treatment or tooth extraction after determining the depth of spread and the area of localization of the inflammatory process. It is mandatory to first carry out professional cleaning using an ultrasonic scaler, an AirFlow water-abrasive device and hand tools.
Initial caries is treated with conservative retherapy. For hard tissue defects, preparation and filling are performed. In severe cases, the tooth is removed.
Treatment of the initial stage of root caries
Conservative retherapy includes:
- fluoridation of teeth;
- covering teeth with protective agents
- training in proper oral hygiene
When bleeding is not associated with gum inflammation
In some cases, bleeding gums may not be associated with problems in the oral cavity, but indicate that a person needs to pay attention to his own health. For example, gums bleed due to a severe lack of vitamins in the body. This can be noticed in the fall or spring, when vitamin deficiency is pronounced, and the immune system is weakened and susceptible to exacerbations of chronic diseases.
A number of diseases are accompanied by bleeding gums, such as diabetes. People who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract and kidney disease also note weak gums and bleeding. With age, calcium is washed out of the body, which leads to osteoporosis, that is, weakness of bone tissue. In this case, the jaw bones also become thinner, hence sensitivity and looseness of the teeth and bleeding.
Blood during brushing is also observed in the presence of endocrine diseases, malignant tumors, leukemia and hemophilia. In such cases, if you notice blood in your mouth, you need to visit a therapist who will prescribe an additional examination to find out the problem.
It also happens that a tooth bleeds in a certain place due to an incorrectly placed filling or crown. In this case, the edges of the installed patch rest against the gum and injure it. You can correct the situation in the dentist's office. The doctor carefully grinds off the excess filling, and the gums will heal.
What is the danger of this disease?
Caries is dangerous because there are no symptoms for a number of years. It is detected more often in an advanced stage, when tooth extraction becomes the solution.
Visual diagnosis is difficult because all destructive processes occur inside the tooth. Pronounced plaque or tartar hides any stains on the enamel.
The root is hidden under the gum and external irritants do not affect it until a certain time. On the other hand, the root walls are thin, so they are destroyed quickly and with complications.
Cleaning in dentistry from stone and plaque
1243900247100
Professional teeth cleaning involves removing the accumulation of all pathogenic microflora around the root.
It involves not only removing plaque, but also stones. This elimination of negative factors protects teeth for a long time.
Antiseptic treatment of affected areas
Treatment of root caries involves drilling out all affected areas with a drill and treating the carious cavity with antiseptics and special preparations. A 2% chlorhexidine solution or a gel based on it is used as an antiseptic for the treatment of carious cavities.
What to do to protect your gums
If the gum is not treated, inflammation will remain and all treatment will become meaningless. The gums are protected by diathermocoagulation and retraction.
Diathermocoagulation
Diathermocoagulation – excision of excess areas of periodontitis with a coagulation knife. The knife immediately cauterizes the bleeding edges. The procedure is performed when there are severe changes in the gums. In such cases, filling is postponed until the soft tissue is completely regenerated.
Retraction
If the condition of the gums is advanced, treatment of caries becomes impossible - the mucous membrane bleeds and interferes with tooth treatment. This gum is excised or a special device is applied to move the gum back. But more often, retraction is performed - lowering the gingival contour or moving apart the overhanging edges of the gums using special hemostatic threads. A temporary filling is placed until complete healing.
Symptoms of the disease
The process usually occurs without symptoms, but pain may occur when brushing a toothbrush, eating sour, salty, sweet, cold or hot foods.
After eliminating the irritant, everything goes away. The patient can see a doctor if a stain is found on the front surface of the incisors, but often it is hidden under plaque or tartar.
The ongoing carious process gradually reaches the dentin junction, penetrating first into its surface layers and then further. The cavity deepens with bacteria and food debris. There is a smell from the mouth. Irritants cause pain more and more frequently.
With cement caries, teeth become mobile and lose their support, and bleeding gums occur. These are already symptoms of periodontitis. Now, even when chewing food or brushing teeth, severe discomfort occurs.
Digestion begins to suffer. Teeth become hypersensitive to hot or cold.
Next, the process follows the Leus classification:
- Active lesion - the edges of the cavity are undermined. The cavity is filled with softened tissues and tends to grow.
- Suspended caries - no increase in the affected area is observed. The cavity is clean, the bottom is shiny and smooth, the edges are even and dense.
- Secondary caries - occurs under a filling.